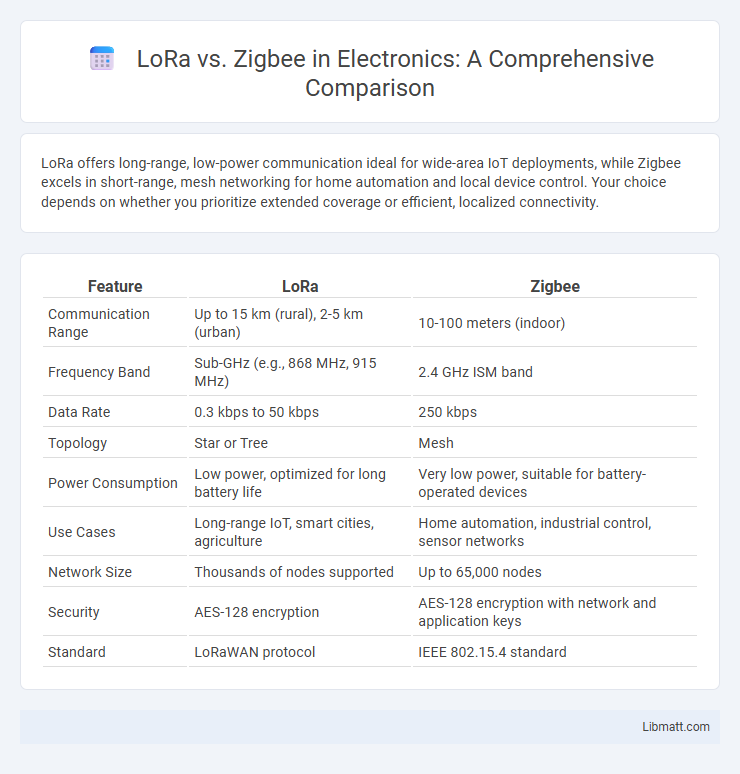
LoRa offers long-range, low-power communication ideal for wide-area IoT deployments, while Zigbee excels in short-range, mesh networking for home automation and local device control. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize extended coverage or efficient, localized connectivity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LoRa | Zigbee |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Range | Up to 15 km (rural), 2-5 km (urban) | 10-100 meters (indoor) |
| Frequency Band | Sub-GHz (e.g., 868 MHz, 915 MHz) | 2.4 GHz ISM band |
| Data Rate | 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps | 250 kbps |
| Topology | Star or Tree | Mesh |
| Power Consumption | Low power, optimized for long battery life | Very low power, suitable for battery-operated devices |
| Use Cases | Long-range IoT, smart cities, agriculture | Home automation, industrial control, sensor networks |
| Network Size | Thousands of nodes supported | Up to 65,000 nodes |
| Security | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption with network and application keys |
| Standard | LoRaWAN protocol | IEEE 802.15.4 standard |
Introduction to LoRa and Zigbee
LoRa is a long-range, low-power wireless communication protocol designed for IoT applications requiring extensive coverage and minimal energy consumption, operating in sub-GHz frequency bands. Zigbee is a short-range, low-power mesh networking standard ideal for home automation and smart devices, functioning primarily in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Both technologies prioritize energy efficiency but differ fundamentally in range, topology, and targeted use cases within wireless communication networks.
Overview of Wireless Communication Protocols
LoRa and Zigbee are wireless communication protocols designed for low-power, long-range connectivity in IoT applications, with LoRa providing ranges up to 10 kilometers using sub-GHz frequencies, ideal for wide-area networks. Zigbee operates on the 2.4 GHz band with shorter ranges of approximately 10-100 meters, optimized for mesh networking in smart home environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize extensive coverage with LoRa or robust local mesh capabilities with Zigbee.
Technical Architecture Comparison
LoRa utilizes a star topology with long-range, low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) capabilities, operating on sub-GHz frequencies for extended coverage and minimal interference. Zigbee employs a mesh topology supporting short-range communication on the 2.4 GHz ISM band, enabling robust device-to-device connections and network self-healing. The architecture of LoRa prioritizes long-distance data transmission with lower data rates, while Zigbee emphasizes low-latency communication and network scalability within localized environments.
Range and Coverage Capabilities
LoRa technology offers extensive range and coverage capabilities, often reaching up to 15 kilometers in rural areas and 2-5 kilometers in urban environments, making it ideal for wide-area IoT applications. Zigbee provides shorter range coverage, typically around 10-100 meters, suitable for local area networks and smart home devices with mesh networking to extend its reach. The superior long-range performance of LoRa supports large-scale deployments, while Zigbee excels in low-power, short-range communication within confined spaces.
Data Rate and Bandwidth Differences
LoRa operates with low data rates typically between 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps, optimized for long-range communication with narrow bandwidths of 125 kHz or less. Zigbee supports higher data rates up to 250 kbps using wider bandwidths around 2 MHz, suitable for short-range, high-density network environments. The trade-off between LoRa's extended range and low bandwidth versus Zigbee's higher bandwidth with limited range defines their distinct application scenarios.
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
LoRa technology offers ultra-low power consumption ideal for long-range, low-data-rate applications, enabling devices to operate for years on a single battery. Zigbee excels in energy efficiency within short-range, mesh network environments, allowing frequent data transmission with minimal power use. Your choice between LoRa and Zigbee should consider the balance between range requirements and device power longevity for optimal energy management.
Network Topology and Scalability
LoRa utilizes a star topology where end devices communicate directly with gateways, enabling long-range connectivity and supporting thousands of devices in a wide-area network. Zigbee employs a mesh topology, allowing devices to relay data through multiple nodes, which enhances network reliability and scalability within localized environments. Your choice depends on whether you need extensive coverage with fewer hops (LoRa) or robust, flexible networking with many interconnected devices (Zigbee).
Security Features and Protocols
LoRa employs robust AES-128 encryption at the network, application, and device levels, ensuring comprehensive security for long-range IoT communications, while Zigbee uses AES-128 encryption with key establishment protocols like SKKE and Trust Center for device authentication. LoRa's decentralized network architecture reduces single points of failure, enhancing resilience against attacks, whereas Zigbee's centralized Trust Center manages key distribution and security policies but may introduce vulnerabilities if compromised. Your choice between LoRa and Zigbee should consider the specific security requirements of your IoT deployment, especially in terms of network range, scalability, and threat models.
Typical Use Cases and Applications
LoRa excels in long-range, low-power communication suited for wide-area IoT deployments such as smart agriculture, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring. Zigbee is ideal for short-range, low-power mesh networking in home automation, industrial control, and sensor networks requiring reliable device interconnection. Your choice depends on whether the application demands extensive coverage with minimal power consumption or a robust, low-latency local network.
Summary: Choosing Between LoRa and Zigbee
LoRa offers long-range communication with low power consumption, ideal for wide-area IoT applications such as smart agriculture and city infrastructure, while Zigbee excels in short-range, low-power mesh networking suitable for home automation and industrial control. LoRa operates primarily in sub-GHz frequency bands, providing kilometers of coverage, whereas Zigbee uses the 2.4 GHz band with limited range but supports robust device-to-device routing. Choosing between LoRa and Zigbee depends on project requirements for range, network topology, power efficiency, and data transmission frequency.
LoRa vs Zigbee Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com