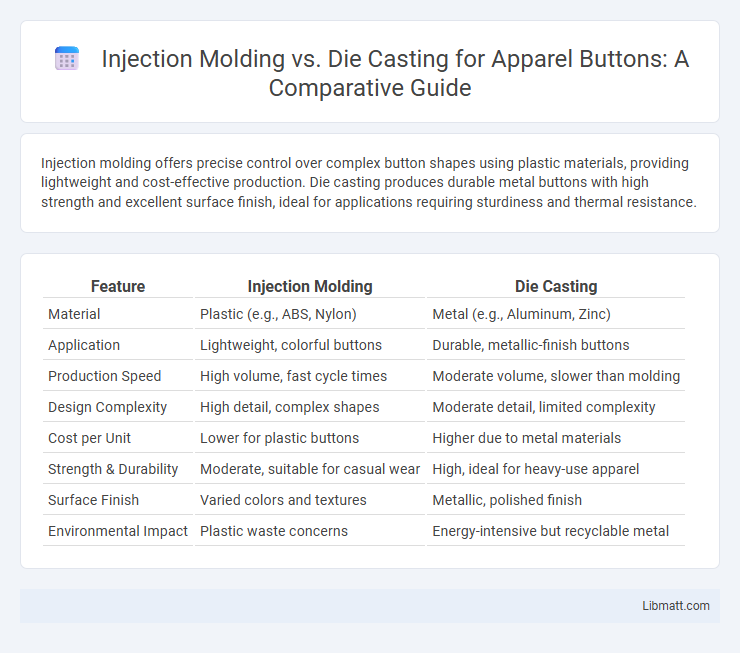
Injection molding offers precise control over complex button shapes using plastic materials, providing lightweight and cost-effective production. Die casting produces durable metal buttons with high strength and excellent surface finish, ideal for applications requiring sturdiness and thermal resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Injection Molding | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic (e.g., ABS, Nylon) | Metal (e.g., Aluminum, Zinc) |
| Application | Lightweight, colorful buttons | Durable, metallic-finish buttons |
| Production Speed | High volume, fast cycle times | Moderate volume, slower than molding |
| Design Complexity | High detail, complex shapes | Moderate detail, limited complexity |
| Cost per Unit | Lower for plastic buttons | Higher due to metal materials |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate, suitable for casual wear | High, ideal for heavy-use apparel |
| Surface Finish | Varied colors and textures | Metallic, polished finish |
| Environmental Impact | Plastic waste concerns | Energy-intensive but recyclable metal |
Introduction: Comparing Injection Molding and Die Casting for Buttons
Injection molding offers precise control and high-quality plastic buttons with complex shapes, making it ideal for lightweight, durable designs. Die casting produces metal buttons with excellent strength and heat resistance, suitable for premium, sturdy applications. Your choice depends on material preference, production volume, and the desired durability of the buttons.
Material Suitability: Plastics vs Metals
Injection molding is ideal for producing plastic buttons, utilizing thermoplastics such as ABS, polypropylene, and polycarbonate that offer high durability, flexibility, and color versatility. Die casting suits metal buttons, commonly using aluminum, zinc, or magnesium alloys known for their strength, wear resistance, and premium finish quality. Material suitability depends on desired button properties: injection molding excels with lightweight, corrosion-resistant plastics, while die casting provides robust, heat-resistant metal components.
Manufacturing Processes Overview
Injection molding and die casting are distinct manufacturing processes used for producing buttons with different material requirements and design complexities. Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to form lightweight, durable buttons suitable for high-volume production with detailed geometries. Die casting, on the other hand, forces molten metal into a steel mold under high pressure, resulting in robust metal buttons with fine surface finishes and superior mechanical properties.
Cost Analysis: Tooling and Production Expenses
Injection molding generally involves lower initial tooling costs compared to die casting, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs of plastic buttons. Die casting requires expensive metal molds and higher setup expenses, but it offers faster production cycles and better material strength for metal buttons, which can reduce per-unit costs at high volumes. Understanding your production scale and material preferences helps optimize costs between tooling investment and ongoing manufacturing expenses.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Injection molding offers superior design flexibility and customization for buttons, enabling complex geometries, intricate details, and a wide range of material options including various plastics and elastomers. Die casting is more limited in design complexity but excels in producing durable metal buttons with consistent dimensions and smoother finishes, optimal for high-strength applications. The choice between injection molding and die casting depends on the desired material properties, intricacy of design, and production volume requirements.
Production Speed and Volume Capabilities
Injection molding offers faster production cycles for buttons, making it ideal for high-volume runs with consistent quality. Die casting provides excellent dimensional accuracy but often involves longer cycle times, limiting speed compared to injection molding. Your choice depends on whether rapid volume production or precise metal button components are the priority.
Surface Finishes and Aesthetic Considerations
Injection molding offers a wider variety of surface finishes for buttons, including smooth, textured, and glossy options that enhance aesthetic appeal and tactile experience. Die casting provides superior surface detail with a characteristic metallic finish and can achieve fine textures, though it is generally limited to metal materials like aluminum or zinc. Both processes allow for secondary treatments such as painting, plating, or polishing to further customize the appearance of buttons according to design specifications.
Durability and Performance of Buttons
Injection molding produces buttons with excellent impact resistance and flexibility due to the plastic materials used, enhancing their durability under repeated use. Die casting creates metal buttons offering superior strength, heat resistance, and wear performance optimal for high-stress applications. Selecting between injection molding and die casting hinges on the required button resilience, environmental exposure, and tactile performance demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Injection molding for buttons typically produces less waste due to precise material usage and allows for easier recycling of thermoplastic resins, reducing environmental impact. Die casting, while energy-intensive and reliant on metal alloys, benefits from metal recyclability and can result in longer-lasting products, contributing to sustainability through durability. Selecting the optimal process depends on balancing material efficiency, energy consumption, and product lifecycle to minimize ecological footprint.
Choosing the Right Process for Button Manufacturing
Injection molding offers high precision and intricate design capabilities, making it ideal for producing lightweight, detailed buttons with consistent quality. Die casting excels in creating durable metal buttons with superior strength and finer surface finishes, suitable for applications requiring robust performance. Your choice depends on the desired material properties, production volume, and aesthetic requirements to ensure optimal button manufacturing.
injection molding vs die casting (for buttons) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com