A splitter box distributes electrical power or signals to multiple outputs, optimizing the flow for systems like cable TV or networking, while a junction box primarily serves as a protective enclosure for connecting wiring in electrical installations. Your choice depends on whether you need to split signals or simply secure and organize wiring connections safely.
Table of Comparison
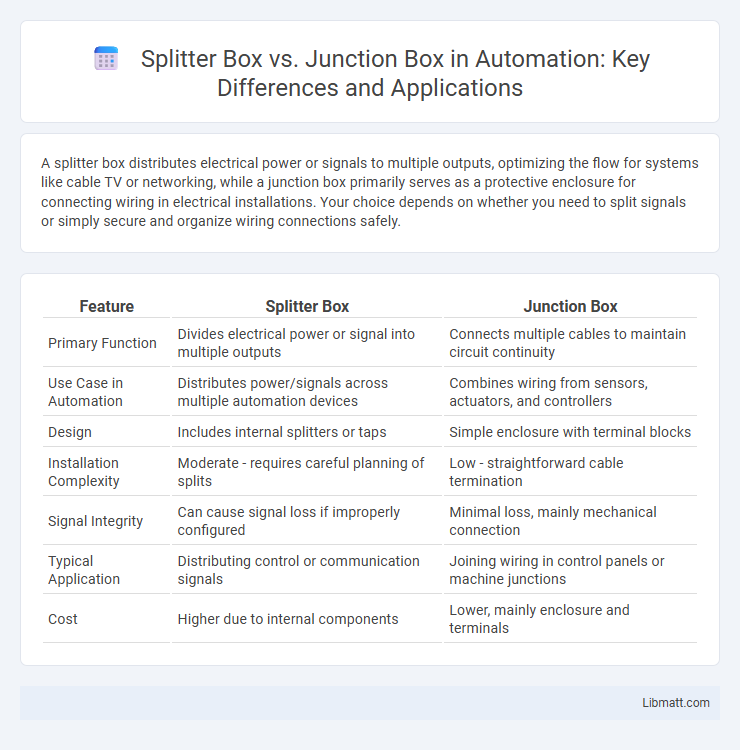
| Feature | Splitter Box | Junction Box |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Divides electrical power or signal into multiple outputs | Connects multiple cables to maintain circuit continuity |
| Use Case in Automation | Distributes power/signals across multiple automation devices | Combines wiring from sensors, actuators, and controllers |
| Design | Includes internal splitters or taps | Simple enclosure with terminal blocks |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate - requires careful planning of splits | Low - straightforward cable termination |
| Signal Integrity | Can cause signal loss if improperly configured | Minimal loss, mainly mechanical connection |
| Typical Application | Distributing control or communication signals | Joining wiring in control panels or machine junctions |
| Cost | Higher due to internal components | Lower, mainly enclosure and terminals |
Introduction to Electrical Enclosures
Splitter boxes and junction boxes are essential types of electrical enclosures designed to protect and organize wiring connections within electrical systems. Splitter boxes distribute power or signals from a single input into multiple outputs, commonly used in telecommunications and audio systems, while junction boxes primarily serve as centralized points where multiple electrical cables connect and branch out in residential or commercial wiring. Both enclosures provide safety by housing connections, preventing electrical hazards, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes.
What is a Splitter Box?
A splitter box is an electrical device designed to divide electrical power from a single input into multiple outputs, facilitating the distribution of electricity to various circuits or devices. Unlike a junction box, which primarily serves as a protective enclosure for electrical connections, a splitter box actively manages and directs power flow, making it essential in wiring systems requiring organized and efficient power distribution. Splitter boxes are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to streamline complex electrical networks.
What is a Junction Box?
A junction box is an essential electrical enclosure designed to protect and organize wire connections, providing a safe and accessible point for branching circuits in your home or commercial installations. It safeguards wiring from environmental damage and prevents accidental contact with live wires, ensuring electrical safety compliance. By consolidating multiple cables, a junction box simplifies troubleshooting and future maintenance tasks.
Key Differences Between Splitter Box and Junction Box
A splitter box divides a single electrical input into multiple outputs, commonly used in telecommunications and cable systems to distribute signals efficiently. In contrast, a junction box serves as a protective enclosure that joins multiple electrical wires, ensuring safety and organization in residential or commercial wiring. Your choice depends on whether you need signal distribution (splitter box) or wire connection and protection (junction box) in your electrical setup.
Common Applications of Splitter Boxes
Splitter boxes are commonly used in electrical and telecommunication systems to divide power or signal lines into multiple branches, making them ideal for distributing electricity in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They are often found in data centers, security camera systems, and fiber optic networks where signal splitting is required without degradation. Their design facilitates organized cable management and ensures efficient connectivity across multiple devices or locations.
Typical Uses of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes are typically used in electrical wiring systems to protect and organize wire connections, ensuring safety and preventing short circuits. They serve as a centralized point for branching circuits, facilitating easy access for maintenance and future expansions. Common applications include residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations where multiple wires and cables converge.
Pros and Cons of Splitter Boxes
Splitter boxes efficiently distribute power or signals to multiple outputs, making them ideal for complex wiring systems in telecommunications and electrical setups. They provide enhanced organization and troubleshoot convenience but can introduce signal loss or interference if not properly shielded or installed. Their higher initial cost and maintenance requirements may outweigh benefits in simpler applications where a junction box suffices.
Pros and Cons of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes protect electrical connections by housing wiring splices, reducing the risk of electrical hazards and simplifying maintenance. They offer easy access for inspections, upgrades, and repairs, but can become bulky and may require additional space in confined installations. Your choice of a junction box ensures organized wiring but might increase installation complexity compared to a splitter box.
Choosing the Right Box for Your Project
Selecting the right enclosure depends on your project's wiring complexity and electrical distribution needs. A junction box serves as a centralized point for connecting multiple wires safely, ideal for straightforward circuit connections, while a splitter box efficiently divides power from a single source into several outputs, perfect for systems requiring organized power distribution. Understanding your project's scale and functionality ensures you choose between a splitter box or junction box, optimizing safety and wiring efficiency for your installation.
Safety Considerations and Compliance Standards
Splitter boxes and junction boxes differ significantly in safety considerations and compliance standards, with junction boxes typically designed to house and protect electrical connections, reducing the risk of electrical shorts and fires by complying with NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements. Splitter boxes, often used for distributing power or signals, must meet specific industry standards such as UL certification to ensure safe operation under load and prevent hazards related to overcurrent or faulty wiring. Ensuring both devices comply with relevant codes and are installed by qualified electricians minimizes electrical hazards and enhances overall system safety.
Splitter Box vs Junction Box Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com