Busbars offer superior current-carrying capacity and better heat dissipation compared to cables, making them ideal for high-power electrical distribution systems. Your choice between busbars and cables depends on factors like space constraints, installation complexity, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
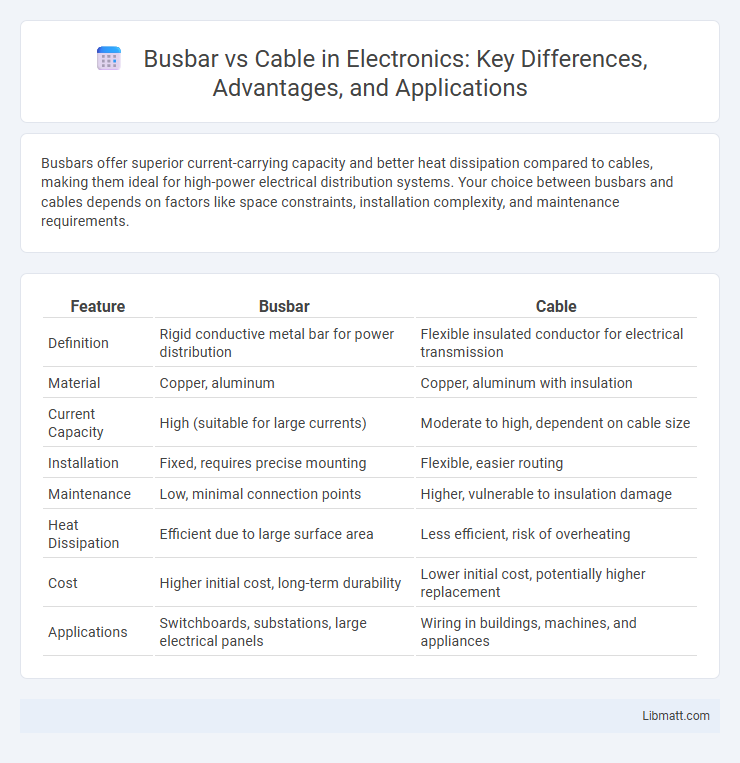
| Feature | Busbar | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rigid conductive metal bar for power distribution | Flexible insulated conductor for electrical transmission |
| Material | Copper, aluminum | Copper, aluminum with insulation |
| Current Capacity | High (suitable for large currents) | Moderate to high, dependent on cable size |
| Installation | Fixed, requires precise mounting | Flexible, easier routing |
| Maintenance | Low, minimal connection points | Higher, vulnerable to insulation damage |
| Heat Dissipation | Efficient due to large surface area | Less efficient, risk of overheating |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term durability | Lower initial cost, potentially higher replacement |
| Applications | Switchboards, substations, large electrical panels | Wiring in buildings, machines, and appliances |
Introduction to Busbar and Cable
Busbars are metallic strips or bars used for distributing electrical power within switchboards, panel boards, and busway enclosures, offering compact and efficient current-carrying capabilities. Cables consist of insulated wires bundled together to transmit electrical power or signals over distances, commonly used for flexible connections and installations. Busbars provide high current capacity and reduced electrical resistance, while cables enable versatile routing and ease of installation in complex layouts.
Key Differences Between Busbar and Cable
Busbars provide a compact, low-resistance method for conducting high current in electrical distribution, whereas cables offer flexible, insulated conductor solutions suitable for varied routing. Busbars excel in minimizing power losses and heat generation due to their large surface area and solid construction, while cables are more adaptable for complex installations and longer distances. Your choice depends on factors such as current capacity, installation space, and maintenance requirements.
Construction and Design Features
Busbars are rigid metal strips or bars, typically made from copper or aluminum, designed for high-current electrical distribution with minimal resistance and heat generation. Cables consist of flexible, insulated conductors encased in protective sheathing, allowing for versatile routing in complex installations. Your choice between busbars and cables depends on factors like current capacity, space constraints, and ease of installation, with busbars excelling in compact, high-current setups and cables providing flexibility.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Busbars offer superior electrical performance compared to cables due to their lower resistance and inductance, enabling efficient current flow and reduced power loss. They provide better heat dissipation and higher current carrying capacity, making them ideal for high-power applications and minimizing voltage drops. Your electrical system benefits from enhanced reliability and reduced energy waste when choosing busbars over traditional cables.
Installation and Space Requirements
Busbars require less installation space than cables due to their compact, flat design that can be mounted directly on panels or busway systems. Installation of busbars is faster and cleaner, reducing labor costs and minimizing wiring complexity compared to multiple cable runs. Cables, on the other hand, need larger conduit spaces and more frequent supports, which increase overall installation time and spatial footprint.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Busbars offer superior safety and reliability compared to cables due to their robust design, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical faults in high-current applications. Their solid metal construction ensures better heat dissipation and mechanical strength, minimizing the likelihood of failure or fire hazards. Choosing busbars can enhance your electrical system's safety and operational reliability, particularly in industrial and commercial settings.
Cost Analysis: Busbar vs Cable
Busbars generally offer lower installation and maintenance costs compared to cables due to their simpler layout and reduced need for extensive insulation. Cable systems often incur higher expenses from labor-intensive installation, increased material usage, and periodic replacement costs. In large-scale electrical distribution, busbars provide a more cost-effective solution by minimizing energy losses and improving system reliability.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Busbars require less maintenance due to their solid, corrosion-resistant design and minimal connection points, reducing the risk of loose connections and electrical faults. Cables often demand more regular inspection and maintenance as they are prone to insulation wear, physical damage, and connector degradation over time. Busbars generally offer a longer lifespan in industrial applications, with durability that surpasses cables, which may need more frequent replacement due to environmental stressors.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Busbars are commonly used in high-current applications such as power distribution panels, switchgear, and electrical substations due to their efficient current-carrying capacity and reduced resistance. Cables are preferred in flexible, long-distance power transmission and distribution where routing around obstacles is necessary, including residential wiring, industrial machinery, and underground installations. Busbars excel in centralized power management systems, while cables are ideal for dynamic, adaptable electrical connections.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting between busbars and cables depends on the specific electrical load, installation space, and maintenance requirements of your project. Busbars offer higher current capacity, easier scalability, and improved heat dissipation, making them ideal for large industrial applications and power distribution systems. Cables provide greater flexibility, simpler installation, and cost-effectiveness for smaller-scale or less complex electrical networks.
Busbar vs Cable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com