HMI panels offer intuitive touchscreens designed specifically for real-time control and monitoring in industrial settings, providing a user-friendly interface for operators. Industrial PCs deliver higher processing power and flexibility, enabling complex data analysis and integration across diverse systems in manufacturing environments.
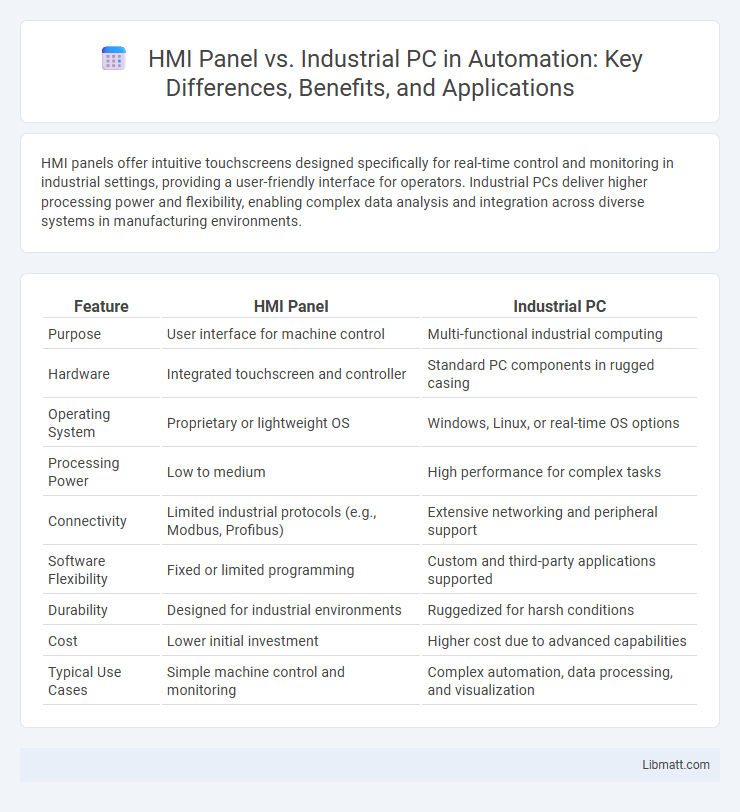
Table of Comparison
| Feature | HMI Panel | Industrial PC |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | User interface for machine control | Multi-functional industrial computing |
| Hardware | Integrated touchscreen and controller | Standard PC components in rugged casing |
| Operating System | Proprietary or lightweight OS | Windows, Linux, or real-time OS options |
| Processing Power | Low to medium | High performance for complex tasks |
| Connectivity | Limited industrial protocols (e.g., Modbus, Profibus) | Extensive networking and peripheral support |
| Software Flexibility | Fixed or limited programming | Custom and third-party applications supported |
| Durability | Designed for industrial environments | Ruggedized for harsh conditions |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher cost due to advanced capabilities |
| Typical Use Cases | Simple machine control and monitoring | Complex automation, data processing, and visualization |
Introduction to HMI Panels and Industrial PCs
HMI panels serve as user-friendly interfaces designed for real-time monitoring and control in industrial environments, offering touchscreen capabilities tailored to specific machinery and processes. Industrial PCs provide robust computing power with enhanced durability, capable of running complex applications and data processing for automation systems. Understanding your operational needs helps determine whether an HMI panel or an Industrial PC best supports your control and interface requirements.
Key Differences: HMI Panel vs Industrial PC
HMI panels are designed primarily for user interface tasks with touchscreen displays, focusing on real-time control and monitoring of industrial machinery, whereas industrial PCs offer greater processing power and flexibility for complex computing tasks and data analysis in industrial environments. HMI panels typically feature simplified hardware and software tailored for specific machine control, while industrial PCs support diverse applications with higher storage, expandability, and connectivity options for integration with multiple systems. The choice between HMI panels and industrial PCs depends on the requirement for dedicated interface simplicity versus advanced computational capability and multitasking in industrial automation.
Hardware Specifications Comparison
HMI panels typically feature resistive or capacitive touchscreens with integrated microprocessors optimized for real-time data visualization and control, while industrial PCs offer higher processing power with multi-core CPUs, expanded RAM, and versatile input/output options for complex automation tasks. Industrial PCs support extensive connectivity through PCIe slots, USB ports, and Ethernet interfaces, making them suitable for demanding applications requiring robust hardware performance. Your choice depends on whether you need specialized, compact hardware for direct machine interfacing (HMI panel) or powerful, scalable computing capabilities (industrial PC) for advanced industrial processes.
Software Capabilities and Compatibility
HMI panels typically offer user-friendly interfaces with built-in software optimized for specific industrial control applications, providing seamless integration with PLC systems and standard automation protocols. Industrial PCs deliver greater software versatility, supporting a wide range of operating systems like Windows and Linux, and enabling complex data processing, custom applications, and advanced analytics. Compatibility with diverse industrial communication standards and third-party software makes industrial PCs ideal for scalable and multi-functional automation environments.
User Interface Design and Usability
HMI panels offer simplified, purpose-built user interface designs optimized for specific industrial processes, ensuring intuitive and quick operation for users. Industrial PCs provide greater flexibility in interface customization, supporting complex applications and multitasking with advanced graphical capabilities. Your choice depends on the balance between straightforward usability in HMI panels and the extensive, adaptable interface options available through industrial PCs.
Performance and Processing Power
Industrial PCs offer superior performance and processing power compared to HMI panels, featuring advanced multi-core processors capable of handling complex automation tasks and data analysis in real time. HMI panels typically use embedded processors optimized for touchscreen interface and basic control functions, limiting their ability to process large datasets or run demanding applications. The enhanced computing capabilities of Industrial PCs make them ideal for applications requiring high-speed data processing, machine learning, or extensive connectivity in industrial environments.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
HMI panels are designed primarily for operator interface tasks in industrial applications such as machine control, data visualization, and real-time monitoring on the factory floor. Industrial PCs provide more advanced computing power and flexibility, supporting complex automation, predictive maintenance, and integration with enterprise systems in industries like manufacturing, energy, and transportation. Your choice depends on whether your application prioritizes simplicity and direct operator control or requires extensive data processing and connectivity for advanced industrial automation.
Integration with Automation Systems
HMI Panels are specifically designed for seamless integration with automation systems, offering direct control and real-time monitoring through built-in communication protocols like Modbus, ProfiBus, and Ethernet/IP. Industrial PCs provide greater flexibility and processing power, enabling advanced data analysis and complex automation tasks while supporting a wide range of interfaces for diverse industrial equipment. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize dedicated, straightforward automation interaction or customizable, high-performance computing within your industrial environment.
Cost Analysis and ROI Considerations
HMI panels generally offer lower initial costs and simpler integration, making them cost-effective for basic monitoring and control tasks in industrial settings. Industrial PCs present a higher upfront investment but deliver superior processing power, scalability, and multi-application capabilities, contributing to long-term operational efficiency. Evaluating ROI involves balancing initial expenditure against productivity gains, system flexibility, and maintenance costs, with Industrial PCs often yielding higher returns in complex or future-proof deployments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Industry
Choosing the right solution for your industry depends on the complexity and scale of your automation needs. HMI Panels offer intuitive, user-friendly interfaces ideal for straightforward control and monitoring tasks, while Industrial PCs provide robust computing power and flexibility for advanced data processing and integration. Evaluate your operational requirements, budget, and desired level of customization to determine whether an HMI Panel or Industrial PC best supports your industrial processes.
HMI Panel vs Industrial PC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com