Inductive sensors detect metallic objects by generating an electromagnetic field, making them ideal for metal detection in industrial automation. Capacitive sensors sense both metallic and non-metallic materials by detecting changes in capacitance, providing versatile options for detecting liquids, plastics, and other substances in various applications.
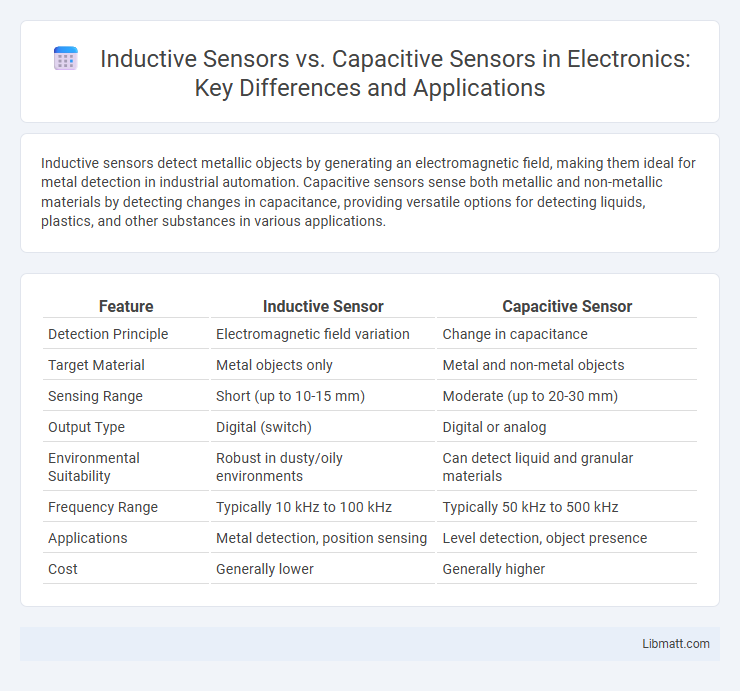
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inductive Sensor | Capacitive Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Principle | Electromagnetic field variation | Change in capacitance |
| Target Material | Metal objects only | Metal and non-metal objects |
| Sensing Range | Short (up to 10-15 mm) | Moderate (up to 20-30 mm) |
| Output Type | Digital (switch) | Digital or analog |
| Environmental Suitability | Robust in dusty/oily environments | Can detect liquid and granular materials |
| Frequency Range | Typically 10 kHz to 100 kHz | Typically 50 kHz to 500 kHz |
| Applications | Metal detection, position sensing | Level detection, object presence |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Inductive and Capacitive Sensors
Inductive sensors detect metallic objects by generating an electromagnetic field that changes when a metal target enters the sensing zone. Capacitive sensors, on the other hand, sense both metallic and non-metallic materials by measuring changes in capacitance caused by the presence of an object. Your choice between inductive and capacitive sensors depends on the material type and application requirements, with inductive sensors ideal for metal detection and capacitive sensors suited for detecting liquids, plastics, or granular materials.
Basic Operating Principles
Inductive sensors operate based on electromagnetic induction, detecting metallic objects by generating a magnetic field and measuring changes in its intensity when a metal target enters the sensing range. Capacitive sensors function by detecting changes in capacitance caused by the presence of any object, conductive or non-conductive, that alters the dielectric constant between the sensor and the target. Both sensors rely on distinct physical phenomena: inductive sensors utilize eddy currents in metals, while capacitive sensors sense variations in electric fields.
Key Differences Between Inductive and Capacitive Sensors
Inductive sensors detect metallic objects using electromagnetic fields, providing reliable performance in harsh industrial environments, while capacitive sensors detect both metallic and non-metallic materials by sensing changes in capacitance, allowing for versatile applications like liquid level detection. The sensing range of capacitive sensors is generally longer than that of inductive sensors, but capacitive sensors are more sensitive to environmental factors such as humidity and dust. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate sensor type for your specific detection needs and operational conditions.
Materials Detected by Each Sensor Type
Inductive sensors detect metallic objects by generating an electromagnetic field that responds to conductive materials like steel, iron, and aluminum but are ineffective with non-metallic substances. Capacitive sensors sense changes in capacitance caused by both metallic and non-metallic materials, including plastics, glass, liquids, and powders, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. The choice between these sensors depends on the target material's conductivity and dielectric properties, ensuring accurate detection and operational efficiency.
Applications of Inductive Sensors
Inductive sensors are widely used in industrial automation for detecting metal objects, such as in conveyor systems, robotic arms, and manufacturing equipment. Their robust design makes them ideal for harsh environments where dust, oil, or moisture are present, ensuring reliable object detection without physical contact. You can rely on inductive sensors for precise position sensing and speed measurement in metal detection applications.
Applications of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive sensors excel in detecting non-metallic materials such as plastics, liquids, and glass, making them ideal for applications in food and beverage processing, packaging, and level sensing. Their ability to sense through non-conductive containers allows accurate monitoring of fluid levels and material presence without direct contact, enhancing automation efficiency. You can leverage capacitive sensors for precise object detection and integration in environments requiring sensitivity to a wide range of materials.
Advantages of Inductive Sensors
Inductive sensors offer high durability and reliability in harsh industrial environments due to their ability to detect metallic objects without physical contact. These sensors provide precise and fast detection with excellent immunity to dirt, oil, and moisture, making them ideal for automated manufacturing processes. Your equipment benefits from low maintenance costs and long service life when using inductive sensors for metal detection.
Advantages of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive sensors offer the advantage of detecting both metallic and non-metallic objects, making them highly versatile compared to inductive sensors that only detect metals. Their ability to sense through transparent or non-conductive materials enhances application flexibility in industries such as packaging, plastics, and food processing. Your choice of capacitive sensors ensures improved sensitivity and adaptability for a wide range of surface and material detection needs.
Limitations and Challenges
Inductive sensors are limited by their inability to detect non-metallic objects, restricting their use to metal detection only, and can be affected by electromagnetic interference in harsh environments. Capacitive sensors face challenges with sensitivity to environmental factors such as humidity, dust, and temperature variations, which may cause false triggers or reduced accuracy. Your choice depends on the application's material detection needs and environmental conditions, as both sensor types have distinct limitations impacting performance.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Inductive sensors excel in detecting metallic objects with high accuracy and durability, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments where metal presence is dominant. Capacitive sensors offer versatility by detecting both metallic and non-metallic materials such as liquids, plastics, and powders, making them suitable for applications requiring material differentiation or level sensing. Selecting the right sensor depends on factors like target material, environmental conditions, detection range, and required sensitivity for optimal performance.
Inductive Sensor vs Capacitive Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com