Polyphenols are a broad class of natural compounds found in plants, characterized by multiple phenol units, while flavonoids represent a specific subclass of polyphenols known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Understanding the differences between polyphenols and flavonoids can help you choose foods and supplements that maximize health benefits.
Table of Comparison
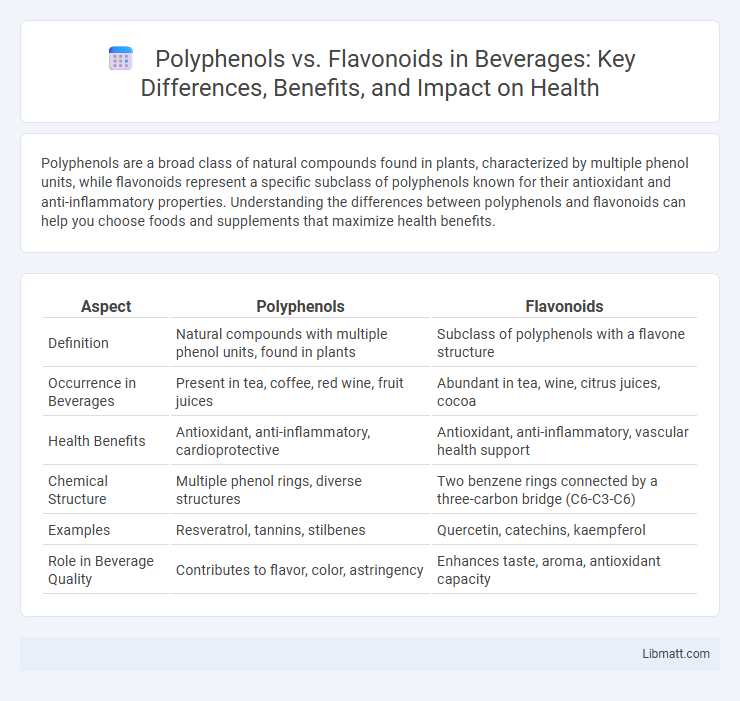
| Aspect | Polyphenols | Flavonoids |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural compounds with multiple phenol units, found in plants | Subclass of polyphenols with a flavone structure |
| Occurrence in Beverages | Present in tea, coffee, red wine, fruit juices | Abundant in tea, wine, citrus juices, cocoa |
| Health Benefits | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, vascular health support |
| Chemical Structure | Multiple phenol rings, diverse structures | Two benzene rings connected by a three-carbon bridge (C6-C3-C6) |
| Examples | Resveratrol, tannins, stilbenes | Quercetin, catechins, kaempferol |
| Role in Beverage Quality | Contributes to flavor, color, astringency | Enhances taste, aroma, antioxidant capacity |
Understanding Polyphenols: An Overview
Polyphenols are a diverse group of naturally occurring compounds found in plants, characterized by multiple phenol units that contribute to their antioxidant properties. Flavonoids, a major subclass of polyphenols, encompass over 6,000 identified compounds with distinct structures influencing their health benefits. Understanding the broad classification and specific roles of polyphenols versus flavonoids reveals their significance in preventing oxidative stress and promoting cardiovascular health.
What Are Flavonoids? Classification & Structure
Flavonoids are a diverse group of polyphenolic compounds found in fruits, vegetables, and beverages like tea and wine, known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They are classified into six main subclasses: flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavanols, isoflavones, and anthocyanins, each distinguished by variations in their chemical structure, specifically the arrangement of hydroxyl groups and the oxidation state of the central pyran ring. Understanding the structure and classification of flavonoids helps you identify their specific health benefits and dietary sources.
Polyphenols vs Flavonoids: Key Differences
Polyphenols are a broad category of naturally occurring compounds in plants, characterized by multiple phenol units, while flavonoids represent a large subclass of polyphenols distinguished by their specific 15-carbon skeleton structure. Flavonoids include subclasses such as flavones, flavonols, flavanones, and anthocyanins, each with distinct chemical properties and health benefits. Understanding these key differences helps in targeted nutritional research and maximizes their use in functional foods and supplements.
Sources of Polyphenols in Foods
Polyphenols are abundant in a variety of plant-based foods such as berries, green tea, red wine, dark chocolate, nuts, and whole grains, providing potent antioxidant properties. Flavonoids, a major subgroup of polyphenols, are primarily found in citrus fruits, onions, apples, and legumes, contributing to cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory health benefits. Rich sources of polyphenols also include olive oil, coffee, and certain spices like cloves and cinnamon, which play a vital role in reducing oxidative stress.
Dietary Sources of Flavonoids
Flavonoids, a subclass of polyphenols, are abundant in a variety of dietary sources including fruits such as apples, berries, and citrus fruits, as well as vegetables like onions, kale, and broccoli. Beverages like tea, red wine, and cocoa are also rich in flavonoids, contributing significantly to their antioxidant intake. These compounds play a crucial role in promoting health by providing anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular benefits.
Health Benefits of Polyphenols
Polyphenols, a broad category of plant compounds that includes flavonoids, exhibit potent antioxidant properties that help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. These bioactive substances improve vascular health by enhancing endothelial function and decreasing oxidative stress, which supports overall heart health. Polyphenols also promote gut health by modulating the microbiota composition, aiding digestion, and strengthening immune response.
Flavonoids and Their Health Effects
Flavonoids, a prominent subclass of polyphenols, are powerful antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables, and beverages like tea and wine, known to support cardiovascular health by improving blood vessel function and reducing inflammation. These compounds also aid in boosting your immune system and protecting cells from oxidative damage linked to chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Research highlights flavonoids' potential in enhancing brain function, making them essential for overall disease prevention and health maintenance.
Absorption and Bioavailability: Polyphenols vs Flavonoids
Polyphenols encompass a broad group of plant compounds with varied absorption rates, while flavonoids, a subclass, generally exhibit higher bioavailability due to their simpler molecular structures. Flavonoids like quercetin and catechins are absorbed more efficiently in the small intestine, aided by specific transporters and metabolic enzymes. Polyphenols often undergo extensive transformation by gut microbiota, influencing their systemic bioavailability and health effects.
Role of Polyphenols and Flavonoids in Disease Prevention
Polyphenols and flavonoids are bioactive compounds with potent antioxidant properties that contribute significantly to disease prevention by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Flavonoids, a subclass of polyphenols found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, and tea, exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and cardioprotective effects that lower risks of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders. Research highlights the role of these compounds in modulating signaling pathways, enhancing immune function, and improving endothelial health, thereby supporting their therapeutic potential in mitigating disease progression.
Choosing the Right Phytochemicals for Better Health
Polyphenols, a broad category of plant compounds, encompass flavonoids, which represent the largest subclass known for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Selecting foods rich in specific polyphenols, such as green tea catechins, red wine resveratrol, or citrus flavonoids, can target cardiovascular health, cancer prevention, and cognitive function. Understanding the distinct roles and bioavailability of these phytochemicals enhances dietary strategies for optimizing health outcomes.
Polyphenols vs flavonoids Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com