Multiturn encoders process multiple conversational turns to capture contextual information, enhancing the understanding of dialogues, whereas singleturn encoders focus solely on individual turns, limiting context awareness. Choosing a multiturn encoder improves the accuracy of response generation by utilizing your conversation history effectively.
Table of Comparison
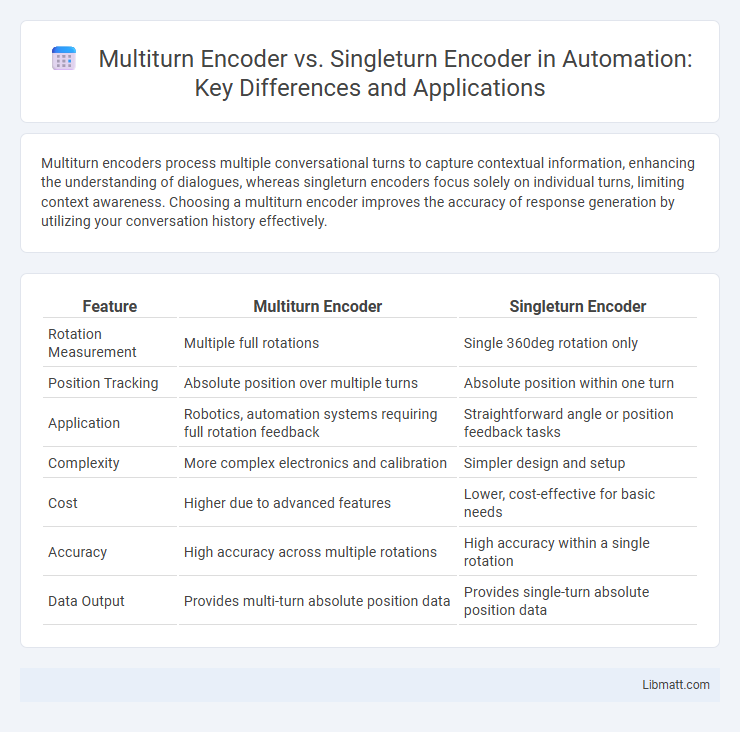
| Feature | Multiturn Encoder | Singleturn Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation Measurement | Multiple full rotations | Single 360deg rotation only |
| Position Tracking | Absolute position over multiple turns | Absolute position within one turn |
| Application | Robotics, automation systems requiring full rotation feedback | Straightforward angle or position feedback tasks |
| Complexity | More complex electronics and calibration | Simpler design and setup |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced features | Lower, cost-effective for basic needs |
| Accuracy | High accuracy across multiple rotations | High accuracy within a single rotation |
| Data Output | Provides multi-turn absolute position data | Provides single-turn absolute position data |
Introduction to Rotary Encoder Technologies
Rotary encoder technologies include multiturn and singleturn encoders, both essential for precise angular position measurement in industrial automation and robotics. Singleturn encoders track the position within one revolution, while multiturn encoders incorporate gear or battery-backed counters to monitor multiple revolutions, enabling accurate shaft angle tracking over extended rotations. The choice between multiturn and singleturn encoders depends on application requirements such as resolution, range of motion, and system complexity.
What is a Singleturn Encoder?
A Singleturn Encoder is a type of rotary encoder that measures the angular position within one full rotation, typically providing precise position data for 360 degrees of motion. It relies on internal sensors, such as optical or magnetic components, to detect the encoder's shaft position without storing positions beyond a single turn. Singleturn encoders are commonly used in applications where absolute position tracking within a single rotation is sufficient, such as motor feedback and robotics.
What is a Multiturn Encoder?
A Multiturn Encoder is a position sensor designed to track multiple complete rotations, often using an internal gear mechanism or battery backup to maintain absolute position data across turns. Unlike Singleturn Encoders that measure position within one rotation only, Multiturn Encoders provide enhanced precision for applications requiring detailed rotational history and long-range angular information. Your systems benefit from improved accuracy and reliability in robotic arms, industrial automation, and motor control with Multiturn Encoder technology.
Core Differences: Multiturn vs Singleturn Encoders
Multiturn encoders provide absolute position feedback over multiple revolutions by counting each full turn, making them ideal for applications requiring precise rotational tracking beyond a single 360-degree rotation. Singleturn encoders measure position within a single revolution, offering high-resolution angular data but resetting after each full rotation, which limits their use in continuous rotation scenarios. Understanding your system's need for continuous positional accuracy or high-resolution angular measurement helps determine whether a multiturn or singleturn encoder is best suited.
Accuracy and Resolution Comparison
Multiturn encoders provide higher accuracy and resolution by tracking multiple rotations, enabling precise position measurement beyond a single revolution. Singleturn encoders typically offer resolution limited to one full turn, making them less suitable for applications requiring exact multi-revolution tracking. The ability of multiturn encoders to maintain real-time position data over extended rotations results in improved precision and better performance in complex motion control systems.
Application Use Cases for Singleturn Encoders
Singleturn encoders are primarily used in applications requiring precise position measurement within a single rotation, such as robotics, CNC machines, and servo motor control. They excel in environments where the exact angle of a shaft needs to be determined without tracking multiple rotations. Your choice of a singleturn encoder is ideal for cost-sensitive systems that demand high accuracy without the complexity of multiturn tracking.
Application Use Cases for Multiturn Encoders
Multiturn encoders are essential in applications requiring precise shaft position tracking over multiple revolutions, such as robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation systems. They enable accurate determination of the absolute position in complex motion control scenarios, improving system reliability and performance. Multiturn encoders are preferred over singleturn encoders in use cases involving continuous rotation and long-term position monitoring.
Pros and Cons of Singleturn Encoders
Singleturn encoders provide precise angular position measurement within a single rotation, offering high-resolution feedback ideal for applications requiring limited rotational range. They are typically more cost-effective and simpler to install compared to multiturn encoders, reducing system complexity and maintenance needs. However, their limitation to one rotation restricts use in applications requiring tracking over multiple rotations, necessitating additional sensors or estimations for extended position monitoring.
Pros and Cons of Multiturn Encoders
Multiturn encoders offer precise position tracking over multiple rotations, making them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy in continuous motion, such as robotics and industrial automation. Their main advantage is the ability to maintain absolute position data without power loss, but they tend to be more complex and costly compared to singleturn encoders. Your choice depends on whether continuous position monitoring and higher resolution outweigh budget and system simplicity constraints.
Choosing the Right Encoder: Key Decision Factors
Choosing the right encoder depends on the complexity and context of your dialogue system, where multiturn encoders excel at capturing conversational history by processing multiple turns simultaneously, enhancing context understanding. Singleturn encoders focus on individual inputs, offering faster processing and simplicity suited for tasks with isolated queries or limited context dependency. Your choice should prioritize dialogue continuity in dynamic interactions for multiturn encoders, while singleturn encoders are ideal for straightforward, independent query processing.
Multiturn Encoder vs Singleturn Encoder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com