Isolated power supplies provide galvanic separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing electrical noise, making them ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Non-isolated power supplies directly connect input and output grounds, offering higher efficiency and simpler design, suitable for low-voltage devices where isolation is not critical.
Table of Comparison
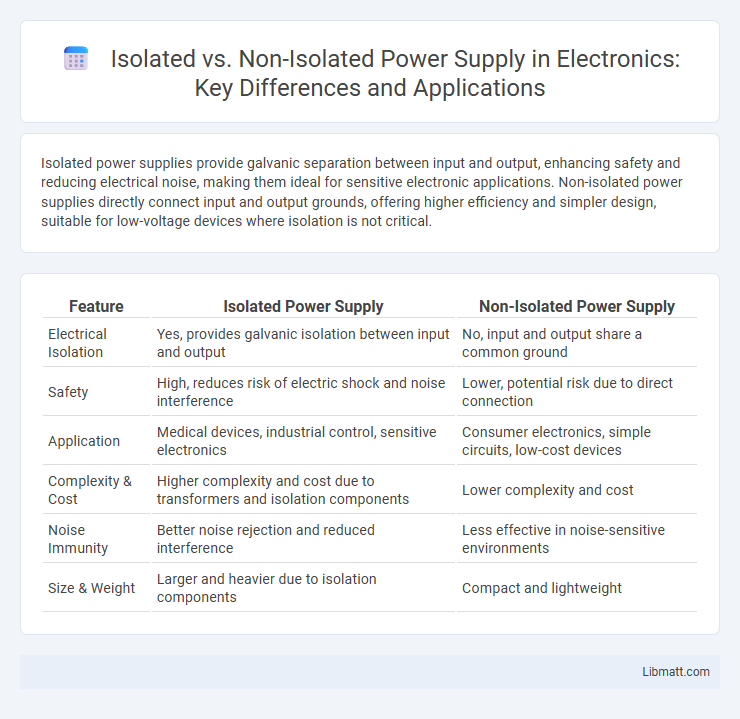
| Feature | Isolated Power Supply | Non-Isolated Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Yes, provides galvanic isolation between input and output | No, input and output share a common ground |
| Safety | High, reduces risk of electric shock and noise interference | Lower, potential risk due to direct connection |
| Application | Medical devices, industrial control, sensitive electronics | Consumer electronics, simple circuits, low-cost devices |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher complexity and cost due to transformers and isolation components | Lower complexity and cost |
| Noise Immunity | Better noise rejection and reduced interference | Less effective in noise-sensitive environments |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier due to isolation components | Compact and lightweight |
Introduction to Power Supplies
Power supplies convert electrical energy to the required voltage and current for electronic circuits, categorized into isolated and non-isolated types based on electrical separation. Isolated power supplies use transformers or optocouplers to provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety and noise reduction in sensitive applications. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, offering simpler design and higher efficiency for low-voltage, low-power devices.
What Is an Isolated Power Supply?
An isolated power supply features electrical separation between its input and output through a transformer, ensuring no direct conductive path and enhancing safety and noise reduction. It is commonly used in medical, industrial, and communication equipment where grounding and interference protection are critical. Non-isolated power supplies, by contrast, share a common ground, leading to potential noise issues and limited protection in sensitive applications.
What Is a Non-isolated Power Supply?
A non-isolated power supply directly connects its input and output grounds, enabling a common reference point and simpler design but limiting safety isolation. It is typically used in applications where isolation from the mains or different voltage domains is not required, such as low-voltage DC-DC converters or point-of-load regulators. This type of power supply offers higher efficiency and reduced cost but lacks protection against electrical shock and noise interference compared to isolated power supplies.
Key Differences Between Isolated and Non-isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies feature electrical separation between input and output, providing enhanced safety, noise reduction, and protection from surges, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, offering simpler design and higher efficiency but with less noise immunity and safety isolation. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate power supply based on your application's requirements for safety, noise tolerance, and efficiency.
Applications of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies are essential in medical devices, industrial automation, and telecommunications to ensure user safety and prevent electrical noise interference by separating the input and output circuits. These power supplies provide galvanic isolation, which protects sensitive equipment from ground loops and voltage spikes, making them ideal for precision measurement and control systems. In contrast, non-isolated power supplies are typically used in applications where isolation is not critical, such as in low-cost consumer electronics or simple power conversion tasks.
Applications of Non-isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies are commonly used in applications where electrical isolation is not critical, such as powering low-voltage circuits, LED drivers, and battery charging systems. These power supplies provide a direct connection between input and output grounds, making them ideal for cost-sensitive, compact devices in consumer electronics and industrial automation. Your projects benefit from the simplicity and efficiency of non-isolated designs when isolation safety requirements are minimal.
Advantages of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies provide superior safety by separating the input and output, preventing electrical shock and reducing the risk of short circuits in sensitive equipment. They also minimize noise interference and enhance signal integrity, which is crucial for precision electronics and medical devices. Your systems benefit from improved reliability and protection against ground loops, making isolated power supplies ideal for critical applications.
Advantages of Non-isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies offer higher efficiency and lower cost compared to isolated designs, making them ideal for applications with tight budget and space constraints. Your system benefits from simpler circuits and reduced component count, which leads to easier integration and maintenance. These power supplies are well-suited for low-voltage, low-current devices where electrical isolation is not a critical requirement.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Project
Choosing the right power supply for your project requires understanding the difference between isolated and non-isolated power supplies. Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output, enhancing safety and noise reduction, making them ideal for sensitive or medically-related applications. Non-isolated power supplies are more compact and efficient for simple, low-cost devices where electrical isolation is not critical.
Conclusion: Isolated vs Non-isolated Power Supply
Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference, making them ideal for sensitive electronics and medical devices. Non-isolated power supplies are more efficient and cost-effective for applications where electrical isolation is not critical, such as simple consumer electronics. Your choice depends on whether isolation is necessary for safety, noise reduction, or regulatory compliance in your specific project.
Isolated vs Non-isolated power supply Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com