Spray foam provides superior air sealing and insulating properties by expanding to fill gaps and cracks, making it ideal for irregular or hard-to-reach spaces. Rigid foam panels offer consistent thermal resistance and moisture resistance, often used in walls and foundations for long-lasting insulation results.
Table of Comparison
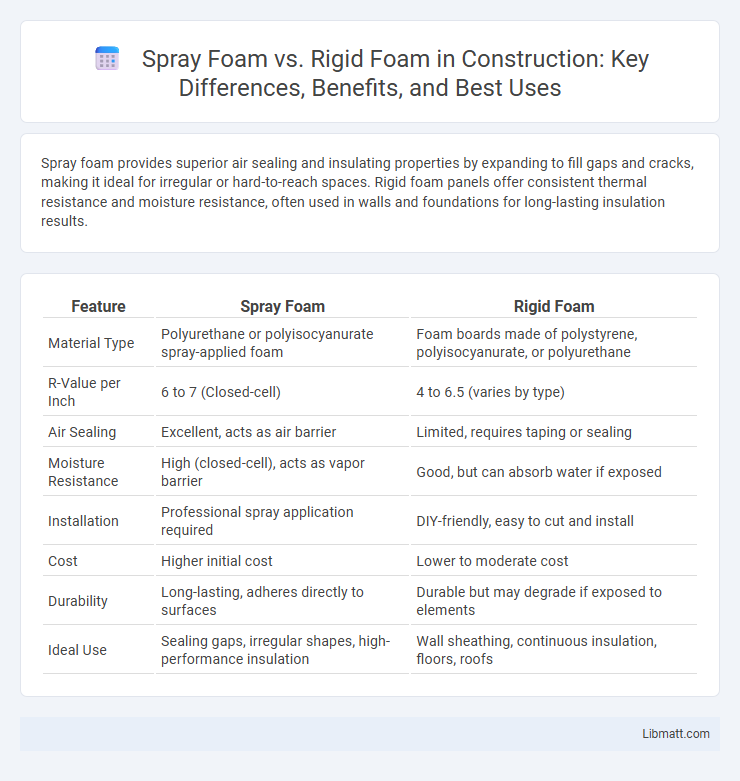
| Feature | Spray Foam | Rigid Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane or polyisocyanurate spray-applied foam | Foam boards made of polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane |
| R-Value per Inch | 6 to 7 (Closed-cell) | 4 to 6.5 (varies by type) |
| Air Sealing | Excellent, acts as air barrier | Limited, requires taping or sealing |
| Moisture Resistance | High (closed-cell), acts as vapor barrier | Good, but can absorb water if exposed |
| Installation | Professional spray application required | DIY-friendly, easy to cut and install |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower to moderate cost |
| Durability | Long-lasting, adheres directly to surfaces | Durable but may degrade if exposed to elements |
| Ideal Use | Sealing gaps, irregular shapes, high-performance insulation | Wall sheathing, continuous insulation, floors, roofs |
Introduction to Spray Foam and Rigid Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation expands upon application to fill gaps and create an airtight seal, making it ideal for irregular or hard-to-reach areas, while rigid foam insulation comes in solid panels offering high compressive strength and consistent thermal resistance. Both spray foam and rigid foam provide excellent R-values per inch, contributing to energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Your choice depends on specific project requirements, moisture control needs, and installation preferences.
Composition and Material Differences
Spray foam insulation consists of polyurethane or polyisocyanurate compounds that expand upon application, creating an airtight seal that conforms to cavities and irregular surfaces. Rigid foam insulation, typically made from polystyrene (EPS or XPS) or polyisocyanurate, comes in solid panels that provide consistent thickness and compressive strength but lack flexibility. The chemical composition of spray foam allows for superior adhesion and expansion, while rigid foam's dense, uniform structure offers high R-value and moisture resistance.
Installation Process: Spray Foam vs Rigid Foam
Spray foam insulation requires professional equipment for application, as it expands and seals gaps on contact, creating an airtight barrier quickly but demanding precise handling. Rigid foam panels are easier to install with basic tools by cutting and fitting them into place, offering a straightforward DIY option with consistent thickness and R-value. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the quick, seamless installation of spray foam or the simplicity and control of placing rigid foam boards.
Thermal Performance and R-Value Comparison
Spray foam insulation typically offers higher thermal performance with an R-value ranging from 6.0 to 7.0 per inch, compared to rigid foam boards which generally provide an R-value between 3.8 and 5.0 per inch depending on the material (EPS, XPS, or polyiso). Closed-cell spray foam not only insulates but also acts as an air and moisture barrier, increasing overall energy efficiency beyond just R-value metrics. Rigid foam boards excel in applications requiring moisture resistance and structural support but may require additional air sealing measures to match the thermal efficiency of spray foam systems.
Moisture Resistance and Air Sealing Capabilities
Spray foam insulation offers superior moisture resistance and air sealing capabilities by expanding to fill gaps and creating an airtight barrier that prevents water vapor and air infiltration. Rigid foam boards provide good moisture resistance due to their closed-cell structure but may require additional sealing to eliminate air leaks around seams and edges. Your choice depends on the level of airtightness and moisture control needed for optimal energy efficiency and durability.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Investment
Spray foam typically has a higher upfront cost compared to rigid foam, but its superior insulation performance can lead to significant energy savings over time, reducing your utility bills. Rigid foam offers a lower initial investment and easier installation, making it cost-effective for smaller projects or budget-conscious homeowners. Evaluating long-term investment, spray foam's air-sealing properties often result in better durability and moisture resistance, potentially lowering maintenance and repair expenses over the life of the building.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing capabilities, reducing energy loss and lowering your heating and cooling costs significantly compared to rigid foam. Rigid foam boards typically have lower embodied energy but may allow more air leaks, impacting overall energy efficiency. Considering the environmental impact, spray foam's chemicals can be more harmful unless low-VOC or soy-based options are used, while rigid foam often contains fewer harmful emissions but can contribute to plastic waste.
Durability and Longevity
Spray foam insulation offers superior durability due to its ability to expand and seal gaps, preventing air and moisture infiltration that can degrade materials over time. Rigid foam panels provide consistent thermal resistance and maintain their shape, making them long-lasting but prone to damage if physically impacted. Your choice should consider the specific application environment, as spray foam excels in creating a seamless barrier while rigid foam delivers reliable, durable insulation where structural integrity is critical.
Best Applications for Each Insulation Type
Spray foam insulation excels in sealing complex surfaces and hard-to-reach areas, making it ideal for attic spaces, crawl spaces, and irregularly shaped walls where airtightness is crucial. Rigid foam boards are best suited for insulating foundations, basements, and exterior walls due to their high compressive strength and moisture resistance. Consider your specific insulation needs and structural conditions to determine whether spray foam or rigid foam will maximize your energy efficiency and comfort.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Key Considerations
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch compared to rigid foam, making it ideal for irregularly shaped spaces and reducing energy loss effectively. Rigid foam insulation provides consistent thermal resistance, moisture resistance, and structural durability, often preferred for basement walls and exterior sheathing. Evaluate factors such as climate, budget, vapor barrier needs, and installation complexity to determine the optimal choice for energy efficiency and building longevity.
Spray foam vs rigid foam Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com