Perforated boards offer individual holes for custom component placement and wiring flexibility, making them ideal for prototyping complex circuits, while stripboards feature pre-made copper strips that simplify soldering and track connections automatically. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize design customization or ease of assembly for your electronic projects.
Table of Comparison
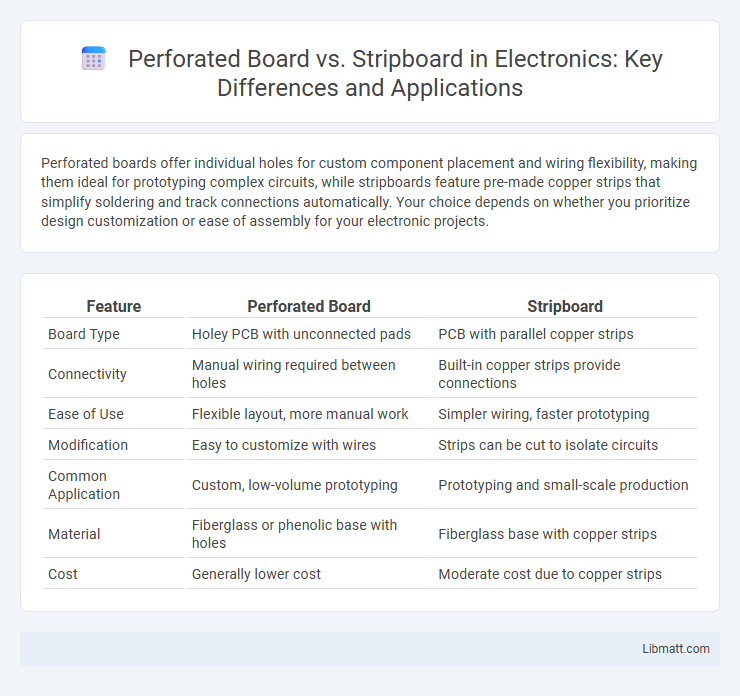
| Feature | Perforated Board | Stripboard |
|---|---|---|
| Board Type | Holey PCB with unconnected pads | PCB with parallel copper strips |
| Connectivity | Manual wiring required between holes | Built-in copper strips provide connections |
| Ease of Use | Flexible layout, more manual work | Simpler wiring, faster prototyping |
| Modification | Easy to customize with wires | Strips can be cut to isolate circuits |
| Common Application | Custom, low-volume prototyping | Prototyping and small-scale production |
| Material | Fiberglass or phenolic base with holes | Fiberglass base with copper strips |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost due to copper strips |
Introduction to Perforated Board and Stripboard
Perforated board, often known as perfboard, features a grid of pre-drilled holes for individually mounting electronic components, allowing flexible custom circuit layouts without fixed copper tracks. Stripboard, or Veroboard, consists of parallel copper strips on a fiberglass base, enabling easy soldering and connections along the strips for simplified prototyping. Both are essential prototyping tools in electronics, with perfboard offering maximum component placement freedom and stripboard providing organized conductive paths.
What is a Perforated Board?
A perforated board, also known as a perfboard, is a flat, rigid material with a grid of evenly spaced holes used for mounting and soldering electronic components. It provides flexibility for custom circuit designs without predefined copper traces, allowing you to create unique connections with wires or solder bridges. Perfboards are ideal for prototyping and experimentation in electronics, offering an accessible platform for assembling circuits before finalizing a design.
What is a Stripboard?
A Stripboard is a type of prototyping board characterized by a grid of holes with parallel copper strips running underneath to create electrical connections. It allows you to easily solder electronic components onto the board, enabling quick circuit assembly and modifications without the need for a printed circuit board (PCB). Unlike perforated boards, which have isolated holes, the continuous copper strips on stripboards facilitate efficient connectivity and streamlined circuit design.
Key Differences Between Perforated Board and Stripboard
Perforated board features a grid of isolated holes allowing flexible, point-to-point wiring, ideal for prototyping custom circuits, while stripboard contains parallel copper strips that provide continuous electrical connections along rows. Stripboard simplifies circuit assembly by reducing the need for additional wiring but limits layout flexibility compared to perforated board. The choice between these boards depends on the desired complexity, ease of modification, and circuit design preference.
Advantages of Using Perforated Boards
Perforated boards offer enhanced flexibility for prototyping electronic circuits due to their pre-drilled holes arranged in a grid, allowing easy component placement and wiring customization. They support rapid modifications and repairs, making them ideal for experimental designs and iterative development. Your projects benefit from improved durability and cleaner layouts compared to stripboards, which have fixed copper strips that can limit circuit complexity and require careful cutting.
Benefits of Stripboards in Electronics Projects
Stripboards offer superior ease of use in electronics projects due to their pre-connected copper strips that simplify circuit assembly and reduce wiring errors. Their standardized grid layout enhances component organization and speeds up prototyping, making them ideal for quick design iterations. The durable, heat-resistant material of stripboards ensures reliable solder joints and long-lasting performance in various electronic applications.
Application Areas: Perforated Board vs Stripboard
Perforated board is ideal for prototyping and small-scale electronic projects due to its flexibility in component placement and easy soldering without predefined connections. Stripboard, featuring parallel copper strips, suits more structured circuit designs and semi-permanent installations where consistent electrical connectivity is required. Your choice depends on whether you need customizable layouts or ready-made conductive pathways for reliable connections.
Choosing the Right Board for Your Project
Choosing the right board for your project depends on the complexity and permanence of your circuit design. Perforated boards offer flexibility with individually drilled holes for custom wiring, ideal for prototyping and one-off builds, while stripboards provide pre-connected copper strips that simplify assembly and are better suited for more structured layouts. Understanding your project's needs for ease of modifications and durability will help you decide between perforated board and stripboard effectively.
Cost Comparison: Perforated Board vs Stripboard
Perforated boards typically offer a lower cost option compared to stripboards due to their simpler manufacturing process and less material usage. Stripboards, featuring pre-made copper strips, tend to be priced higher but provide enhanced wiring convenience and reliability for complex circuits. For budget-conscious projects, perforated boards minimize expenses, while stripboards balance cost with efficiency in prototype development.
Conclusion: Which Board Should You Use?
Perforated boards offer greater flexibility for custom layouts with individually spaced holes, ideal for complex or one-off projects requiring tailored circuit designs. Stripboards provide pre-connected copper strips that simplify circuit assembly and reduce soldering time, making them suitable for prototype development and straightforward electronic circuits. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize customization with perforated boards or ease of use and rapid prototyping with stripboards.
Perforated Board vs Stripboard Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com