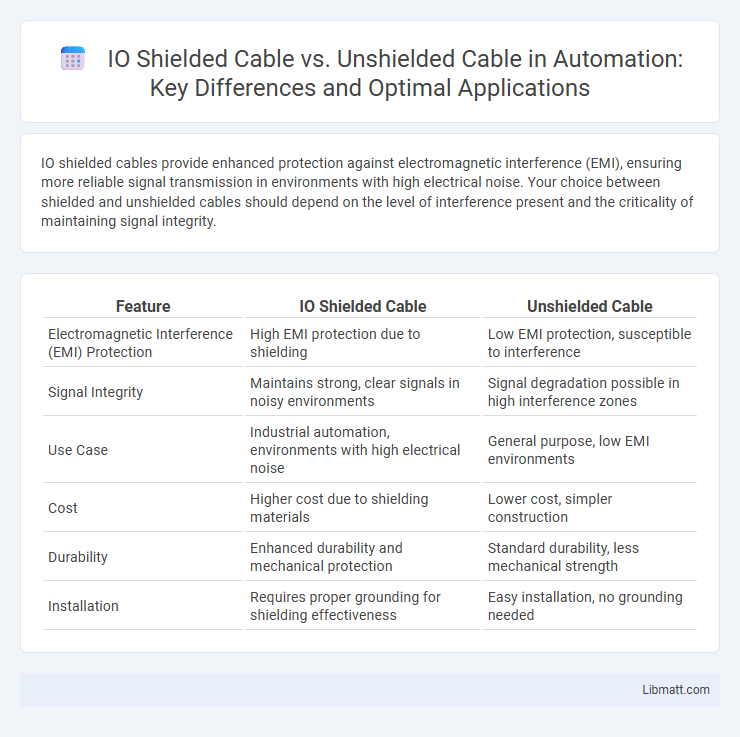
IO shielded cables provide enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring more reliable signal transmission in environments with high electrical noise. Your choice between shielded and unshielded cables should depend on the level of interference present and the criticality of maintaining signal integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | IO Shielded Cable | Unshielded Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection | High EMI protection due to shielding | Low EMI protection, susceptible to interference |
| Signal Integrity | Maintains strong, clear signals in noisy environments | Signal degradation possible in high interference zones |
| Use Case | Industrial automation, environments with high electrical noise | General purpose, low EMI environments |
| Cost | Higher cost due to shielding materials | Lower cost, simpler construction |
| Durability | Enhanced durability and mechanical protection | Standard durability, less mechanical strength |
| Installation | Requires proper grounding for shielding effectiveness | Easy installation, no grounding needed |
Introduction to IO Shielded and Unshielded Cables
IO shielded cables feature a protective metallic layer that reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensures signal integrity in high-speed data transmission. Unshielded cables lack this metallic barrier, making them more susceptible to noise but generally more flexible and cost-effective. The choice between shielded and unshielded IO cables depends on environmental factors, required signal quality, and budget constraints.
What Is an IO Shielded Cable?
An IO shielded cable is designed with a protective metallic layer that minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring uninterrupted signal transmission in sensitive electronic environments. This shielding enhances data integrity and reduces noise, making it ideal for high-performance input/output (IO) applications that demand reliability and stable connectivity. Your choice of an IO shielded cable over an unshielded variant can significantly improve overall system performance in environments prone to electrical disturbances.
What Is an Unshielded Cable?
An unshielded cable consists of twisted pairs of wires encased in a simple plastic jacket without additional shielding layers, making it more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to shielded cables. Commonly used in Ethernet networks, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables provide cost-effective and flexible connectivity but require careful installation to minimize crosstalk and noise. These cables are ideal for environments with limited electrical interference, such as residential or office settings.
Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables feature a protective layer of conductive material that reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise, while unshielded cables lack this protective layer, offering greater flexibility and cost efficiency. Shielded cables typically have a heavier design and enhanced durability, suitable for industrial or outdoor installations, whereas unshielded cables prioritize ease of installation in low-interference settings like residential or office networks. The choice between shielded and unshielded cables depends on factors such as EMI exposure, installation environment, and budget constraints.
Electromagnetic Interference: Protection and Vulnerabilities
Shielded IO cables provide superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) by incorporating a conductive layer that blocks external noise, making them ideal for environments with high EMI exposure. Unshielded cables lack this protective layer, leaving your data transmission vulnerable to signal degradation and potential interference from nearby electronic devices. Choosing shielded cables enhances signal integrity and reduces errors, especially in industrial or densely wired installations.
Performance and Signal Integrity Comparison
IO shielded cables provide superior performance and signal integrity by minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring cleaner data transmission in high-frequency applications. Unshielded cables are more vulnerable to external noise, leading to increased signal degradation and potential data errors in environments with significant electrical interference. Shielding in IO cables enhances reliability and maintains consistent bandwidth, making them ideal for sensitive and high-speed communication systems.
Applications and Use Cases for Shielded Cables
Shielded cables are widely used in environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI), such as industrial automation, medical equipment, and audio systems, to ensure signal integrity and reduce noise. Applications in data centers and telecommunications also benefit from shielded cables to maintain high-speed data transmission without disruption. In contrast to unshielded cables, shielded cables are crucial in settings requiring enhanced protection against external electrical disturbances and crosstalk.
Applications and Use Cases for Unshielded Cables
Unshielded cables excel in residential and office environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is minimal, supporting applications like basic Ethernet networking, telephone wiring, and audiovisual setups. They are preferred in cost-sensitive projects requiring flexibility and ease of installation without the need for heavy grounding or additional shielding measures. Common use cases include local area networks (LANs) in low-interference zones, simple data transmission, and connecting peripheral devices in controlled environments.
Cost Considerations: Shielded vs Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables typically cost more than unshielded cables due to the additional materials and manufacturing processes required to provide electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection. While unshielded cables are more budget-friendly, they may result in signal degradation in environments with high electrical noise, potentially increasing maintenance or replacement costs over time. Consider your environment and budget carefully to choose the cable that balances cost with performance for your specific application.
How to Choose Between IO Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Choosing between IO shielded and unshielded cables depends on your environment's susceptibility to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and the sensitivity of your connected devices. Shielded cables offer superior protection against EMI, making them ideal for industrial settings or dense electronic installations, while unshielded cables are sufficient for low-interference environments and offer greater flexibility and cost savings. Your decision should prioritize signal integrity and noise reduction requirements to ensure optimal performance.
IO Shielded Cable vs Unshielded Cable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com