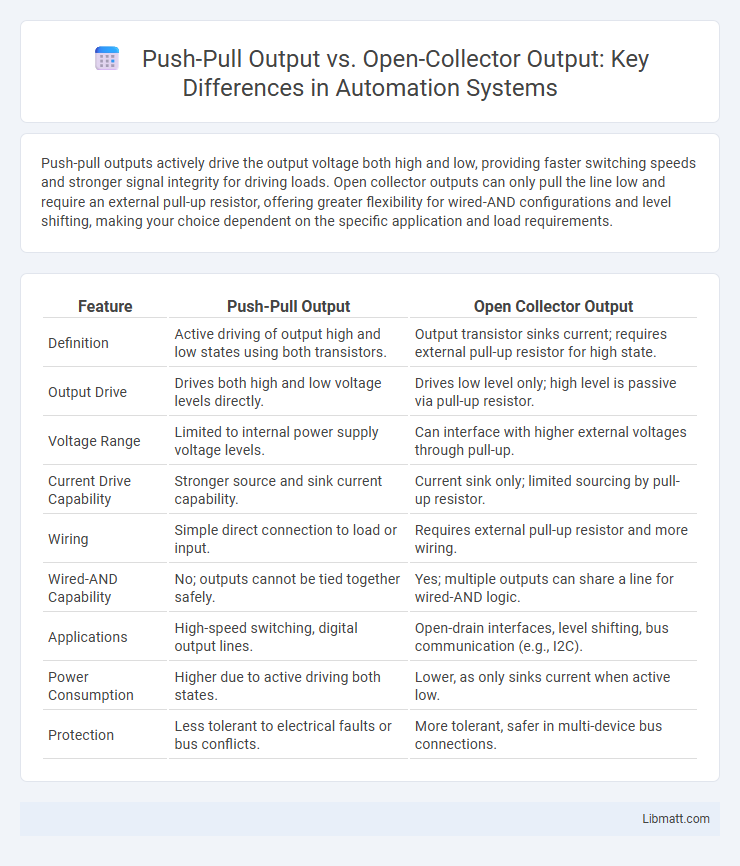
Push-pull outputs actively drive the output voltage both high and low, providing faster switching speeds and stronger signal integrity for driving loads. Open collector outputs can only pull the line low and require an external pull-up resistor, offering greater flexibility for wired-AND configurations and level shifting, making your choice dependent on the specific application and load requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Push-Pull Output | Open Collector Output |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active driving of output high and low states using both transistors. | Output transistor sinks current; requires external pull-up resistor for high state. |
| Output Drive | Drives both high and low voltage levels directly. | Drives low level only; high level is passive via pull-up resistor. |
| Voltage Range | Limited to internal power supply voltage levels. | Can interface with higher external voltages through pull-up. |
| Current Drive Capability | Stronger source and sink current capability. | Current sink only; limited sourcing by pull-up resistor. |
| Wiring | Simple direct connection to load or input. | Requires external pull-up resistor and more wiring. |
| Wired-AND Capability | No; outputs cannot be tied together safely. | Yes; multiple outputs can share a line for wired-AND logic. |
| Applications | High-speed switching, digital output lines. | Open-drain interfaces, level shifting, bus communication (e.g., I2C). |
| Power Consumption | Higher due to active driving both states. | Lower, as only sinks current when active low. |
| Protection | Less tolerant to electrical faults or bus conflicts. | More tolerant, safer in multi-device bus connections. |
Introduction to Output Configurations
Push-pull output configurations use two transistors to actively drive a signal both high and low, enabling faster switching and stronger drive capabilities. Open collector output relies on a transistor to pull the line low, requiring an external pull-up resistor to achieve high state, offering simpler wiring for wired-AND logic. Understanding these configurations helps you select the optimal interface for signal integrity and power efficiency in your electronic design.
What is Push-Pull Output?
Push-pull output is a type of digital output stage that can actively drive the output voltage both high and low by using two transistors, one connected to the positive supply and the other to ground. This configuration allows for faster switching speeds and stronger drive capabilities, making it ideal for driving loads directly without external components. Your devices benefit from push-pull outputs when precise voltage control and rapid response times are essential in applications such as microcontroller GPIO pins or communication interfaces.
What is Open Collector Output?
Open collector output is a type of transistor output used in digital circuits where the output transistor's collector is left open and connected externally to a voltage through a pull-up resistor. This configuration allows multiple open collector outputs to be wired together for wired-AND logic or to interface with different voltage levels safely. If you need flexible voltage control or to implement simple wired logic functions, open collector outputs provide an efficient solution.
Circuit Design Differences
Push-pull output stages feature two transistors working in tandem to actively drive the output both high and low, providing faster switching speeds and stronger signal levels. Open collector outputs use an open transistor that can only pull the output to ground, requiring an external pull-up resistor to achieve a high state, which allows multiple outputs to be wired together for wired-AND logic. Your circuit design must account for these differences, as push-pull configurations simplify driving loads directly while open collector outputs offer greater flexibility for wired logic connections and voltage level shifting.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Push-pull output stages actively drive the output high and low using complementary transistors, resulting in faster switching speeds and lower output impedance, which improves signal integrity. Open collector outputs can only pull the line low and require an external pull-up resistor to drive the line high, leading to slower rise times and higher power consumption due to continuous current flow through the resistor. Voltage levels in push-pull outputs closely match the supply rails, while open collector outputs rely on external pull-up voltage, making them more flexible for wired-AND configurations but less efficient electrically.
Advantages of Push-Pull Output
Push-pull output offers faster switching speeds and better drive capability compared to open collector output, enabling efficient signal transmission in digital circuits. It provides both sourcing and sinking current, allowing direct driving of loads without external pull-up resistors, which simplifies circuit design. Your applications benefit from reduced power dissipation and improved signal integrity when using push-pull outputs.
Advantages of Open Collector Output
Open collector outputs offer significant advantages in interfacing with multiple devices and enable easy wired-AND configurations, making them ideal for shared signal lines. They provide the flexibility to use various voltage levels beyond the logic device's supply, ensuring compatibility with diverse system voltages. Your design benefits from enhanced noise immunity and fault tolerance since open collector outputs can safely handle short circuits and external voltage spikes.
Common Applications of Push-Pull Outputs
Push-pull outputs are widely used in applications requiring fast switching and strong driving capabilities, such as LED displays, motor control circuits, and digital signal transmission. These outputs can source and sink current efficiently, making them ideal for driving loads directly without additional components. Your choice of push-pull output ensures better performance in circuits demanding precise control and quick response times.
Typical Uses for Open Collector Outputs
Open collector outputs are commonly used in applications requiring wired-AND logic, level shifting, or interfacing with different voltage domains. They allow multiple devices to share a single line for signaling, such as in I2C bus communication or alarm systems for fault detection. Open collector outputs are ideal for driving relays, LEDs, and other devices needing external pull-up resistors to control current flow.
Choosing the Right Output for Your Project
Push-pull output circuits provide both sourcing and sinking current capabilities, delivering faster switching speeds and better noise immunity, making them ideal for driving loads directly or interfacing with logic-level devices. Open collector outputs, which can only sink current, require an external pull-up resistor and are well-suited for wired-AND logic, level shifting, or interfacing with different voltage domains. Selecting the right output depends on your project's voltage compatibility, speed requirements, and whether multiple outputs need to be connected to a common line for shared control.
Push-Pull Output vs Open Collector Output Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com