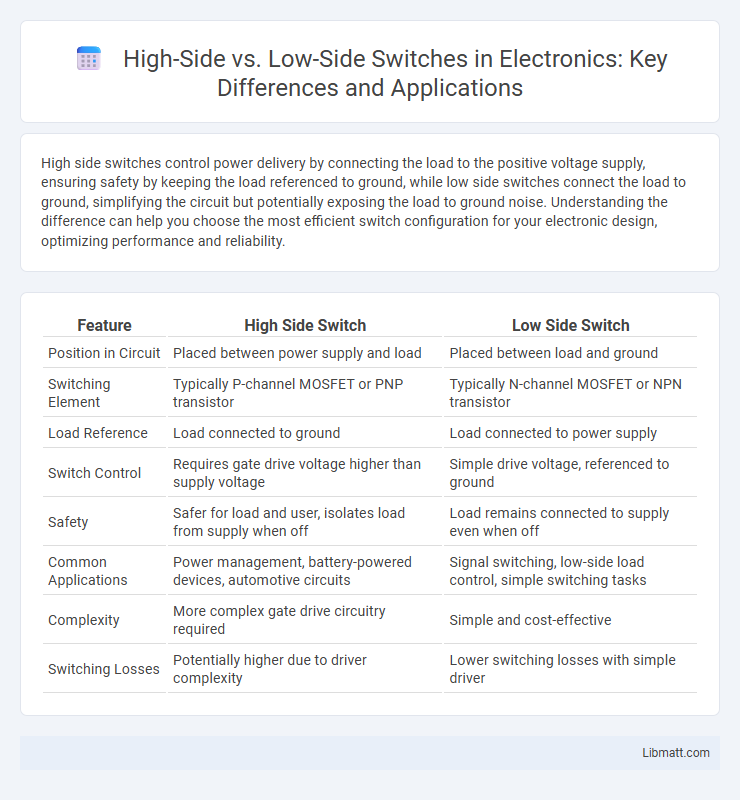
High side switches control power delivery by connecting the load to the positive voltage supply, ensuring safety by keeping the load referenced to ground, while low side switches connect the load to ground, simplifying the circuit but potentially exposing the load to ground noise. Understanding the difference can help you choose the most efficient switch configuration for your electronic design, optimizing performance and reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Side Switch | Low Side Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Position in Circuit | Placed between power supply and load | Placed between load and ground |
| Switching Element | Typically P-channel MOSFET or PNP transistor | Typically N-channel MOSFET or NPN transistor |
| Load Reference | Load connected to ground | Load connected to power supply |
| Switch Control | Requires gate drive voltage higher than supply voltage | Simple drive voltage, referenced to ground |
| Safety | Safer for load and user, isolates load from supply when off | Load remains connected to supply even when off |
| Common Applications | Power management, battery-powered devices, automotive circuits | Signal switching, low-side load control, simple switching tasks |
| Complexity | More complex gate drive circuitry required | Simple and cost-effective |
| Switching Losses | Potentially higher due to driver complexity | Lower switching losses with simple driver |
Introduction to High Side and Low Side Switching
High side and low side switches are crucial components in electronic circuits, controlling the flow of current to loads by connecting either the positive voltage (high side) or ground (low side) to the load. High side switches typically use P-channel MOSFETs or PNP transistors to connect the load to the positive supply voltage, enabling current flow when activated. Low side switches generally employ N-channel MOSFETs or NPN transistors to connect the load to ground, turning the load on by completing the circuit to the negative terminal.
Basic Principles of Electronic Switching
High side switches control the positive voltage supply to the load, while low side switches manage the connection to ground, each using transistors or MOSFETs to regulate current flow. Your choice between high side and low side switching depends on the circuit design and safety considerations, with high side switches often preferred for controlling loads in automotive or industrial applications due to their ability to isolate the load from ground. Effective electronic switching relies on understanding voltage references, switching speed, and load requirements to ensure optimal performance and protection.
What is a High Side Switch?
A high side switch controls the power supply line by connecting the load to the positive voltage rail, typically using a P-channel MOSFET or a PNP transistor. It ensures the load is connected to the voltage source only when the switch is active, offering safer operation by avoiding direct grounding risks. High side switching is commonly used in automotive and industrial electronics for load management and protection.
What is a Low Side Switch?
A low side switch is an electronic component used to control the connection between the load and ground, typically switching the negative side of the circuit. It operates by grounding the load to complete the circuit, enabling devices to turn on or off with minimal voltage drop across the switch. Your low side switching design offers simplicity and cost savings but requires careful consideration of load grounding and potential noise issues.
Key Differences Between High Side and Low Side Switching
High side switches control the power supply to the load by connecting it to the positive voltage rail, while low side switches connect the load to ground. High side switching is often preferred for safety and protection reasons, as it ensures the load is disconnected from the power source, reducing the risk of shorts. Your choice between high side and low side switching depends on factors like circuit complexity, load type, and voltage requirements.
Advantages of High Side Switching
High side switching offers enhanced safety by connecting the load to the positive voltage supply, reducing the risk of short circuits and ground faults. It provides better control in systems where the common ground needs to remain uninterrupted, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. High side switches also enable easier implementation of load monitoring and diagnostics, improving system reliability and maintenance efficiency.
Benefits of Low Side Switching
Low side switching offers simplified circuit design by connecting the load directly to the positive power supply, while the switch controls the ground path. This approach reduces cost and complexity by using common NPN transistors or N-channel MOSFETs that are easier to drive and require less complex circuitry. Your system benefits from improved reliability and straightforward troubleshooting due to the stable reference voltage maintained on the high side.
Applications of High Side and Low Side Switches
High side switches are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications for controlling loads connected to the positive voltage supply, ensuring safer operation by isolating the control circuit from high voltage. Low side switches are typically employed in lighting and motor control systems where the load is connected to ground, offering simpler wiring and cost-effective solutions. Your choice between high side and low side switching depends on factors like load type, safety requirements, and circuit design preferences.
Choosing Between High Side and Low Side Switches
Choosing between high side and low side switches depends primarily on the load type and control requirements; high side switches connect the load to the positive supply, ideal for switching the power supply line in DC circuits, while low side switches connect the load to ground, offering simpler control and protection in many applications. High side switching is preferred when isolating the load from the power supply is critical to prevent accidental damage or when controlling devices requiring positive voltage reference. Low side switching suits applications where controlling the return path is sufficient, often simplifying circuit design and reducing switching element stress.
Conclusion: Which Switch is Right for Your Application?
High side switches are ideal for applications requiring load control with a stable reference to ground, offering better protection and ease of troubleshooting in positive voltage systems. Low side switches are typically used when switching the ground path is simpler and cost-effective, especially in circuits with common positive supply rails. Selecting the right switch depends on the specific circuit design, safety requirements, and whether load or ground switching aligns better with the overall system architecture.
High Side vs Low Side Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com