Straight cut gears have teeth that are aligned parallel to the gear axis, providing efficient power transmission with minimal axial thrust but tend to be noisier under load. Helical gears feature teeth angled diagonally across the gear face, offering smoother and quieter operation by distributing contact more gradually, making them ideal for high-speed applications where noise reduction is important.
Table of Comparison
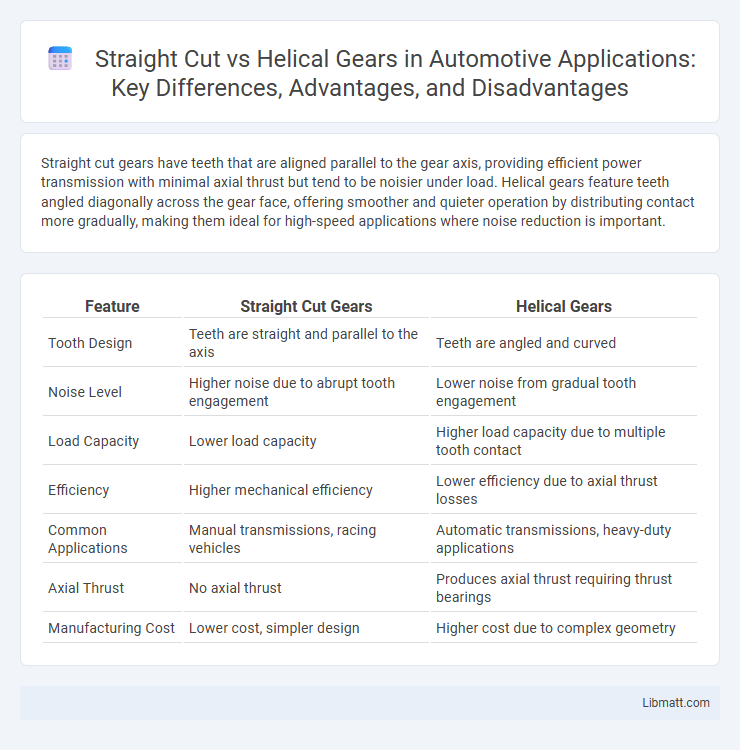
| Feature | Straight Cut Gears | Helical Gears |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Design | Teeth are straight and parallel to the axis | Teeth are angled and curved |
| Noise Level | Higher noise due to abrupt tooth engagement | Lower noise from gradual tooth engagement |
| Load Capacity | Lower load capacity | Higher load capacity due to multiple tooth contact |
| Efficiency | Higher mechanical efficiency | Lower efficiency due to axial thrust losses |
| Common Applications | Manual transmissions, racing vehicles | Automatic transmissions, heavy-duty applications |
| Axial Thrust | No axial thrust | Produces axial thrust requiring thrust bearings |
| Manufacturing Cost | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost due to complex geometry |
Introduction to Gear Types
Straight cut gears feature teeth aligned parallel to the gear axis, providing efficient power transmission with simpler design and easier manufacturing. Helical gears have angled teeth that engage gradually, offering smoother operation, reduced noise, and higher load capacity compared to straight cut gears. Understanding these core differences helps you select the optimal gear type for specific mechanical applications.
What Are Straight Cut Gears?
Straight cut gears, also known as spur gears, feature teeth that are cut parallel to the gear's axis, allowing direct and efficient power transfer between parallel shafts. These gears offer simplicity in design and manufacturing, making them ideal for applications requiring high load capacity and straightforward torque transmission. Due to their tooth orientation, straight cut gears produce more noise and vibration compared to helical gears, which have angled teeth for smoother engagement.
What Are Helical Gears?
Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother and quieter operation compared to straight cut gears with parallel teeth. Their design allows for higher load capacity and efficiency in transmitting power between non-parallel shafts. Commonly used in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery, helical gears reduce vibration and wear, enhancing durability and performance.
Key Differences Between Straight Cut and Helical Gears
Straight cut gears feature teeth that are parallel to the gear axis, enabling simple manufacturing and efficient power transmission at lower speeds but generating higher noise and vibration levels. Helical gears have angled teeth that engage gradually, resulting in smoother, quieter operation and the ability to handle higher loads and speeds due to increased tooth contact area. The choice between straight cut and helical gears depends on application requirements for noise reduction, load capacity, and operational speed.
Efficiency Comparison: Straight Cut vs. Helical Gears
Straight cut gears offer higher efficiency due to their simpler tooth design, resulting in less sliding friction and reduced energy loss. Helical gears, while smoother and quieter, experience more sliding action between teeth, causing slightly lower efficiency and increased heat generation. Your choice depends on prioritizing maximum efficiency with straight cut gears or quieter operation with helical gears.
Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Straight cut gears produce higher noise and vibration due to their teeth engaging suddenly along the entire width, causing intense impact forces. Helical gears generate smoother and quieter operation by engaging teeth gradually with angled teeth, reducing shock and vibration levels significantly. Your choice between these gears impacts mechanical noise control and operational smoothness in precision machinery.
Load Capacity and Strength Analysis
Straight cut gears offer high load capacity due to their simple tooth design that ensures direct contact along the gear teeth, making them strong under high torque conditions. Helical gears distribute loads more gradually across multiple teeth through angled teeth, enhancing strength and reducing noise, which improves load capacity under continuous or heavy-duty operations. Your choice between straight cut and helical gears should consider the specific load requirements and strength demands of your mechanical system to optimize performance and durability.
Applications of Straight Cut Gears
Straight cut gears are predominantly used in applications requiring high torque transmission and efficiency, such as automotive gearboxes, industrial machinery, and heavy equipment. Their simple design enables easy manufacturing and maintenance, making them ideal for low-speed, high-load scenarios where noise is less of a concern. Your choice of straight cut gears can enhance reliability and performance in environments where precision and durability outweigh the need for quiet operation.
Applications of Helical Gears
Helical gears are widely used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and robotics due to their ability to transmit power smoothly and quietly under high load conditions. Their angled teeth provide gradual engagement, reducing noise and vibration, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Common applications include gearboxes, conveyors, and printing presses where efficiency and durability are critical.
Choosing the Right Gear for Your Needs
Straight cut gears feature teeth parallel to the gear axis, providing efficient power transmission with minimal axial thrust, ideal for applications requiring high torque and simplicity. Helical gears have angled teeth that engage more gradually, producing smoother and quieter operation suitable for high-speed and heavy-load environments. Your choice depends on balancing noise levels, load capacity, and mechanical complexity to optimize gear performance for specific machinery requirements.
straight cut vs helical gears Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com