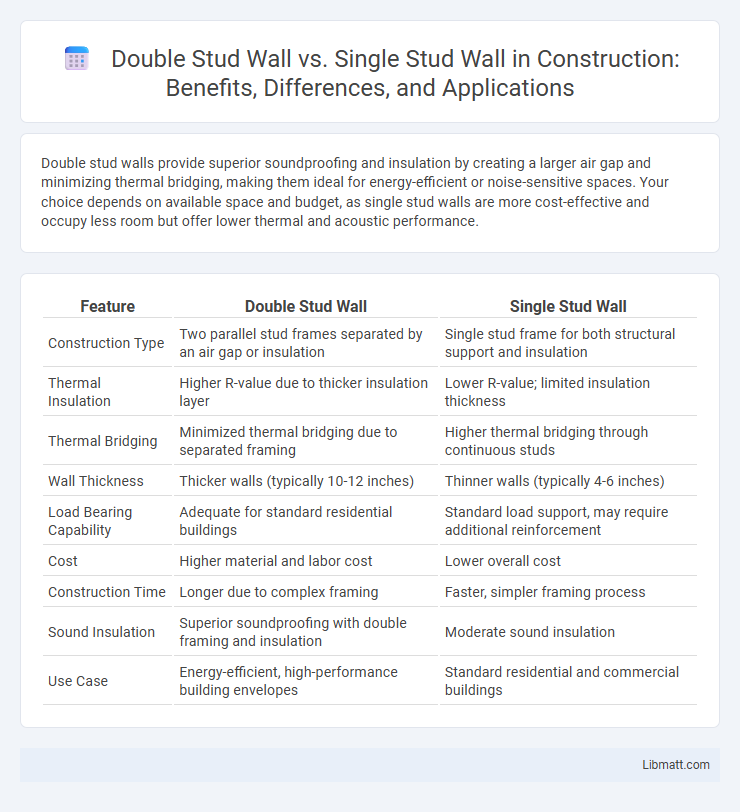
Double stud walls provide superior soundproofing and insulation by creating a larger air gap and minimizing thermal bridging, making them ideal for energy-efficient or noise-sensitive spaces. Your choice depends on available space and budget, as single stud walls are more cost-effective and occupy less room but offer lower thermal and acoustic performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Double Stud Wall | Single Stud Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Type | Two parallel stud frames separated by an air gap or insulation | Single stud frame for both structural support and insulation |
| Thermal Insulation | Higher R-value due to thicker insulation layer | Lower R-value; limited insulation thickness |
| Thermal Bridging | Minimized thermal bridging due to separated framing | Higher thermal bridging through continuous studs |
| Wall Thickness | Thicker walls (typically 10-12 inches) | Thinner walls (typically 4-6 inches) |
| Load Bearing Capability | Adequate for standard residential buildings | Standard load support, may require additional reinforcement |
| Cost | Higher material and labor cost | Lower overall cost |
| Construction Time | Longer due to complex framing | Faster, simpler framing process |
| Sound Insulation | Superior soundproofing with double framing and insulation | Moderate sound insulation |
| Use Case | Energy-efficient, high-performance building envelopes | Standard residential and commercial buildings |
Introduction to Double Stud Wall vs Single Stud Wall
Double stud walls feature two parallel frames separated by an insulating gap, offering superior thermal performance and reduced thermal bridging compared to single stud walls, which consist of a single frame with standard insulation. Your choice between these framing methods impacts the energy efficiency, sound insulation, and overall durability of the building envelope. Double stud walls are particularly advantageous in high-performance, energy-efficient construction where minimizing heat loss is critical.
Structural Differences: Double Stud vs Single Stud
Double stud walls consist of two parallel framing rows separated by an air gap or insulation, enhancing thermal performance and reducing thermal bridging compared to single stud walls that use a single row of framing. Structurally, single stud walls are simpler and provide sufficient support for standard residential loads, while double stud walls require more materials and careful alignment to maintain structural integrity. The added thickness of double stud walls necessitates stronger connections and may influence load distribution, making them suitable for advanced energy-efficient building designs.
Soundproofing Capabilities Comparison
Double stud walls offer superior soundproofing capabilities compared to single stud walls due to their increased mass and the air gap that reduces sound transmission between rooms. The staggered framing in double stud walls minimizes direct vibration paths, effectively blocking noise especially in high-traffic or multi-family buildings. If soundproofing is a priority for your space, double stud walls provide a more effective solution by significantly dampening airborne and impact noises.
Thermal Performance and Insulation
Double stud walls provide superior thermal performance compared to single stud walls by creating a thicker cavity that accommodates more insulation, reducing thermal bridging through framing. The increased depth in double stud construction allows for higher R-values, enhancing your home's energy efficiency and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. In contrast, single stud walls have limited space for insulation, resulting in lower R-values and greater heat loss.
Moisture Management and Durability
Double stud walls provide superior moisture management by creating a thicker insulation layer that reduces thermal bridging and condensation risks compared to single stud walls. This design enhances durability by minimizing moisture accumulation within the framing, preventing mold growth and wood rot. You can improve your building's longevity and indoor air quality by opting for double stud construction in moisture-prone environments.
Construction Costs and Material Usage
Double stud walls generally incur higher construction costs due to increased material usage and labor compared to single stud walls. The additional framing in double stud walls requires more lumber and insulation, leading to improved thermal performance but elevated expenses. Single stud walls use fewer materials, reducing costs but offering less insulation and soundproofing benefits.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Double stud walls significantly improve energy efficiency by providing thicker insulation cavities that reduce thermal bridging and enhance overall R-values compared to single stud walls. This design allows for the incorporation of advanced insulation materials such as spray foam or dense-packed cellulose, minimizing air leakage and heat loss. Consequently, double stud walls contribute to lower heating and cooling costs while promoting a more stable indoor temperature throughout the year.
Installation Process and Labor Requirements
Double stud walls require more complex installation due to framing two separate stud bays, which increases labor time and demands precise alignment to optimize insulation. Single stud walls have a simpler, faster installation process with fewer materials, reducing overall labor costs and complexity. Your choice impacts project timelines and workforce needs, with double stud walls offering better thermal performance at the expense of increased labor.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Double stud walls are ideal for high-performance insulation and acoustic separation in residential and commercial buildings, making them suitable for passive houses or sound-sensitive spaces. Single stud walls are best for standard framing in typical interior partition walls where cost-efficiency and simpler installation are priorities. Applications requiring enhanced thermal insulation and reduced thermal bridging benefit most from double stud wall construction.
Pros and Cons: Double Stud Wall vs Single Stud Wall
Double stud walls offer superior thermal insulation and reduced thermal bridging, making them ideal for energy-efficient building designs, but they require more material and occupy more space compared to single stud walls. Single stud walls are more cost-effective, easier to construct, and take up less room, but they typically have lower insulation values and higher risk of heat loss. Choosing between double and single stud walls depends on balancing insulation performance with budget and spatial constraints.
Double stud wall vs Single stud wall Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com