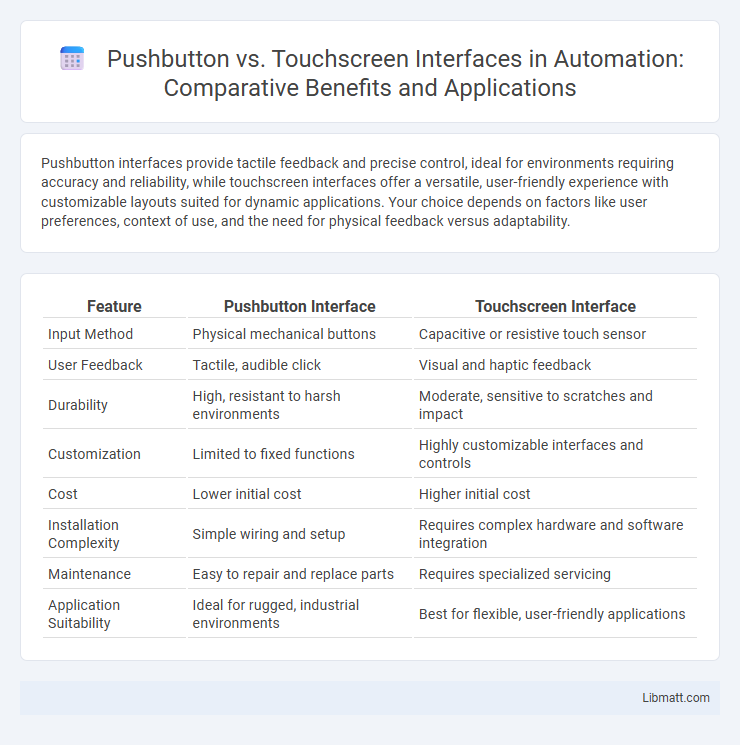
Pushbutton interfaces provide tactile feedback and precise control, ideal for environments requiring accuracy and reliability, while touchscreen interfaces offer a versatile, user-friendly experience with customizable layouts suited for dynamic applications. Your choice depends on factors like user preferences, context of use, and the need for physical feedback versus adaptability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pushbutton Interface | Touchscreen Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Input Method | Physical mechanical buttons | Capacitive or resistive touch sensor |
| User Feedback | Tactile, audible click | Visual and haptic feedback |
| Durability | High, resistant to harsh environments | Moderate, sensitive to scratches and impact |
| Customization | Limited to fixed functions | Highly customizable interfaces and controls |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Installation Complexity | Simple wiring and setup | Requires complex hardware and software integration |
| Maintenance | Easy to repair and replace parts | Requires specialized servicing |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for rugged, industrial environments | Best for flexible, user-friendly applications |
Overview of Pushbutton and Touchscreen Interfaces
Pushbutton interfaces use physical buttons to provide tactile feedback and precise control, making them ideal for environments requiring durability and reliability. Touchscreen interfaces rely on capacitive or resistive sensors to detect user input on a flat display, offering dynamic, versatile interaction with customizable on-screen controls. Pushbuttons excel in applications demanding mechanical robustness, while touchscreens dominate in devices prioritizing compact design and multi-functionality.
Historical Evolution of Human-Machine Interfaces
The historical evolution of human-machine interfaces highlights the transition from mechanical pushbutton controls, widely used in early industrial and consumer devices for their tactile feedback and durability, to modern touchscreen interfaces that offer dynamic, flexible user experiences through capacitive or resistive sensing technology. Pushbutton interfaces dominated the mid-20th century, exemplified by typewriters and early telephones, while touchscreens became prevalent in the 21st century with the advent of smartphones and interactive kiosks, driven by advancements in display technologies and miniaturized electronics. This shift reflects a broader trend towards more intuitive, versatile, and space-efficient input methods in human-machine interaction design.
Design Principles of Pushbutton Interfaces
Pushbutton interfaces prioritize tactile feedback and physical actuation, ensuring users receive clear confirmation through touch and sound when a command is registered. Strategic spacing, size, and labeling of buttons follow ergonomic principles to reduce user error and enhance accessibility, especially for visually impaired individuals. Your interaction becomes intuitive as the design emphasizes simplicity, reliability, and the minimization of accidental presses.
Touchscreen Interface Technology Explained
Touchscreen interface technology relies on capacitive or resistive sensors to detect input directly from your finger or a stylus, enabling intuitive and precise control. Capacitive touchscreens use the electrical properties of the human body to register touch, while resistive screens respond to pressure, allowing for versatile functionality across devices. This technology enhances user interaction by providing seamless access to applications with minimal physical effort compared to traditional pushbutton interfaces.
User Experience: Tactile Feedback vs. Visual Cues
Pushbutton interfaces provide distinct tactile feedback, enabling users to confirm inputs through physical sensation, which enhances accuracy and confidence, especially in low-visibility or high-stress environments. Touchscreen interfaces rely primarily on visual cues and subtle haptic responses, offering a versatile and sleek design but may lack the certainty of physical press for some users. Your choice between the two should consider the context of use, prioritizing tactile feedback for precise controls and touchscreens for adaptable, dynamic interfaces.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Pushbutton interfaces typically offer greater durability and lower maintenance costs due to their mechanical simplicity and resistance to wear in harsh environments. Touchscreen interfaces, while more modern and versatile, can be prone to scratches, cracks, and sensitivity issues, often requiring more frequent cleaning and potential repairs. Your choice should consider the operating environment and maintenance resources to ensure long-term functionality.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Interface Design
Pushbutton interfaces offer tactile feedback and simplicity, making them highly accessible for users with visual impairments or limited dexterity, as physical buttons are easier to locate and operate without sight. Touchscreen interfaces provide dynamic, customizable layouts but can pose challenges for users with motor skill difficulties or those requiring assistive technologies due to lack of physical feedback. Designing inclusive interfaces often involves integrating both pushbutton and touchscreen elements to accommodate diverse user needs and ensure broad accessibility compliance.
Application Scenarios: When to Choose Pushbutton or Touchscreen
Pushbutton interfaces excel in environments requiring tactile feedback and high reliability, such as industrial machinery, medical devices, and outdoor equipment where gloves or moisture are present. Touchscreen interfaces are ideal for applications demanding dynamic, customizable controls and rich visual feedback, including consumer electronics, kiosks, and smart home systems. Selecting between pushbutton and touchscreen depends on factors like user context, environmental conditions, durability requirements, and interface complexity.
Cost Implications and Scalability
Pushbutton interfaces generally incur lower initial costs due to simpler hardware and manufacturing processes, making them cost-effective for small to medium-scale applications. Touchscreen interfaces, though more expensive upfront, offer greater scalability by supporting software-based customization and multi-functionality without additional physical components. The long-term cost efficiency of touchscreens improves as scalability demands rise, especially in dynamic environments requiring frequent updates or feature expansions.
Future Trends in Interface Innovation
Future trends in interface innovation reveal a shift towards hybrid systems combining pushbutton tactile feedback with touchscreen versatility to enhance user experience and accessibility. Advances in haptic technology enable touchscreens to simulate the physical sensation of pushbuttons, improving precision and user confidence. Integration of AI-driven adaptive interfaces is expected to personalize interaction modes, optimizing responsiveness based on user preferences and environmental context.
Pushbutton vs Touchscreen Interface Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com