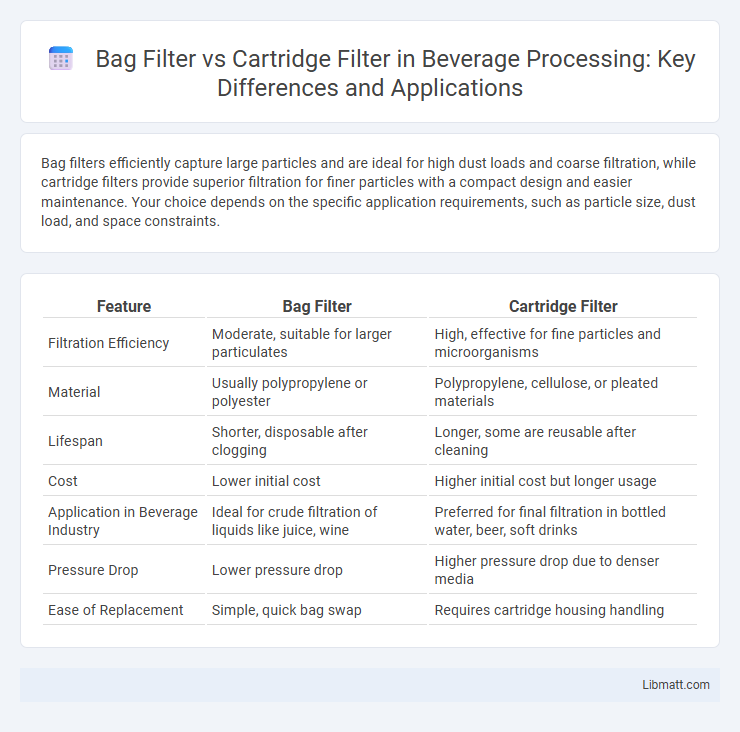
Bag filters efficiently capture large particles and are ideal for high dust loads and coarse filtration, while cartridge filters provide superior filtration for finer particles with a compact design and easier maintenance. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, such as particle size, dust load, and space constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bag Filter | Cartridge Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Efficiency | Moderate, suitable for larger particulates | High, effective for fine particles and microorganisms |
| Material | Usually polypropylene or polyester | Polypropylene, cellulose, or pleated materials |
| Lifespan | Shorter, disposable after clogging | Longer, some are reusable after cleaning |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer usage |
| Application in Beverage Industry | Ideal for crude filtration of liquids like juice, wine | Preferred for final filtration in bottled water, beer, soft drinks |
| Pressure Drop | Lower pressure drop | Higher pressure drop due to denser media |
| Ease of Replacement | Simple, quick bag swap | Requires cartridge housing handling |
Introduction to Bag Filters and Cartridge Filters
Bag filters consist of a fabric or felt bag designed to capture particulate matter from fluids in industrial processes, offering high dirt-holding capacity and ease of cleaning or replacement. Cartridge filters are cylindrical filter elements typically made from pleated media that provide finer filtration and higher surface area, suitable for applications requiring precise particle removal. Both filter types are essential in dust collection, air purification, and liquid filtration systems, with selection depending on flow rate, particle size, and maintenance preferences.
How Bag Filters Work
Bag filters operate by forcing liquid through a fabric filter bag that captures and retains particulate matter based on pore size, making them ideal for high flow applications with large volumes of contaminant. The filtration process involves mechanical straining and sometimes surface loading, which allows bag filters to handle heavier solids and larger particles compared to cartridge filters. Understanding how your bag filter works can help optimize maintenance schedules and ensure efficient removal of debris in industrial or commercial filtration systems.
How Cartridge Filters Work
Cartridge filters operate by forcing liquid through a cylindrical filter element made of pleated fibers or membranes, capturing contaminants on the surface or within the media. The pleated design increases the filtration area, improving dirt-holding capacity and flow rates compared to bag filters. These filters are commonly used in applications requiring fine particle removal and high efficiency, such as water purification, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Key Differences Between Bag and Cartridge Filters
Bag filters feature a large surface area and are designed to capture coarse particles in applications such as liquid filtration and dust collection, while cartridge filters offer finer filtration with pleated media suitable for removing smaller particles in liquid and air purification. Bag filters typically have lower pressure drops and are more cost-effective for large volume filtration, whereas cartridge filters provide higher filtration efficiency and are easier to replace but at a higher cost. Material compatibility, maintenance requirements, and the specific filtration rating are critical factors that distinguish the optimal use of bag filters versus cartridge filters in industrial and commercial settings.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Bag filters typically offer lower filtration efficiency, capturing particles down to 5-10 microns, whereas cartridge filters provide superior filtration, effectively removing particles as small as 1 micron or less. Cartridge filters feature pleated media that increases surface area for enhanced particle retention and longer service life, while bag filters rely on fabric bags with relatively larger pores. Your choice impacts the filtration quality, with cartridge filters being preferable for applications requiring higher efficiency and cleaner output.
Applications and Industries Suitability
Bag filters excel in heavy-duty applications such as dust collection, chemical processing, and food production due to their high capacity and ability to handle large volumes of particulate matter. Cartridge filters are typically preferred in industries requiring finer filtration, like pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and HVAC systems, offering greater precision and cleanliness. Choosing the right filter depends on your specific industry demands and the nature of the contaminants to ensure optimal performance and compliance.
Maintenance and Replacement Needs
Bag filters require frequent maintenance and replacement due to their larger surface area that traps more particles but clogs faster, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications with high particulate loads. Cartridge filters offer easier maintenance with their compact design and longer lifespan, as they typically filter finer particles and need less frequent replacement. Choosing the right filter depends on your specific filtration needs and maintenance capacity.
Cost Analysis: Bag Filters vs Cartridge Filters
Bag filters generally offer lower initial investment and maintenance costs compared to cartridge filters, making them more cost-effective for large-volume applications. Cartridge filters, while more expensive upfront, provide finer filtration and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and operational downtime. The total cost analysis depends on the filtration efficiency, application requirements, and the frequency of filter changes, with bag filters favored for bulk particulate removal and cartridge filters chosen for precision filtration.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
Bag filters generate larger amounts of bulky waste that often require disposal in designated landfills, posing challenges for efficient waste management and potential environmental contamination. Cartridge filters produce less waste volume, often consisting of compact cartridges that can sometimes be recycled or incinerated, reducing landfill dependency and associated environmental risks. The choice between bag and cartridge filters significantly influences the sustainability of filtration processes through differences in waste generation, disposal methods, and potential for material recovery.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Needs
Selecting between a bag filter and a cartridge filter depends on factors such as particle size, flow rate, and maintenance frequency. Bag filters are ideal for large volumes and coarse particles, offering easy cleaning and replacement, while cartridge filters excel in fine filtration with higher efficiency for smaller contaminants. Evaluating your specific application requirements ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in filtration systems.
Bag filter vs cartridge filter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com