Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) both refer to connected devices in industrial settings but IIoT specifically emphasizes advanced analytics, machine learning, and cybersecurity to optimize manufacturing and production processes. Understanding the differences helps you leverage the right technologies for improved operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Table of Comparison
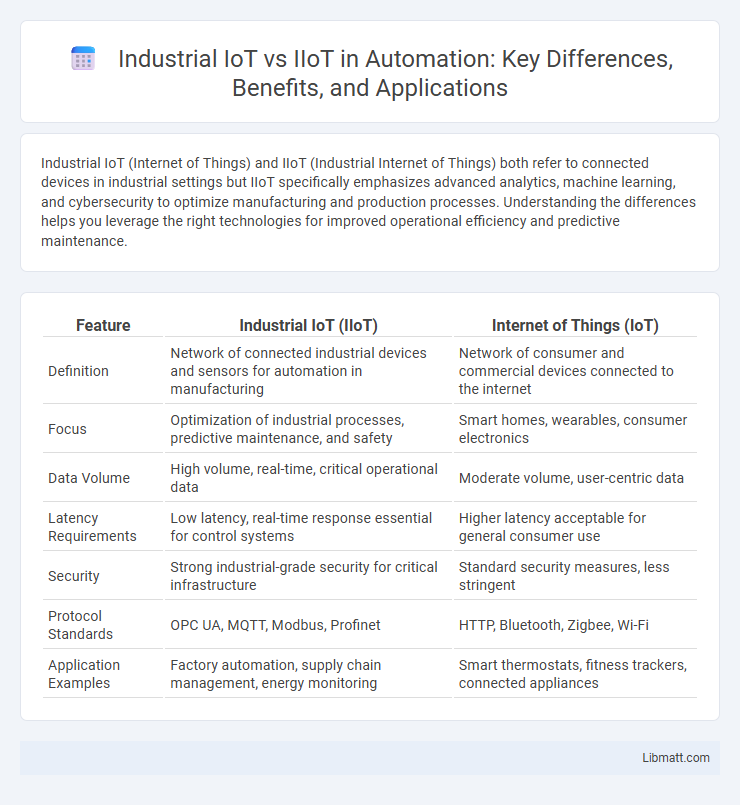
| Feature | Industrial IoT (IIoT) | Internet of Things (IoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected industrial devices and sensors for automation in manufacturing | Network of consumer and commercial devices connected to the internet |
| Focus | Optimization of industrial processes, predictive maintenance, and safety | Smart homes, wearables, consumer electronics |
| Data Volume | High volume, real-time, critical operational data | Moderate volume, user-centric data |
| Latency Requirements | Low latency, real-time response essential for control systems | Higher latency acceptable for general consumer use |
| Security | Strong industrial-grade security for critical infrastructure | Standard security measures, less stringent |
| Protocol Standards | OPC UA, MQTT, Modbus, Profinet | HTTP, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Wi-Fi |
| Application Examples | Factory automation, supply chain management, energy monitoring | Smart thermostats, fitness trackers, connected appliances |
Understanding Industrial IoT and IIoT: Terminology Explained
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) refers to the interconnected network of devices used to collect and exchange data in industrial environments, enhancing automation and operational efficiency. IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is a subset of IoT specifically focused on industrial applications, emphasizing advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to optimize manufacturing and supply chain processes. Understanding the distinction between Industrial IoT and IIoT helps you leverage targeted technologies for improved asset management and predictive maintenance.
Core Differences between Industrial IoT and IIoT
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) broadly encompasses connected devices in manufacturing and industrial settings, while IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) specifically targets advanced industrial applications with a focus on automation, data analytics, and machine-to-machine communication. IIoT integrates complex industrial equipment, sensors, and software platforms to optimize operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring. Your understanding of these core differences helps leverage IIoT for enhanced industrial performance beyond general Industrial IoT capabilities.
Historical Evolution of Industrial Connectivity
The Industrial Internet of Things (Industrial IoT) and IIoT both represent the evolution of industrial connectivity, evolving from traditional automation systems and SCADA networks to advanced data-driven platforms leveraging cloud computing and edge analytics. Early industrial connectivity relied heavily on wired connections and isolated control systems, while modern IIoT integrates wireless sensor networks, AI, and real-time data exchange to optimize manufacturing and operational efficiency. The shift from simple machine-to-machine communication to interconnected smart devices marks the historical progression that distinguishes Industrial IoT as a transformative force in Industry 4.0.
Key Technologies Powering IIoT and Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Industrial Internet of Things share foundational technologies such as sensors, edge computing, and cloud platforms that enable real-time data collection and analysis. IIoT leverages advanced machine learning algorithms, digital twins, and industrial-grade cybersecurity protocols to optimize manufacturing processes and enhance operational efficiency. Key technologies powering both systems include Industrial Ethernet, wireless communication standards like 5G, and AI-driven predictive maintenance tools.
Use Cases: Industrial IoT vs IIoT in Action
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) encompasses connected devices across various industries such as smart agriculture, energy management, and healthcare, enabling real-time data collection and analytics for operational efficiency. IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) specifically targets manufacturing, supply chain optimization, and predictive maintenance in heavy industries like automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals by integrating advanced sensors and machine learning. Use cases for Industrial IoT emphasize broad sector applications, whereas IIoT focuses on industrial automation, equipment monitoring, and production process improvements to increase productivity and reduce downtime.
Security Challenges and Solutions in IIoT Environments
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) environments face complex security challenges, including increased attack surfaces due to interconnected devices, legacy system vulnerabilities, and real-time data integrity risks. Effective solutions encompass implementing robust encryption protocols, continuous network monitoring with AI-driven anomaly detection, and deploying zero-trust architectures tailored for industrial operations. Integrating secure firmware updates and stringent access controls further mitigates threats, ensuring operational resilience and safety in critical IIoT infrastructures.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) both significantly enhance operational efficiency and productivity by enabling real-time data collection and analytics across manufacturing processes. IIoT specifically focuses on industrial applications, integrating advanced sensors, machine learning, and automation to optimize asset performance, reduce downtime, and improve predictive maintenance. By leveraging IIoT platforms, industries achieve higher throughput, lower operational costs, and increased overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), driving smarter decision-making and streamlined workflows.
Integration with Legacy Industrial Systems
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things) generally emphasizes consumer-oriented and new smart devices, while IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) focuses on integration with legacy industrial systems such as SCADA, PLCs, and DCS. IIoT solutions are designed to seamlessly connect and enhance existing equipment, improving operational efficiency and predictive maintenance without disrupting established workflows. Understanding the differences helps you tailor technology investments to maximize compatibility and performance in your industrial environment.
Future Trends in Industrial IoT and IIoT Development
Future trends in Industrial IoT (IIoT) emphasize enhanced connectivity through 5G and AI-driven analytics, enabling real-time data processing and predictive maintenance. IIoT development prioritizes cybersecurity advancements and seamless integration with edge computing to improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Your industrial systems will benefit from increased automation and intelligent decision-making, driving innovation across manufacturing and supply chain processes.
Choosing the Right IoT Solution for Your Industrial Needs
Choosing the right IoT solution for your industrial needs depends on understanding the difference between Industrial IoT (IIoT) and broader IoT technologies. IIoT emphasizes advanced sensor networks, real-time data analytics, and machine-to-machine communication tailored specifically for manufacturing, energy, and supply chain industries. Selecting an IIoT platform optimized for scalability, security, and interoperability ensures improved operational efficiency and predictive maintenance in complex industrial environments.
Industrial IoT vs IIoT Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com