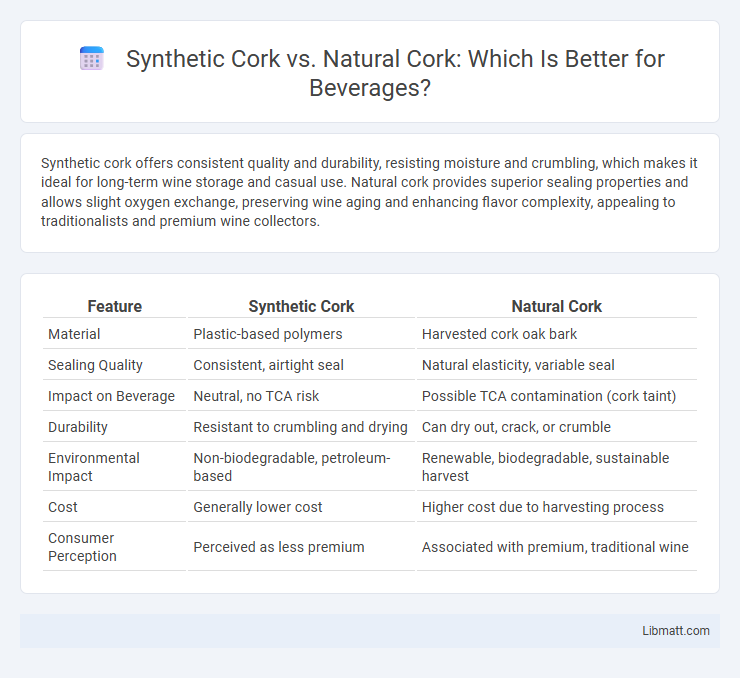
Synthetic cork offers consistent quality and durability, resisting moisture and crumbling, which makes it ideal for long-term wine storage and casual use. Natural cork provides superior sealing properties and allows slight oxygen exchange, preserving wine aging and enhancing flavor complexity, appealing to traditionalists and premium wine collectors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Cork | Natural Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic-based polymers | Harvested cork oak bark |
| Sealing Quality | Consistent, airtight seal | Natural elasticity, variable seal |
| Impact on Beverage | Neutral, no TCA risk | Possible TCA contamination (cork taint) |
| Durability | Resistant to crumbling and drying | Can dry out, crack, or crumble |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Renewable, biodegradable, sustainable harvest |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to harvesting process |
| Consumer Perception | Perceived as less premium | Associated with premium, traditional wine |
Introduction to Cork Closures
Cork closures, essential in wine bottling, come in two main types: synthetic cork and natural cork. Natural cork is harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, offering traditional breathability and eco-friendliness. Synthetic corks, made from plastic or elastomer blends, provide consistent sealing and eliminate cork taint risks, appealing to producers seeking durability and cost efficiency.
What is Synthetic Cork?
Synthetic cork is a man-made material designed to replicate the appearance and function of natural cork, typically made from plastic compounds such as polyethylene or elastomers. It offers consistent quality, resistance to drying out, and reduced risk of cork taint, making it a popular alternative for wine bottle closures. Your choice between synthetic cork and natural cork influences factors like sealing performance, sustainability, and potential flavor impact on the wine.
What is Natural Cork?
Natural cork comes from the bark of the cork oak tree, primarily found in Mediterranean regions like Portugal and Spain, where it is sustainably harvested every 9 to 12 years without harming the tree. Its cellular structure provides excellent elasticity and impermeability, making it ideal for sealing wine bottles by preserving the flavor while allowing minimal air exchange. Your choice of natural cork supports eco-friendly practices and offers a traditional, biodegradable option with a unique texture and scent that synthetic corks often lack.
Production Process: Synthetic vs Natural Cork
Synthetic cork is produced through the molding of plastic polymers such as polyethylene or elastomers, offering consistent quality and resistance to mold and moisture. Natural cork is harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, involving a sustainable and labor-intensive process that preserves the tree and produces an eco-friendly, biodegradable product. Your choice between synthetic and natural cork should consider the environmental impact and desired performance related to the production methods.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic Cork vs Natural Cork
Synthetic cork typically derives from plastic polymers, contributing to non-biodegradable waste and a higher carbon footprint due to fossil fuel extraction and manufacturing processes. Natural cork, harvested from cork oak trees, offers a renewable and biodegradable alternative, with cork oak forests supporting biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Lifecycle assessments reveal natural cork's superior environmental benefits through sustainable forest management and minimal processing emissions.
Wine Preservation and Quality
Synthetic corks offer consistent sealing properties that prevent oxygen ingress, ensuring stable wine preservation and reducing the risk of cork taint. Natural corks provide a traditional breathable barrier, allowing micro-oxygenation which can enhance the aging process of certain wines. However, natural cork variability can lead to inconsistent seals and occasional contamination, impacting wine quality more than the uniform performance of synthetic corks.
Cost Comparison
Synthetic corks generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to natural cork, making them attractive for large-scale wine production without compromising sealing efficiency. While natural corks tend to be pricier due to harvesting and processing from cork oak trees, they provide an eco-friendly and traditional choice that some premium brands prefer. Your selection between synthetic and natural cork will depend on balancing cost constraints with the desired wine storage and aging qualities.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting towards natural cork due to its sustainability, biodegradability, and traditional appeal, which appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. Synthetic corks, favored for their consistency, resistance to cork taint, and cost-effectiveness, attract consumers seeking reliability and affordability in wine preservation. Your choice between synthetic and natural cork depends on valuing eco-friendliness and authenticity or practicality and price.
Pros and Cons of Synthetic Cork
Synthetic cork offers consistent quality and durability resistant to drying and crumbling, making it ideal for long-term wine storage with minimal risk of cork taint. Its uniformity ensures reliable sealing performance, but it may lack the natural breathability of natural cork, potentially affecting wine aging. While synthetic cork is often more cost-effective and environmentally friendly due to recyclability, it may not provide the same aesthetic appeal or traditional experience sought by wine enthusiasts.
Pros and Cons of Natural Cork
Natural cork offers excellent elasticity, biodegradability, and superior oxygen permeability control, making it ideal for wine preservation and sustainability. Its drawbacks include variability in quality, susceptibility to cork taint caused by TCA contamination, and higher cost compared to synthetic alternatives. Despite these cons, natural cork remains the preferred choice for premium wines due to its traditional appeal and environmental benefits.
Synthetic cork vs natural cork Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com