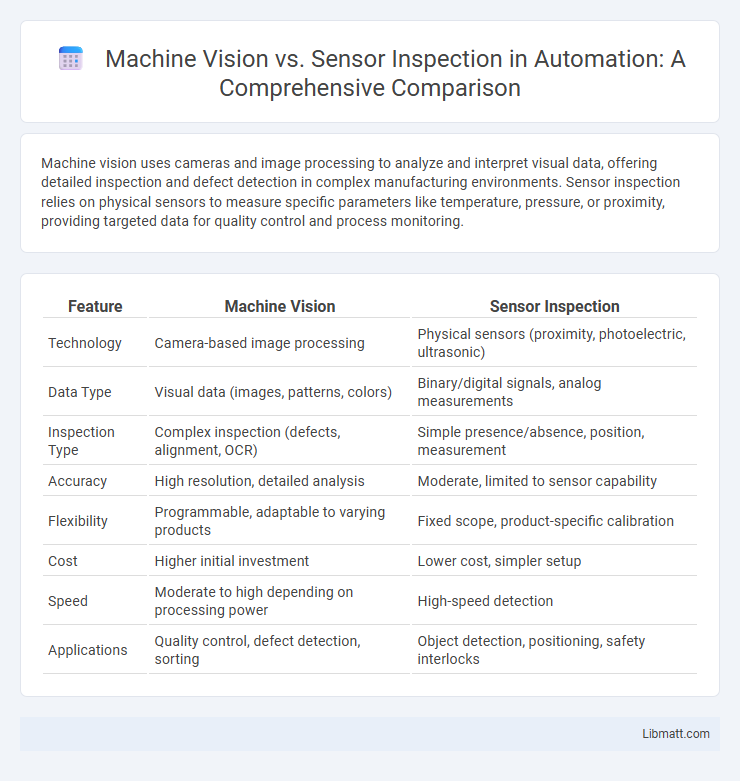
Machine vision uses cameras and image processing to analyze and interpret visual data, offering detailed inspection and defect detection in complex manufacturing environments. Sensor inspection relies on physical sensors to measure specific parameters like temperature, pressure, or proximity, providing targeted data for quality control and process monitoring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Machine Vision | Sensor Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Camera-based image processing | Physical sensors (proximity, photoelectric, ultrasonic) |
| Data Type | Visual data (images, patterns, colors) | Binary/digital signals, analog measurements |
| Inspection Type | Complex inspection (defects, alignment, OCR) | Simple presence/absence, position, measurement |
| Accuracy | High resolution, detailed analysis | Moderate, limited to sensor capability |
| Flexibility | Programmable, adaptable to varying products | Fixed scope, product-specific calibration |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, simpler setup |
| Speed | Moderate to high depending on processing power | High-speed detection |
| Applications | Quality control, defect detection, sorting | Object detection, positioning, safety interlocks |
Introduction to Machine Vision and Sensor Inspection
Machine vision employs cameras and image processing algorithms to capture and analyze visual data for automated inspection, measurement, and identification. Sensor inspection uses specialized sensors such as proximity, ultrasonic, or thermal sensors to detect physical properties and environmental conditions without relying on image data. Both technologies enhance quality control and process automation but differ in data acquisition methods and application scopes.
Key Differences Between Machine Vision and Sensor Inspection
Machine vision systems use digital cameras and image processing to capture and analyze visual information, enabling complex pattern recognition and detailed defect detection. Sensor inspection relies on specific sensors such as proximity, pressure, or temperature sensors to measure physical properties and trigger simple pass/fail decisions. Machine vision offers greater flexibility and accuracy for identifying intricate defects, while sensor inspection provides faster, cost-effective solutions for detecting straightforward anomalies.
How Machine Vision Works
Machine vision works by using cameras and image processing algorithms to capture and analyze visual information from objects or environments, enabling automated inspection and quality control. It processes high-resolution images to detect defects, measure dimensions, and identify patterns with precision and speed. Advanced machine vision systems integrate artificial intelligence and deep learning to improve accuracy and adapt to complex inspection tasks.
How Sensor Inspection Works
Sensor inspection operates by using various physical sensors such as proximity, photoelectric, ultrasonic, or capacitive sensors to detect specific properties like distance, presence, or material characteristics of objects. These sensors convert physical inputs into electrical signals that are processed to identify defects, confirm dimensions, or ensure proper assembly in manufacturing environments. The technology excels in real-time, direct measurement tasks, providing precise and reliable data for automated quality control systems.
Advantages of Machine Vision Systems
Machine vision systems offer higher accuracy and speed in quality control by using advanced image processing algorithms, allowing real-time inspection and defect detection on production lines. Compared to traditional sensor inspection, machine vision provides greater flexibility to handle complex and variable products without physical contact, reducing wear and maintenance costs. Your manufacturing process benefits from enhanced data collection and analysis capabilities, improving overall efficiency and reducing downtime.
Benefits of Sensor-Based Inspection
Sensor-based inspection offers precise detection of physical properties such as temperature, pressure, and chemical composition, enhancing quality control accuracy in manufacturing processes. It enables real-time monitoring and faster response to anomalies, reducing downtime and improving production efficiency. These inspections are less affected by environmental conditions, ensuring consistent performance in harsh or variable settings compared to machine vision systems.
Applications of Machine Vision vs Sensor Inspection
Machine vision excels in applications requiring complex image analysis, such as quality control in electronics manufacturing, automated optical inspection, and robotic guidance systems. Sensor inspection is more suited for detecting presence, position, or simple physical properties like temperature, pressure, or proximity in assembly lines and safety monitoring. Your choice depends on whether detailed visual data processing or basic physical measurement is critical for your industrial process.
Performance Comparison: Accuracy and Speed
Machine vision systems typically offer higher accuracy compared to sensor inspection due to their ability to analyze complex visual data and detect subtle defects. Speed in machine vision is enhanced by advanced image processing algorithms and real-time analysis capabilities, surpassing the point-detection speed of traditional sensors. While sensor inspection provides fast binary outputs for simple presence or measurement checks, machine vision excels in both precise defect classification and high-throughput inspection environments.
Cost Considerations and Investment Factors
Machine vision systems often require a higher initial investment due to advanced cameras, lighting, and processing hardware, but they offer scalable solutions that can reduce long-term operational costs. Sensor inspection typically involves lower upfront costs with simpler components but may lead to increased expenses over time because of limited functionality and frequent maintenance. Evaluating your application's complexity and production volume helps determine whether the cost efficiency of machine vision outweighs the affordability of sensor inspection for your investment.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Industry
Machine vision offers high-resolution image analysis and pattern recognition ideal for complex quality control in automotive and electronics manufacturing. Sensor inspection provides precise measurement and detection capabilities suitable for simpler tasks such as presence verification and environmental monitoring in food processing and pharmaceuticals. Selecting the right technology depends on factors like inspection speed, accuracy requirements, and the complexity of the inspected features specific to the industry application.
Machine Vision vs Sensor Inspection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com