Direct control involves hands-on management of processes or devices in real-time, enabling immediate adjustments to system behavior. Supervisory control oversees multiple direct controllers, allowing your system to optimize overall performance through higher-level decision-making and coordination.
Table of Comparison
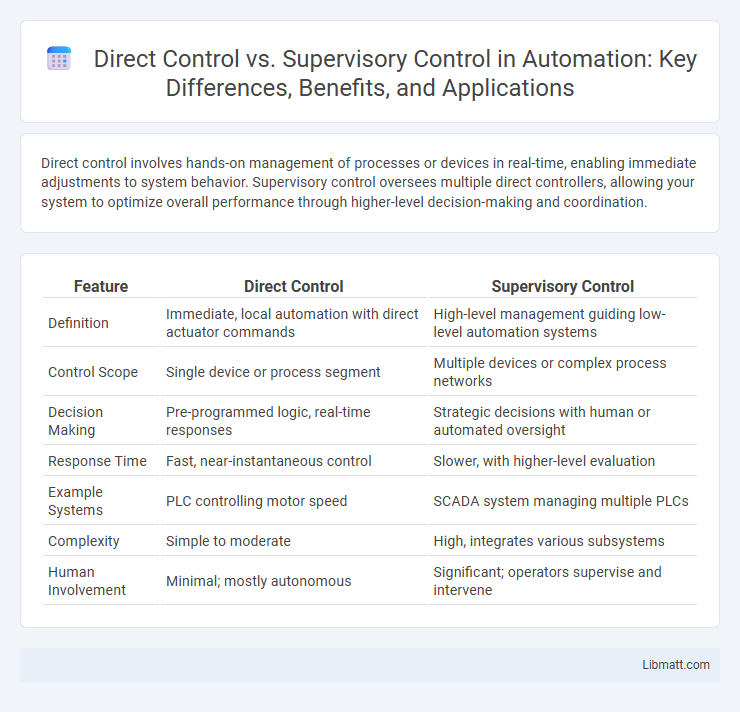
| Feature | Direct Control | Supervisory Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate, local automation with direct actuator commands | High-level management guiding low-level automation systems |
| Control Scope | Single device or process segment | Multiple devices or complex process networks |
| Decision Making | Pre-programmed logic, real-time responses | Strategic decisions with human or automated oversight |
| Response Time | Fast, near-instantaneous control | Slower, with higher-level evaluation |
| Example Systems | PLC controlling motor speed | SCADA system managing multiple PLCs |
| Complexity | Simple to moderate | High, integrates various subsystems |
| Human Involvement | Minimal; mostly autonomous | Significant; operators supervise and intervene |
Introduction to Control Systems
Control systems regulate the behavior of machines or processes by managing inputs to achieve desired outputs. Direct Control involves immediate interaction with a system, allowing real-time adjustments, while Supervisory Control oversees multiple systems, issuing commands without continuous manual input. Understanding these distinctions enhances your ability to design and optimize automation for efficiency and reliability.
Defining Direct Control
Direct Control involves continuous, real-time management of a system or process, where commands are executed immediately without intermediaries. This control type enables precise and instant adjustments, often implemented in automated systems like temperature regulation or motor speed control. Direct Control contrasts with Supervisory Control by requiring constant operator involvement or feedback loops for immediate decision-making and action.
Understanding Supervisory Control
Supervisory control involves a higher-level system overseeing and adjusting the operations of multiple direct control devices, enabling efficient management of complex processes. This approach allows for real-time monitoring, decision-making, and adjustments without requiring constant human intervention at the device level. Industries such as manufacturing, robotics, and power systems rely on supervisory control for optimized performance and system-wide coordination.
Key Differences: Direct vs Supervisory Control
Direct control involves immediate, hands-on management of processes or systems, enabling real-time adjustments based on instant feedback. Supervisory control oversees multiple direct control units, coordinating and optimizing their performance through higher-level decision-making without intervening in every detail. Key differences include the scope of control, with direct control focusing on individual components and supervisory control managing overall system efficiency and integration.
Advantages of Direct Control
Direct control offers rapid response times by enabling immediate system adjustments without intermediary processing, enhancing operational efficiency in time-sensitive applications. It simplifies system architecture, reducing potential points of failure and maintenance complexity. The straightforward feedback loop in direct control ensures higher reliability and ease of troubleshooting in industrial automation environments.
Benefits of Supervisory Control
Supervisory control enhances system efficiency by allowing high-level management of multiple processes simultaneously, reducing the need for constant human intervention. It improves safety through automated monitoring and quick response mechanisms, minimizing risks associated with manual operations. Your operations gain flexibility and scalability, making it easier to adapt to complex industrial environments and optimize overall performance.
Common Applications in Industry
Direct Control is commonly used in processes requiring immediate response and minimal delay, such as temperature regulation in HVAC systems and speed control in conveyor belts. Supervisory Control is prevalent in complex industrial environments like power plants and manufacturing plants, where it oversees multiple control loops and coordinates system-wide operations. Both control methods optimize efficiency, with Direct Control handling real-time adjustments and Supervisory Control enabling strategic management.
Choosing the Right Control Strategy
Selecting the appropriate control strategy hinges on system complexity and operational goals, where direct control offers immediate response and simplicity for straightforward processes, while supervisory control provides high-level decision-making and adaptability in complex, dynamic environments. Direct control optimizes real-time adjustments through low-level controllers, ensuring precise and rapid execution, whereas supervisory control integrates advanced algorithms and human oversight to manage multiple control loops and system-wide coordination. Evaluating factors such as process variability, required flexibility, and resource availability guides the choice between the immediacy of direct control and the strategic oversight of supervisory control systems.
Technological Trends Influencing Controls
Technological trends such as the integration of IoT devices, advanced sensor networks, and real-time data analytics are shifting control paradigms from direct control systems to more sophisticated supervisory control architectures. Edge computing and AI-driven decision-making enhance supervisory control by enabling predictive maintenance and adaptive process optimization without constant human intervention. Cybersecurity advancements ensure these systems remain resilient against threats, making supervisory control more viable for complex industrial applications.
Future Outlook for Control Systems
Future control systems will increasingly integrate direct control and supervisory control to enhance efficiency and adaptability in complex industrial environments. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable supervisory control systems to interpret vast sensor data, optimize decision-making, and manage autonomous agents with minimal human intervention. The convergence of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and real-time analytics will further drive the evolution of hybrid control architectures, promoting scalability and resilience in smart manufacturing and cyber-physical systems.
Direct Control vs Supervisory Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com