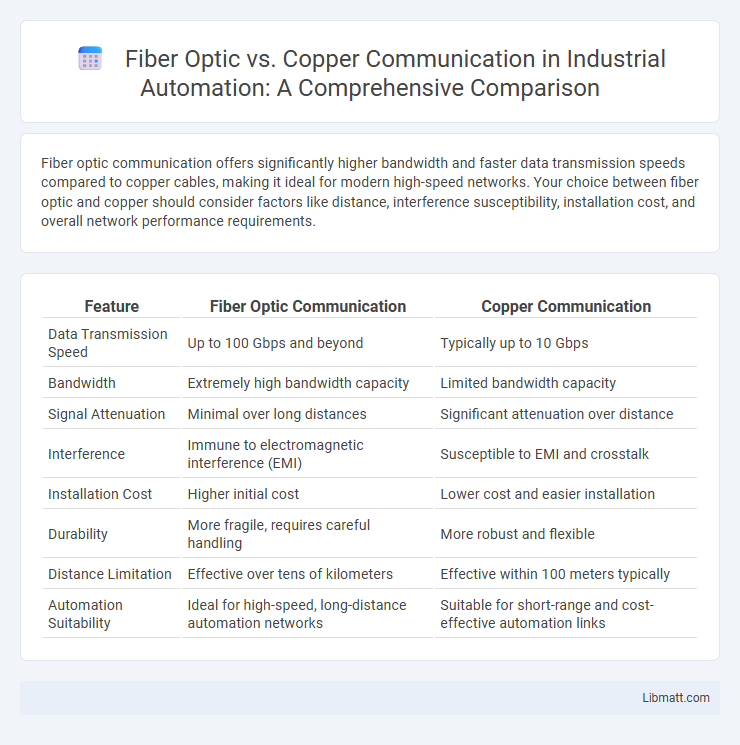
Fiber optic communication offers significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to copper cables, making it ideal for modern high-speed networks. Your choice between fiber optic and copper should consider factors like distance, interference susceptibility, installation cost, and overall network performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiber Optic Communication | Copper Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Typically up to 10 Gbps |
| Bandwidth | Extremely high bandwidth capacity | Limited bandwidth capacity |
| Signal Attenuation | Minimal over long distances | Significant attenuation over distance |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost and easier installation |
| Durability | More fragile, requires careful handling | More robust and flexible |
| Distance Limitation | Effective over tens of kilometers | Effective within 100 meters typically |
| Automation Suitability | Ideal for high-speed, long-distance automation networks | Suitable for short-range and cost-effective automation links |
Introduction to Fiber Optic and Copper Communication
Fiber optic communication uses light to transmit data through thin strands of glass or plastic, offering higher bandwidth and faster transmission speeds compared to copper communication, which relies on electrical signals sent through metal wires like twisted pair or coaxial cables. Copper communication remains widely used for shorter distances and lower-cost installations, but fiber optic technology dominates long-distance and high-performance networking due to its immunity to electromagnetic interference and lower signal attenuation. Understanding these key differences helps you select the best medium for your communication infrastructure needs.
Key Differences Between Fiber Optic and Copper Cables
Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals through glass or plastic fibers, offering significantly higher bandwidth and faster speeds compared to copper cables that rely on electrical signals via copper wires. Fiber optics provide greater resistance to electromagnetic interference, ensuring more reliable data transmission over long distances, while copper cables are more prone to signal degradation and interference. The durability and lower attenuation of fiber optic cables make them ideal for high-performance networks, whereas copper cables remain cost-effective for shorter, less demanding connections.
Data Transmission Speed Comparison
Fiber optic communication offers significantly higher data transmission speeds compared to copper, reaching up to 100 Gbps or more, while copper cables typically max out around 10 Gbps with advanced technologies. The superior bandwidth and low signal attenuation of fiber optic cables enable faster and more reliable long-distance data transfer, reducing latency and interference issues common with copper wiring. Your network's performance can greatly benefit from fiber's enhanced speed capabilities, especially for high-demand applications like video streaming and cloud computing.
Bandwidth Capabilities: Fiber Optic vs Copper
Fiber optic cables offer significantly higher bandwidth capabilities compared to copper cables, supporting data rates up to terabits per second over long distances without signal degradation. Copper cables, such as twisted-pair or coaxial, typically max out at bandwidths of 10 Gbps and suffer from electromagnetic interference and attenuation over extended lengths. The superior bandwidth and low latency of fiber optics make them ideal for high-speed internet, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure.
Signal Loss and Interference Issues
Fiber optic communication experiences significantly lower signal loss compared to copper cables, with attenuation rates as low as 0.2 dB/km for single-mode fibers versus up to 5 dB per 100 meters for copper. Fiber optics are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise. Copper communication, relying on electrical signals, is highly susceptible to signal degradation due to EMI, crosstalk, and external noise sources, impacting data integrity over longer distances.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Fiber optic cables demand more careful handling during installation due to their fragile glass fibers, requiring specialized tools and skills compared to the more robust copper cables. Maintenance for fiber optics usually involves less frequent repairs and can offer longer signal integrity over time, reducing overall downtime. Your choice between fiber optic and copper communication should factor in the higher initial installation cost of fiber optics against its superior durability and lower ongoing maintenance needs.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Investment
Fiber optic communication generally involves higher initial installation costs due to expensive materials and specialized labor, but its long-term investment proves cost-effective with lower maintenance expenses and higher durability. Copper communication systems have lower upfront costs but tend to incur increased expenses over time from signal degradation, interference issues, and frequent repairs or replacements. Your choice should weigh the balance between upfront budget constraints and the potential for substantial savings and performance benefits over the system's lifespan.
Security and Reliability Factors
Fiber optic communication offers superior security and reliability compared to copper due to its immunity to electromagnetic interference and difficulty in signal tapping. Copper cables are more vulnerable to eavesdropping, physical damage, and signal degradation over longer distances. Your network benefits from fiber optics with enhanced data protection and consistent performance in demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fiber optic communication significantly reduces environmental impact compared to copper by consuming less energy during data transmission and offering greater durability, which decreases the need for frequent replacements and waste. Copper mining and processing generate substantial pollution and require extensive resource extraction, while fiber optic cables use silica, a more abundant material with lower environmental degradation. Sustainable network choices that prioritize fiber optics contribute to reducing carbon footprints and conserving natural resources, making your communication infrastructure more eco-friendly.
Future Trends in Communication Technology
Fiber optic communication is rapidly becoming the backbone of future communication networks due to its unmatched bandwidth, low latency, and resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to copper cables. Emerging trends include the integration of fiber optics with 5G networks and the expansion of internet infrastructures through technologies like Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) to meet growing data demands. Your investments in communication infrastructure will benefit from prioritizing fiber optic solutions to ensure scalability and enhanced performance in the evolving digital landscape.
Fiber Optic vs Copper Communication Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com