Human-in-the-loop systems integrate human judgment to enhance decision-making quality, providing flexibility and error correction in complex scenarios. Fully automated systems offer faster processing and scalability but may lack the nuanced understanding that Your involvement brings to ensure accuracy and ethical considerations.
Table of Comparison
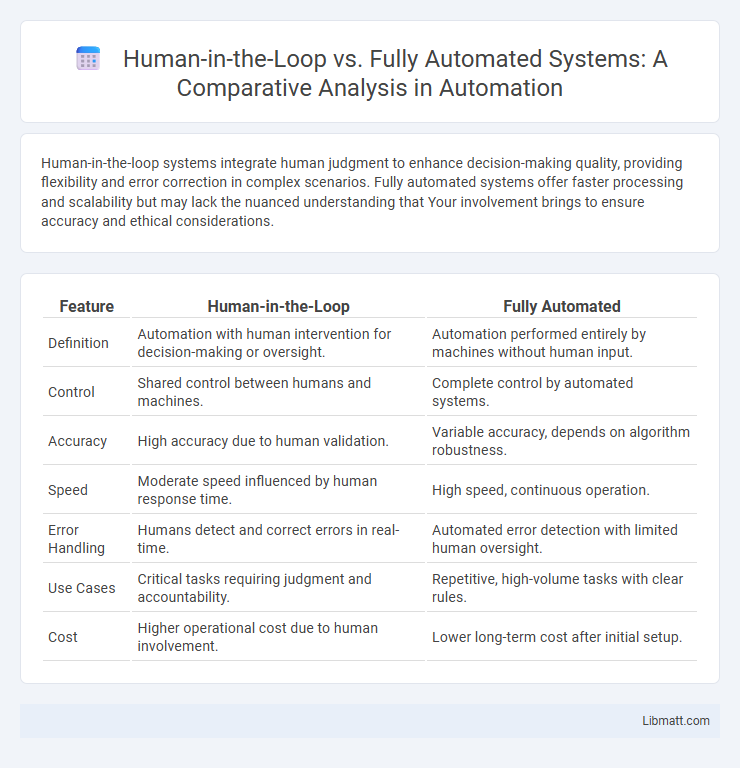
| Feature | Human-in-the-Loop | Fully Automated |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation with human intervention for decision-making or oversight. | Automation performed entirely by machines without human input. |
| Control | Shared control between humans and machines. | Complete control by automated systems. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to human validation. | Variable accuracy, depends on algorithm robustness. |
| Speed | Moderate speed influenced by human response time. | High speed, continuous operation. |
| Error Handling | Humans detect and correct errors in real-time. | Automated error detection with limited human oversight. |
| Use Cases | Critical tasks requiring judgment and accountability. | Repetitive, high-volume tasks with clear rules. |
| Cost | Higher operational cost due to human involvement. | Lower long-term cost after initial setup. |
Understanding Human-in-the-Loop Systems
Human-in-the-loop systems integrate human judgment with automated processes to enhance decision accuracy and adaptability in complex scenarios. These systems leverage human expertise for critical tasks such as quality control, anomaly detection, and ethical decision-making, ensuring higher reliability than fully automated solutions alone. You benefit from improved system transparency and the ability to intervene when machine algorithms encounter uncertain or ambiguous data.
What Defines Fully Automated Processes?
Fully automated processes operate without human intervention, relying on algorithms, machine learning models, and robotic systems to execute tasks from start to finish. These systems continuously collect and analyze data to make real-time decisions, optimizing efficiency and accuracy in workflows like manufacturing, data processing, and customer service. Key characteristics include scalability, consistency, and reduced operational costs, distinguishing them from human-in-the-loop models that require manual oversight or intervention.
Key Differences Between HITL and Automation
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) integrates human judgment with machine processing to enhance decision accuracy, especially in complex or ambiguous scenarios, whereas fully automated systems rely solely on algorithms and pre-defined rules for decision-making. HITL systems excel in tasks requiring contextual understanding and adaptability by leveraging human expertise, while fully automated solutions prioritize speed, scalability, and consistency without human intervention. The key differences lie in error handling capabilities, flexibility in decision-making, and the degree of human involvement during data analysis and operational processes.
Advantages of Human-in-the-Loop Approaches
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) approaches enhance decision accuracy by integrating human judgment with machine learning algorithms, enabling the correction of model errors and reducing bias. HITL systems improve adaptability and contextual understanding in complex scenarios where fully automated systems may struggle due to limited data or unforeseen situations. This hybrid approach supports continuous learning and model refinement by leveraging expert feedback, which ultimately boosts reliability and performance across diverse applications.
Benefits of Fully Automated Solutions
Fully automated solutions deliver unmatched efficiency by processing data and executing tasks without human intervention, reducing errors and operational costs significantly. They enable real-time decision-making and scalability in industries like manufacturing, finance, and customer service, enhancing productivity and consistency. Your business gains faster turnaround times and the ability to handle large-scale operations seamlessly with fully automated systems.
Challenges in Human-in-the-Loop Integration
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) integration faces challenges such as ensuring seamless collaboration between human operators and AI systems, managing latency issues during real-time decision-making, and addressing inconsistencies in human judgment that may affect data quality. Balancing the need for human oversight with the efficiency gains of automation requires robust interface design and continuous training to maintain accuracy and reliability. Your system's success depends on effectively overcoming these challenges to harness human insight while minimizing delays and errors.
Common Pitfalls of Full Automation
Full automation often struggles with handling ambiguous or complex scenarios that require human judgment, leading to errors or unintended consequences in critical processes. Overreliance on automated systems can result in reduced oversight, making it difficult to detect and correct mistakes promptly. You can mitigate these risks by integrating human-in-the-loop approaches, ensuring continuous monitoring and intervention when necessary.
Use Cases: When to Use HITL vs Automation
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) is ideal for use cases involving complex decision-making, where context, nuance, or ethical considerations are critical, such as medical diagnosis, fraud detection, or content moderation. Fully automated systems excel in high-volume, repetitive tasks with clearly defined rules, including data processing, customer service chatbots, and predictive maintenance. Combining HITL with automation enhances accuracy and efficiency in dynamic environments like autonomous vehicles or cybersecurity threat analysis.
Industry Trends: Blending Humans and Automation
Industry trends reveal a growing emphasis on blending human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems with fully automated processes to enhance accuracy, flexibility, and decision-making in AI applications. HITL models integrate human expertise for critical oversight, improving outcomes in complex environments like healthcare, finance, and customer service. Your business can leverage this hybrid approach to balance efficiency and reliability while adapting to evolving technological demands.
Future Outlook: Evolving Role of Human Input
Human-in-the-loop systems will increasingly blend artificial intelligence with human judgment to enhance accuracy and ethical decision-making in complex tasks. Fully automated processes excel in speed and scalability but face challenges in contextual understanding and adaptability, necessitating ongoing human oversight. Future advancements will likely foster hybrid models where human input is strategically integrated to complement automation, ensuring reliability and accountability in evolving technological landscapes.
Human-in-the-Loop vs Fully Automated Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com