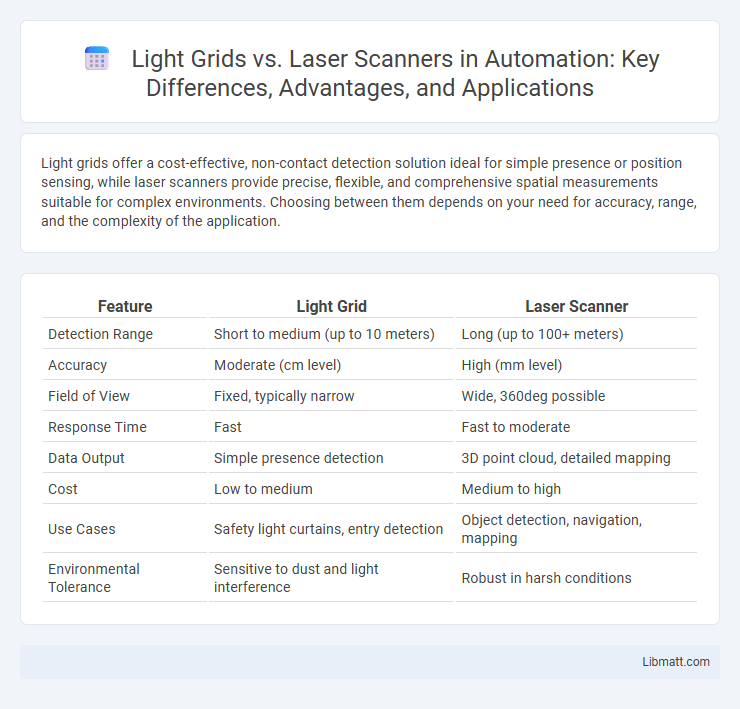
Light grids offer a cost-effective, non-contact detection solution ideal for simple presence or position sensing, while laser scanners provide precise, flexible, and comprehensive spatial measurements suitable for complex environments. Choosing between them depends on your need for accuracy, range, and the complexity of the application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light Grid | Laser Scanner |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Range | Short to medium (up to 10 meters) | Long (up to 100+ meters) |
| Accuracy | Moderate (cm level) | High (mm level) |
| Field of View | Fixed, typically narrow | Wide, 360deg possible |
| Response Time | Fast | Fast to moderate |
| Data Output | Simple presence detection | 3D point cloud, detailed mapping |
| Cost | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Use Cases | Safety light curtains, entry detection | Object detection, navigation, mapping |
| Environmental Tolerance | Sensitive to dust and light interference | Robust in harsh conditions |
Introduction to Light Grid and Laser Scanner Technologies
Light grid technology uses an array of infrared light beams to detect objects or measure distance by registering light interruptions, offering precise positioning in automation and safety systems. Laser scanners emit focused laser beams to map environments with high accuracy, commonly used in 3D scanning, robotics, and surveying due to their ability to capture detailed spatial data. Understanding these technologies helps you choose the right tool based on measurement precision, application requirements, and environmental factors.
How Light Grids Work
Light grids operate by projecting multiple infrared beams between paired transmitters and receivers arranged in a grid pattern, creating an invisible detection field. When an object interrupts one or more beams, the system detects the presence, size, and position of the obstruction with high accuracy. This non-contact sensing method is widely used in automation and safety applications due to its reliability and fast response time.
Principles Behind Laser Scanners
Laser scanners operate based on time-of-flight or phase-shift principles, emitting laser beams that reflect off surfaces to measure distances with high precision. These devices capture detailed 3D point clouds by calculating the time it takes for laser pulses to return, enabling accurate spatial mapping. In contrast, Light Grid technology relies on intersecting light beams to detect object presence or position, offering less detailed spatial data compared to laser scanners.
Key Differences Between Light Grids and Laser Scanners
Light grids use a matrix of infrared beams to create a detection field, ideal for object presence and safety applications, while laser scanners employ rotary laser beams for precise distance measurement and area mapping. Laser scanners provide higher accuracy and longer detection ranges compared to light grids, which are typically limited to short-range sensing and simple presence detection. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed spatial data or basic object interruption detection.
Accuracy and Detection Capabilities
Light grids offer high detection capabilities for object presence and position with reliable accuracy in industrial automation, but their precision is generally limited to simpler geometries. Laser scanners provide superior accuracy with detailed spatial mapping and 3D profiling, enabling precise measurements and intricate detection in complex environments. The enhanced resolution and range of laser scanners make them ideal for applications requiring fine detail and dynamic object tracking.
Application Scenarios for Light Grids
Light grids excel in industrial automation for safety monitoring and object detection on assembly lines, ensuring worker protection and efficient workflow. Their fast response time and easy integration make them ideal for packaging, material handling, and access control systems. Light grids are preferred in scenarios requiring non-contact sensing over large areas with minimal interference.
Application Scenarios for Laser Scanners
Laser scanners excel in high-precision applications such as topographic surveys, construction site monitoring, and heritage preservation by capturing detailed 3D spatial data. They are widely used in industrial settings for quality control, reverse engineering, and inspection of complex components due to their accuracy and ability to scan intricate surfaces. Urban planning and autonomous vehicle navigation also rely on laser scanners to generate accurate environmental models and detect obstacles in real time.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Light grids offer quick, non-intrusive installation with minimal wiring, simplifying integration into existing safety systems and reducing downtime during setup. Laser scanners require precise mounting and alignment, often necessitating professional calibration and periodic recalibration to maintain accuracy, which can increase maintenance efforts and costs. Ongoing maintenance for light grids generally involves routine cleaning and inspection, whereas laser scanners demand regular sensor cleaning and software updates to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Cost Comparison: Light Grid vs Laser Scanner
Light Grid systems generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to Laser Scanners, making them more accessible for smaller projects or budgets. Laser Scanners tend to have higher initial investment but provide greater accuracy and faster data capture, which can reduce long-term operational costs. You should consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and software, when choosing between these technologies for your scanning needs.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Light grids provide reliable detection for access control and safety zones, making them ideal for environments requiring consistent presence sensing. Laser scanners offer precise distance measurement and advanced object detection, suitable for complex navigation and intrusion detection tasks. Your choice depends on factors like the required detection range, environmental conditions, and the specific application demands for accuracy and flexibility.
Light Grid vs Laser Scanner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com