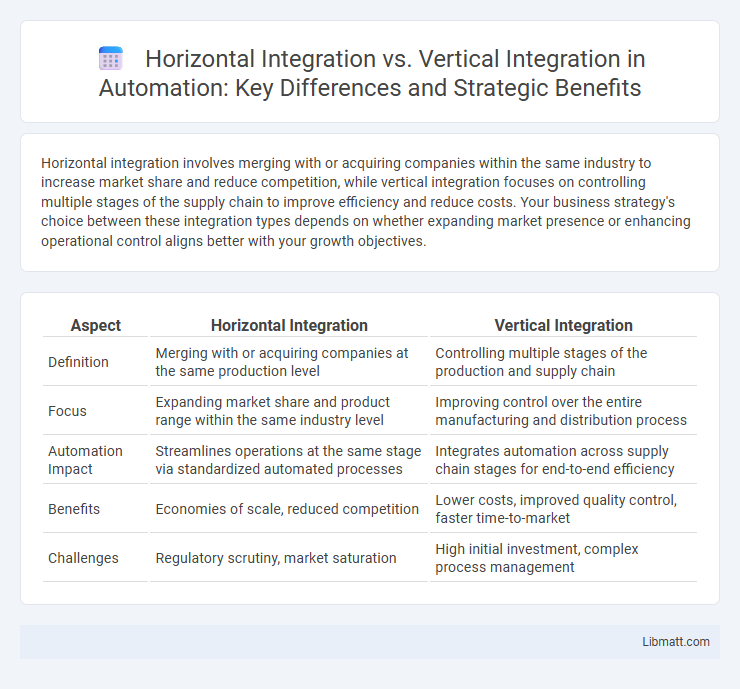
Horizontal integration involves merging with or acquiring companies within the same industry to increase market share and reduce competition, while vertical integration focuses on controlling multiple stages of the supply chain to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Your business strategy's choice between these integration types depends on whether expanding market presence or enhancing operational control aligns better with your growth objectives.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Merging with or acquiring companies at the same production level | Controlling multiple stages of the production and supply chain |
| Focus | Expanding market share and product range within the same industry level | Improving control over the entire manufacturing and distribution process |
| Automation Impact | Streamlines operations at the same stage via standardized automated processes | Integrates automation across supply chain stages for end-to-end efficiency |
| Benefits | Economies of scale, reduced competition | Lower costs, improved quality control, faster time-to-market |
| Challenges | Regulatory scrutiny, market saturation | High initial investment, complex process management |
Introduction to Business Integration Strategies
Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry to increase market share and reduce competition, while vertical integration focuses on controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, from production to distribution. These business integration strategies help companies optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and improve profitability by either expanding their market presence or securing supply chain control. Understanding the differences between horizontal and vertical integration enables you to choose the best approach for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
What is Horizontal Integration?
Horizontal integration is a business strategy where a company acquires or merges with other firms operating at the same stage of the production process within the same industry. This approach aims to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale by consolidating similar businesses. Companies like Facebook acquiring Instagram exemplify horizontal integration by expanding their reach within the social media sector.
What is Vertical Integration?
Vertical integration is a business strategy where a company controls multiple stages of its supply chain, from raw material sourcing to production and distribution. This approach enhances cost efficiency, improves supply chain coordination, and increases control over product quality and delivery timelines. Companies like Apple use vertical integration to streamline operations and maintain competitive advantages through direct oversight of manufacturing and retail.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with companies operating at the same stage of the supply chain, expanding market share within a particular industry. Vertical integration occurs when a company controls multiple stages of production or distribution, enhancing efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers or distributors. Understanding these key differences can help you determine whether expanding your market reach or streamlining your production process best aligns with your business strategy.
Advantages of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration offers significant advantages by enabling companies to expand market share and reduce competition through the acquisition of similar businesses. This strategy allows for economies of scale, lowering production costs and increasing operational efficiency across combined entities. Your business can benefit from enhanced bargaining power with suppliers and improved brand recognition in the marketplace through horizontal integration.
Advantages of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain, reducing dependency on external suppliers and minimizing costs associated with outsourcing. By owning multiple stages of production, companies improve efficiency, ensure consistent quality, and accelerate decision-making processes. Your business can achieve stronger market positioning and greater competitive advantage through better resource coordination and streamlined operations.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Horizontal integration can lead to reduced competition, which may result in antitrust issues, decreased innovation, and higher operational risks due to overdependence on a single market segment. Vertical integration poses challenges such as high capital investment, complex supply chain management, and potential inefficiencies from managing diverse business operations. Both strategies risk regulatory scrutiny and demand careful evaluation of long-term impacts on flexibility and market responsiveness.
Real-World Examples of Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration is exemplified by Facebook's acquisition of Instagram, expanding its social media dominance by absorbing a direct competitor. Vertical integration is illustrated by Apple Inc., which controls multiple stages of production and distribution, from designing hardware to operating retail stores. These strategies enhance market control, reduce costs, and streamline operations within their respective industries.
How to Choose the Right Integration Strategy
Choosing the right integration strategy depends on a company's core objectives and market position; horizontal integration is ideal for expanding market share and reducing competition by acquiring or merging with competitors. Vertical integration suits businesses aiming to control the supply chain, improve production efficiency, and reduce costs by owning multiple stages of the value chain. Analyzing competitive advantage, cost structures, and growth potential guides the decision between these strategies.
Horizontal vs Vertical Integration: Which One Suits Your Business?
Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with competitors to expand market share within the same industry, enhancing economies of scale and reducing competition. Vertical integration focuses on controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, from production to distribution, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers. Choosing between horizontal and vertical integration depends on business goals, industry structure, and desired control over processes or market expansion.
Horizontal Integration vs Vertical Integration Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com