RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and MTU (Master Terminal Unit) are crucial components in SCADA systems, with RTUs collecting data from field devices and transmitting it to MTUs, which act as central controllers managing the overall communication and control processes. Understanding the differences between RTU and MTU helps optimize your industrial automation by ensuring accurate data acquisition and efficient system management.
Table of Comparison
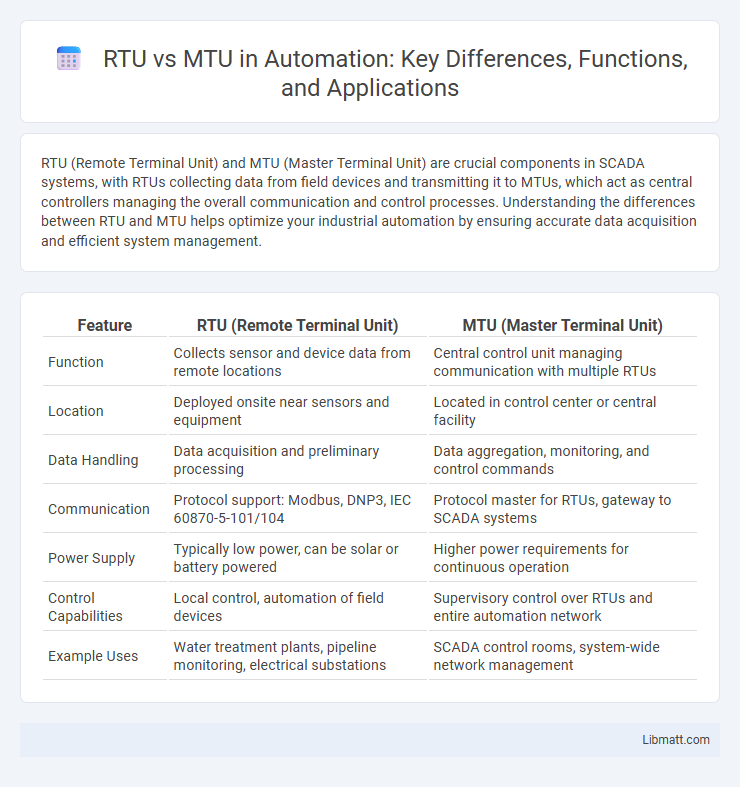
| Feature | RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) | MTU (Master Terminal Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Collects sensor and device data from remote locations | Central control unit managing communication with multiple RTUs |
| Location | Deployed onsite near sensors and equipment | Located in control center or central facility |
| Data Handling | Data acquisition and preliminary processing | Data aggregation, monitoring, and control commands |
| Communication | Protocol support: Modbus, DNP3, IEC 60870-5-101/104 | Protocol master for RTUs, gateway to SCADA systems |
| Power Supply | Typically low power, can be solar or battery powered | Higher power requirements for continuous operation |
| Control Capabilities | Local control, automation of field devices | Supervisory control over RTUs and entire automation network |
| Example Uses | Water treatment plants, pipeline monitoring, electrical substations | SCADA control rooms, system-wide network management |
Introduction to RTU and MTU
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and MTU (Master Terminal Unit) are essential components in SCADA systems used for monitoring and controlling industrial processes. RTUs collect data from sensors and field devices, transmitting this information to the MTU, which serves as the central control device to manage the overall system. Understanding the distinction between RTU and MTU helps optimize your industrial automation and data communication infrastructure.
What is a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)?
A Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) is an electronic device used in industrial control systems to remotely monitor and control equipment and processes. It collects data from sensors and sends commands to actuators through communication networks, often in utilities such as power, water, and oil and gas industries. RTUs enable real-time data acquisition and supervisory control in distributed automation systems, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability.
What is a Master Terminal Unit (MTU)?
A Master Terminal Unit (MTU) acts as the central communication hub in SCADA systems, coordinating data exchange between multiple Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and the control center. It collects, processes, and monitors real-time data from RTUs distributed across various locations, enabling efficient management of infrastructure such as electrical grids, water systems, and industrial processes. Your MTU serves as the core element that ensures accurate and timely decision-making through reliable data aggregation and command dissemination.
Key Functions of RTUs
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) primarily function as data acquisition and control devices in industrial automation, collecting sensor data and transmitting it to central control systems. They monitor field equipment, execute control commands, and support remote monitoring for systems like water treatment, oil and gas, and power distribution. Your industrial network benefits from RTUs' reliable performance in harsh environments and their ability to interface with multiple communication protocols.
Main Roles of MTUs
MTUs (Master Terminal Units) serve as centralized control points in remote monitoring and control systems, aggregating data from multiple RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) for efficient processing and decision-making. They manage communication protocols, coordinate system-wide operations, and facilitate real-time data analysis to ensure optimal performance of industrial and utility networks. MTUs enhance system scalability and reliability by providing high-level interface capabilities between field devices and control centers.
RTU vs MTU: Core Differences
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and MTU (Master Terminal Unit) differ primarily in their roles within a communication network, where RTUs collect data from field devices and transmit it to the MTU, which acts as the central control system. RTUs are designed for on-site data acquisition and local control, while MTUs process data, manage multiple RTUs, and facilitate decision-making. Understanding these core differences helps optimize system design to improve your network's efficiency and reliability.
Communication Protocols in RTU and MTU Systems
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and MTU (Master Terminal Unit) systems utilize distinct communication protocols to ensure reliable data exchange in industrial automation. RTUs often employ Modbus RTU or DNP3 protocols to collect and transmit sensor data, while MTUs use these protocols to coordinate and manage multiple RTUs within the network. Your system's efficiency depends on selecting compatible protocols that support error checking, addressing, and timing synchronization for seamless communication between RTUs and MTUs.
Applications of RTUs and MTUs in SCADA
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) are used in SCADA systems to monitor and control remote equipment in industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, and power distribution due to their ability to operate in harsh environments and handle extensive I/O points. MTUs (Master Terminal Units) serve as central controllers that collect data from multiple RTUs, enabling operators to visualize real-time status, manage alarms, and execute commands across large-scale infrastructure networks. Your SCADA system relies on seamless communication between RTUs and MTUs to ensure efficient remote monitoring and control of critical assets.
Advantages and Limitations of RTUs and MTUs
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) offer advantages like real-time data acquisition and remote control in harsh environments, making them ideal for distributed monitoring systems, but their limitations include higher complexity and cost compared to MTUs (Master Terminal Units). MTUs serve as centralized controllers that aggregate data from multiple RTUs, enabling comprehensive system management with simplified user interfaces, though they depend heavily on reliable communication links and offer less localized control. Understanding these differences helps you optimize system design for efficiency and reliability in industrial automation.
Choosing Between RTU and MTU for Industrial Automation
Selecting between Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Master Terminal Units (MTUs) hinges on the scale and complexity of the industrial automation system. RTUs excel in distributed environments by collecting data from remote sensors and transmitting it to central control, while MTUs serve as centralized hubs that manage and interpret data from multiple RTUs. Optimizing industrial processes requires evaluating factors such as communication protocols, network topology, and real-time data processing capabilities to ensure seamless integration and reliability.
RTU vs MTU Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com