A step-down transformer reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower level, making it ideal for safely powering household appliances from the main electrical supply. In contrast, a step-up transformer increases the voltage from a lower level to a higher level, which is essential for efficient power transmission over long distances.
Table of Comparison
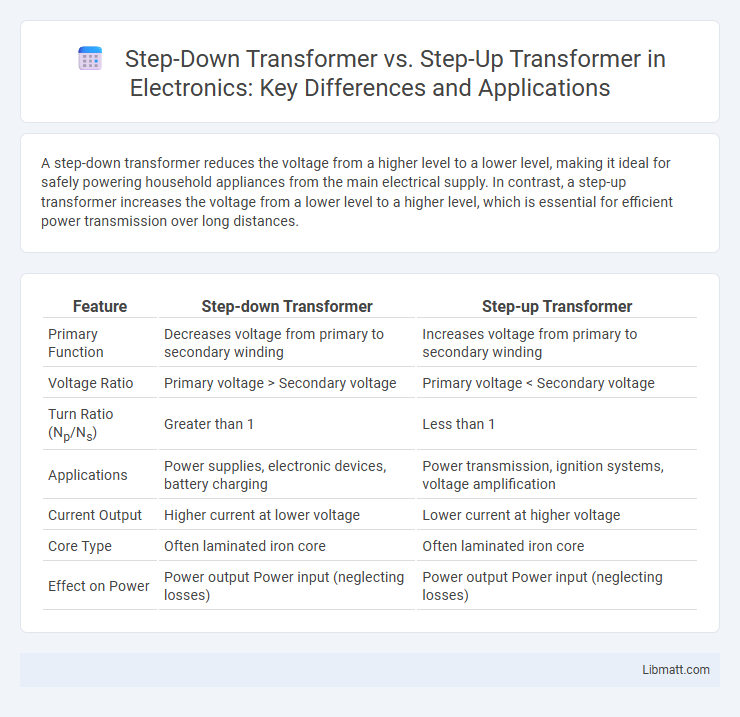
| Feature | Step-down Transformer | Step-up Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Decreases voltage from primary to secondary winding | Increases voltage from primary to secondary winding |
| Voltage Ratio | Primary voltage > Secondary voltage | Primary voltage < Secondary voltage |
| Turn Ratio (Np/Ns) | Greater than 1 | Less than 1 |
| Applications | Power supplies, electronic devices, battery charging | Power transmission, ignition systems, voltage amplification |
| Current Output | Higher current at lower voltage | Lower current at higher voltage |
| Core Type | Often laminated iron core | Often laminated iron core |
| Effect on Power | Power output Power input (neglecting losses) | Power output Power input (neglecting losses) |
Introduction to Transformers
Transformers are electrical devices designed to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, either increasing or decreasing voltage levels. Step-down transformers reduce high voltage to lower voltage levels suitable for household appliances and electronic devices, ensuring safe and efficient power use. Step-up transformers increase voltage for efficient transmission over long distances, minimizing energy loss during distribution in power grids.
What is a Step-down Transformer?
A step-down transformer is an electrical device designed to reduce the voltage from a higher primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage while maintaining the same frequency. It consists of two coils, the primary and the secondary, with the number of turns on the secondary coil being fewer than on the primary coil, resulting in voltage reduction. Step-down transformers are commonly used in power distribution systems to safely lower voltage levels for residential and commercial use.
What is a Step-up Transformer?
A step-up transformer increases the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding, allowing efficient transmission of electrical power over long distances by reducing current and minimizing energy loss. It is commonly used in power generation and distribution systems where voltage needs to be elevated before entering high-voltage transmission lines. The device operates on electromagnetic induction principles, with more turns in the secondary coil compared to the primary coil to achieve voltage amplification.
Core Working Principles
A step-down transformer reduces voltage from a higher primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage by having fewer turns on the secondary coil compared to the primary coil, while a step-up transformer increases voltage by having more turns on the secondary coil than the primary. Both types operate on electromagnetic induction and rely on alternating current to create a changing magnetic flux in the core that induces voltage in the secondary winding. Understanding your application's voltage requirements helps determine whether you need a step-down or step-up transformer to achieve optimal electrical performance.
Key Differences Between Step-down and Step-up Transformers
Step-down transformers decrease voltage from a higher primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage, making them essential for safely powering household electronics. Step-up transformers increase voltage from a lower primary voltage to a higher secondary voltage, commonly used in power transmission to reduce energy loss over long distances. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate transformer type based on your voltage requirements and application needs.
Applications of Step-down Transformers
Step-down transformers are commonly used in residential and commercial power distribution to reduce high voltage from transmission lines to safer, usable levels for appliances and lighting. Industrial equipment often relies on step-down transformers to lower voltage for machinery operation and control circuits. Your electrical devices benefit from the precise voltage regulation these transformers provide, ensuring safety and efficiency in everyday applications.
Applications of Step-up Transformers
Step-up transformers are essential in electrical power transmission, where they increase voltage from power plants to minimize energy loss over long distances, enhancing efficiency. They are widely used in renewable energy systems such as wind turbines and solar panels to elevate the generated voltage for grid compatibility. Industrial applications include high-voltage equipment and testing laboratories that require elevated voltage levels for operation and experimentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Step-down transformers reduce voltage levels to ensure the safe operation of household appliances, minimizing energy loss and enhancing safety, but they may cause voltage drops over long distances. Step-up transformers increase voltage for efficient long-distance power transmission, reducing current and energy loss, though they require robust insulation and safety measures due to high voltage levels. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages helps you select the appropriate transformer type for efficient and safe power distribution.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Transformer
When choosing a transformer, consider voltage requirements, as step-down transformers reduce voltage for devices needing lower input, while step-up transformers increase voltage for equipment requiring higher input. Evaluate power rating and load capacity to ensure the transformer can handle your electrical demand without overheating or efficiency loss. Efficiency, size, and cost also play critical roles in selecting the ideal transformer for your specific application.
Conclusion: Step-down vs Step-up Transformer
Step-down transformers reduce voltage from a higher level to a lower level, making them ideal for safely powering household appliances and electronics. Step-up transformers increase voltage from a lower level to a higher level, essential for efficient long-distance power transmission and specific industrial applications. Understanding Your power requirements helps determine whether a step-down or step-up transformer best suits your electrical system needs.
Step-down Transformer vs Step-up Transformer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com