Managed switches offer advanced features like VLANs, QoS, and network monitoring, giving you greater control and security for complex network environments. Unmanaged switches provide basic plug-and-play connectivity ideal for small or simple networks where easy setup is a priority.
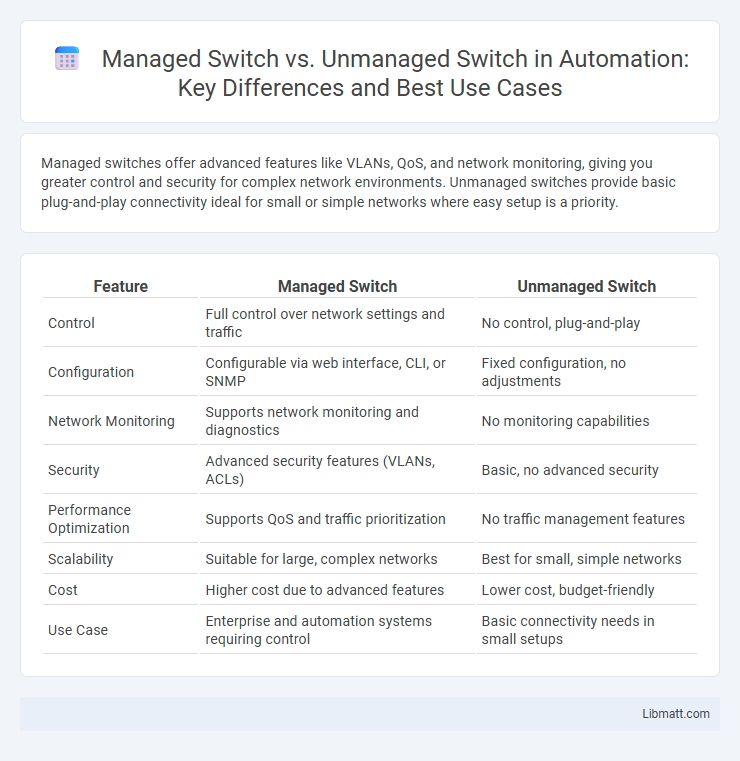
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Managed Switch | Unmanaged Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over network settings and traffic | No control, plug-and-play |
| Configuration | Configurable via web interface, CLI, or SNMP | Fixed configuration, no adjustments |
| Network Monitoring | Supports network monitoring and diagnostics | No monitoring capabilities |
| Security | Advanced security features (VLANs, ACLs) | Basic, no advanced security |
| Performance Optimization | Supports QoS and traffic prioritization | No traffic management features |
| Scalability | Suitable for large, complex networks | Best for small, simple networks |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced features | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Use Case | Enterprise and automation systems requiring control | Basic connectivity needs in small setups |
Overview of Managed and Unmanaged Switches
Managed switches offer advanced features such as VLAN configuration, traffic prioritization, and network monitoring, allowing you to optimize performance and enhance security. Unmanaged switches provide simple plug-and-play connectivity with minimal configuration, ideal for basic network setups or small offices. Choosing between managed and unmanaged switches depends on your network size, control needs, and budget constraints.
Key Features of Managed Switches
Managed switches offer advanced features such as VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, and network traffic monitoring, enabling precise control and segmentation of network data. They provide enhanced security options, including access control lists (ACLs) and port security, to protect sensitive information. Remote management capabilities through protocols like SNMP and CLI allow administrators to configure, troubleshoot, and optimize network performance efficiently.
Key Features of Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged switches offer plug-and-play simplicity with no configuration required, making them ideal for basic network setups. They provide fixed ports, typically ranging from 5 to 48, supporting straightforward data forwarding with minimal latency. Your network benefits from easy deployment and reliable performance without the need for ongoing management or advanced features.
Performance Comparison
Managed switches offer superior performance through advanced features like Quality of Service (QoS), VLAN segmentation, and traffic prioritization, which optimize network efficiency and reduce latency. Unmanaged switches operate with basic plug-and-play functionality, lacking the ability to control data flows or isolate traffic, resulting in potential bottlenecks in high-demand environments. Your network's performance significantly benefits from managed switches when handling complex, high-traffic scenarios that require precise control and monitoring.
Security Capabilities
Managed switches offer advanced security capabilities such as VLAN segmentation, Access Control Lists (ACLs), and port security to prevent unauthorized access and enhance network protection. These switches support features like 802.1X authentication, allowing network administrators to control device access at the port level, reducing the risk of insider threats. Unmanaged switches lack these security features, making them less suitable for environments requiring stringent network protection and access controls.
Network Scalability and Flexibility
Managed switches provide superior network scalability and flexibility by enabling advanced configuration options such as VLAN segmentation, traffic prioritization, and remote management, which support growth and dynamic network demands. Unmanaged switches offer limited scalability, primarily functioning as plug-and-play devices without customizable features, making them suitable for small or static networks. Enterprises requiring expandable, adaptable infrastructures typically invest in managed switches to optimize network performance and future-proof connectivity.
Ease of Use and Configuration
Unmanaged switches offer plug-and-play simplicity, requiring no configuration, making them ideal for users with minimal networking knowledge or small setups. Managed switches provide advanced features such as VLANs, QoS, and port mirroring but demand more technical expertise and time for configuration. Choosing between the two depends on the need for control and customization versus straightforward ease of use.
Cost Considerations
Managed switches command higher prices due to advanced features like VLAN support, traffic prioritization, and enhanced security controls, making them ideal for complex network environments. Unmanaged switches offer a cost-effective solution for small or simple networks by providing basic plug-and-play connectivity without configuration. Your budget and network needs will determine whether the investment in managed switch capabilities justifies the added expense.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Switch Type
Managed switches are ideal for complex networks requiring advanced features like VLAN segmentation, traffic prioritization, and remote monitoring, making them suitable for enterprise environments, data centers, and large-scale deployments. Unmanaged switches are best suited for small offices, home networks, or simple setups where plug-and-play functionality and minimal configuration are priorities. Choosing the appropriate switch depends on network size, required control level, and specific performance needs.
How to Choose the Right Switch for Your Network
Choosing the right switch for your network depends on your specific needs for control, scalability, and budget. Managed switches offer advanced features such as VLAN segmentation, traffic prioritization, and remote monitoring, making them ideal for larger or more complex networks requiring high security and customization. Unmanaged switches provide plug-and-play simplicity with minimal configuration, suitable for smaller or less demanding environments where ease of use and cost-effectiveness are priority.
Managed Switch vs Unmanaged Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com