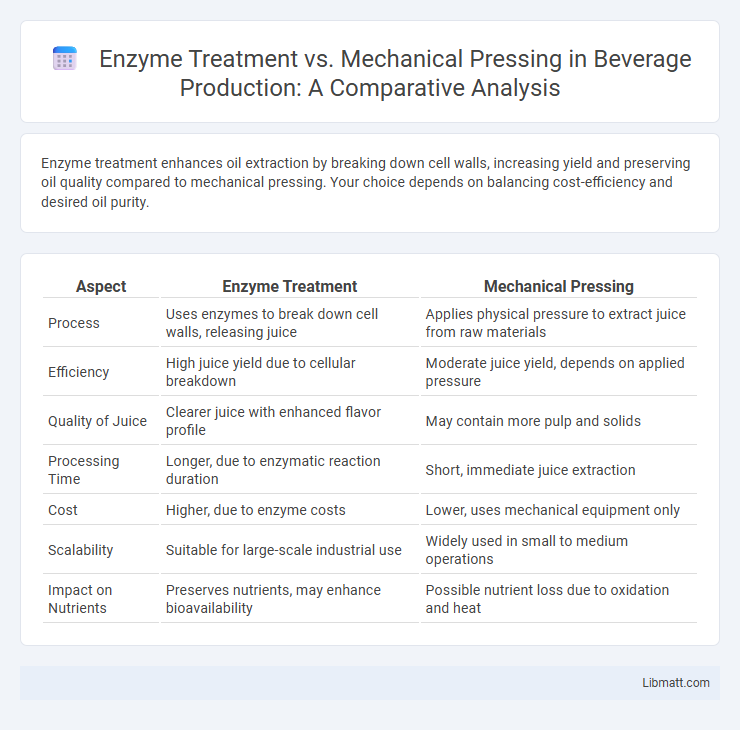
Enzyme treatment enhances oil extraction by breaking down cell walls, increasing yield and preserving oil quality compared to mechanical pressing. Your choice depends on balancing cost-efficiency and desired oil purity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Enzyme Treatment | Mechanical Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses enzymes to break down cell walls, releasing juice | Applies physical pressure to extract juice from raw materials |
| Efficiency | High juice yield due to cellular breakdown | Moderate juice yield, depends on applied pressure |
| Quality of Juice | Clearer juice with enhanced flavor profile | May contain more pulp and solids |
| Processing Time | Longer, due to enzymatic reaction duration | Short, immediate juice extraction |
| Cost | Higher, due to enzyme costs | Lower, uses mechanical equipment only |
| Scalability | Suitable for large-scale industrial use | Widely used in small to medium operations |
| Impact on Nutrients | Preserves nutrients, may enhance bioavailability | Possible nutrient loss due to oxidation and heat |
Introduction to Juice Extraction Methods
Juice extraction methods primarily involve enzyme treatment and mechanical pressing, each enhancing yield through different mechanisms. Enzyme treatment uses pectinases and cellulases to break down cell walls, improving juice flow and clarity while preserving nutritional quality. Mechanical pressing physically squeezes fruit or vegetable tissues, offering a straightforward extraction process but sometimes resulting in lower yield and potential nutrient loss compared to enzymatic methods.
Overview of Enzyme Treatment in Juice Processing
Enzyme treatment in juice processing utilizes specific pectinase enzymes to break down cell walls and pectin substances, enhancing juice yield and clarity compared to mechanical pressing. This biochemical process accelerates juice extraction by softening fruit tissue, reducing viscosity, and minimizing juice loss. Enzyme treatment optimizes processing efficiency and improves juice quality by increasing liquid output while preserving flavor and nutritional content.
Understanding Mechanical Pressing Techniques
Mechanical pressing techniques involve physically extracting oils or juices by applying pressure through equipment like hydraulic or screw presses, ensuring minimal alteration of the raw material's natural properties. This method preserves the integrity of bioactive compounds and is commonly used for cold pressing in industries such as olive oil and juice production. You benefit from mechanical pressing's straightforward operation and reduced chemical use compared to enzyme treatments, which rely on biochemical reactions to break down cell walls.
Extraction Efficiency: Enzyme vs. Mechanical
Enzyme treatment enhances extraction efficiency by breaking down cell walls and releasing more oil and nutrients compared to mechanical pressing, which relies solely on physical force. Studies show enzyme-assisted extraction can achieve oil yields up to 15-20% higher than traditional mechanical methods. This biochemical approach improves the recovery of bioactives and reduces residue waste, making it more effective for comprehensive extraction.
Impact on Juice Yield and Quality
Enzyme treatment significantly enhances juice yield by breaking down cell walls and releasing more liquid, resulting in higher extraction efficiency compared to mechanical pressing. This method also improves juice clarity, flavor, and nutrient retention by reducing pulp and sediment content, whereas mechanical pressing may produce juice with higher particulate levels and a lower sensory profile. Your choice between enzyme treatment and mechanical pressing will depend on balancing the priorities of maximum juice yield and maintaining optimal juice quality characteristics.
Effects on Nutrient Retention
Enzyme treatment enhances nutrient retention by breaking down cell walls, allowing for more efficient extraction of vitamins, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds compared to mechanical pressing. Mechanical pressing often leads to nutrient loss due to the heat and pressure applied, which can degrade sensitive nutrients such as enzymes and polyphenols. Your choice between these methods impacts the quality and nutritional value of the final product.
Influence on Flavor and Aroma Profiles
Enzyme treatment enhances flavor and aroma profiles by breaking down complex molecules into simpler, more aromatic compounds, resulting in richer and more nuanced sensory experiences. Mechanical pressing preserves the natural integrity of ingredients, often yielding a fresher but less intense flavor compared to enzymatic methods. Your choice between enzyme treatment and mechanical pressing significantly impacts the depth and complexity of the final product's taste and aroma.
Cost and Operational Considerations
Enzyme treatment typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the price of biocatalysts but reduces long-term expenses by lowering energy consumption and minimizing equipment wear compared to mechanical pressing. Mechanical pressing demands significant capital investment in heavy-duty presses and ongoing maintenance expenses, as well as higher labor input for operation. Operational efficiency in enzyme treatment benefits from shorter processing times and enhanced yield, whereas mechanical pressing may suffer from variable output quality and increased downtime.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Enzyme treatment in oil extraction significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and minimizing chemical usage compared to mechanical pressing, which relies heavily on electricity and can produce more waste. Enzymatic processes enhance oil yield efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to sustainable production practices. Mechanical pressing, while straightforward, often results in higher residue and resource use, making enzyme treatment a more eco-friendly alternative in sustainable oil industries.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Enzyme treatment offers precise degradation of specific components, making it ideal for applications requiring targeted extraction or modification, such as in food processing and biofuel production. Mechanical pressing delivers high throughput with minimal chemical intervention, suitable for oil extraction and juice pressing where maintaining natural integrity is crucial. Evaluating factors like substrate type, desired yield, and product quality helps determine whether enzymatic treatment or mechanical pressing best meets your operational goals.
Enzyme treatment vs mechanical pressing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com