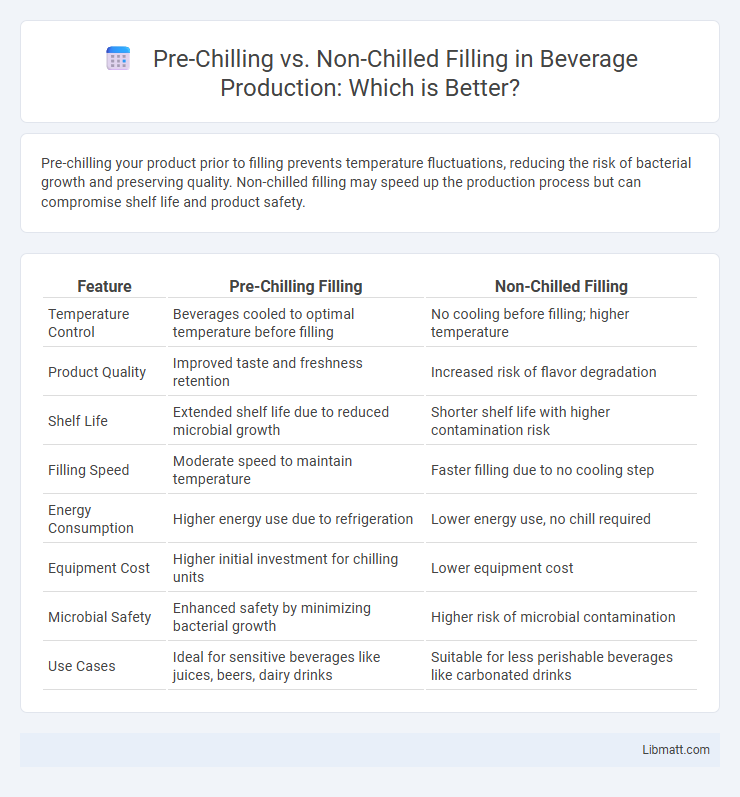
Pre-chilling your product prior to filling prevents temperature fluctuations, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and preserving quality. Non-chilled filling may speed up the production process but can compromise shelf life and product safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pre-Chilling Filling | Non-Chilled Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Beverages cooled to optimal temperature before filling | No cooling before filling; higher temperature |
| Product Quality | Improved taste and freshness retention | Increased risk of flavor degradation |
| Shelf Life | Extended shelf life due to reduced microbial growth | Shorter shelf life with higher contamination risk |
| Filling Speed | Moderate speed to maintain temperature | Faster filling due to no cooling step |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to refrigeration | Lower energy use, no chill required |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for chilling units | Lower equipment cost |
| Microbial Safety | Enhanced safety by minimizing bacterial growth | Higher risk of microbial contamination |
| Use Cases | Ideal for sensitive beverages like juices, beers, dairy drinks | Suitable for less perishable beverages like carbonated drinks |
Understanding Pre-Chilling in Beverage Filling
Pre-chilling in beverage filling involves cooling the product to a specific low temperature before packaging, which helps maintain quality, extends shelf life, and prevents microbial growth. Non-chilled filling skips this cooling step, often leading to reduced freshness and increased risk of spoilage during storage and distribution. Your choice between pre-chilling and non-chilled filling greatly impacts the beverage's taste, safety, and overall consumer satisfaction.
What is Non-Chilled (Ambient) Filling?
Non-chilled (ambient) filling is a packaging process where products are filled and sealed at room temperature without refrigeration. This method is commonly used for shelf-stable beverages and foods, allowing longer storage without the need for cold chain logistics. Non-chilled filling is advantageous for reducing energy costs and simplifying distribution but requires products to be processed for microbial stability.
Key Differences Between Pre-Chilled and Non-Chilled Filling
Pre-chilled filling involves cooling the product before packaging, significantly reducing microbial growth and extending shelf life, whereas non-chilled filling occurs at ambient temperatures, which may compromise product freshness and safety. Pre-chilling enhances temperature control during filling, leading to improved product quality and consistency, while non-chilled filling often requires more robust preservatives. Your choice between the two impacts processing speed, equipment costs, and overall product stability in storage and distribution.
Impact on Product Quality and Shelf Life
Pre-chilling during the filling process significantly reduces microbial growth and enzymatic activity, thereby enhancing product quality and extending shelf life. Non-chilled filling often leads to higher temperatures that accelerate spoilage and degradation, resulting in diminished freshness and shorter shelf stability. Implementing pre-chilled filling ensures consistent taste, texture, and safety, crucial for perishable beverages and dairy products.
Production Efficiency: Speed and Consistency
Pre-chilling in filling processes significantly enhances production efficiency by reducing product temperature, which stabilizes viscosity and facilitates faster, more consistent filling speeds. Non-chilled filling often leads to temperature fluctuations that cause product inconsistency and slower line speeds due to increased equipment strain and fill variability. Optimizing for pre-chilling minimizes downtime, maintains steady throughput, and ensures uniform fill volumes, ultimately boosting overall production speed and consistency.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability Considerations
Pre-chilling filling processes significantly reduce energy consumption by lowering the temperature of the product before packaging, leading to decreased refrigeration demands during storage and transport. Non-chilled filling often requires extended cooling periods post-packaging, resulting in higher electricity use and increased carbon emissions. Optimizing your production line with pre-chilling techniques supports sustainability goals by minimizing energy use and reducing the environmental footprint of beverage manufacturing.
Equipment Requirements for Both Methods
Pre-chilling filling requires specialized chillers and temperature control systems to maintain product stability and prevent microbial growth, impacting the overall equipment cost and setup complexity. Non-chilled filling uses standard filling machinery but demands stricter sanitation protocols and faster processing times to ensure product safety without temperature control. Your choice influences not only the initial investment but also ongoing operational efficiency and compliance with food safety standards.
Cost Comparison: Pre-Chilling vs. Non-Chilled Filling
Pre-chilling filling lines typically incur higher upfront equipment and energy costs due to cooling systems, but they can reduce spoilage and extend shelf life, potentially lowering overall product loss expenses. Non-chilled filling methods have lower initial setup and operational costs but may increase risks related to product quality degradation and shorter shelf life, leading to higher returns and waste management costs. Evaluating your production volume and product type helps determine whether pre-chilling investments optimize long-term cost efficiency compared to non-chilled filling.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Pre-chilling filling technology is widely used in the dairy and beverage industries to maintain product freshness and extend shelf life, particularly for milk, juices, and cold brew coffee. Non-chilled filling is preferred in sectors like sauces, canned goods, and shelf-stable beverages where ambient temperature processing reduces energy costs and simplifies logistics. Both methods serve critical roles in food safety compliance and quality control across diverse manufacturing environments.
Choosing the Right Filling Method for Your Product
Choosing the right filling method depends on product type and shelf life requirements, with pre-chilling essential for heat-sensitive products to maintain quality and freshness. Pre-chilled filling minimizes microbial growth and preserves texture, making it ideal for dairy, juices, and ready-to-eat meals. Non-chilled filling suits products with higher heat tolerance or those intended for immediate consumption, optimizing production speed and reducing energy costs.
Pre-chilling vs non-chilled filling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com