NAND Flash offers faster write and erase speeds with higher density, making it ideal for mass storage solutions like SSDs and USB drives. NOR Flash provides faster read speeds and better random access, which benefits applications requiring reliable code execution and low latency.
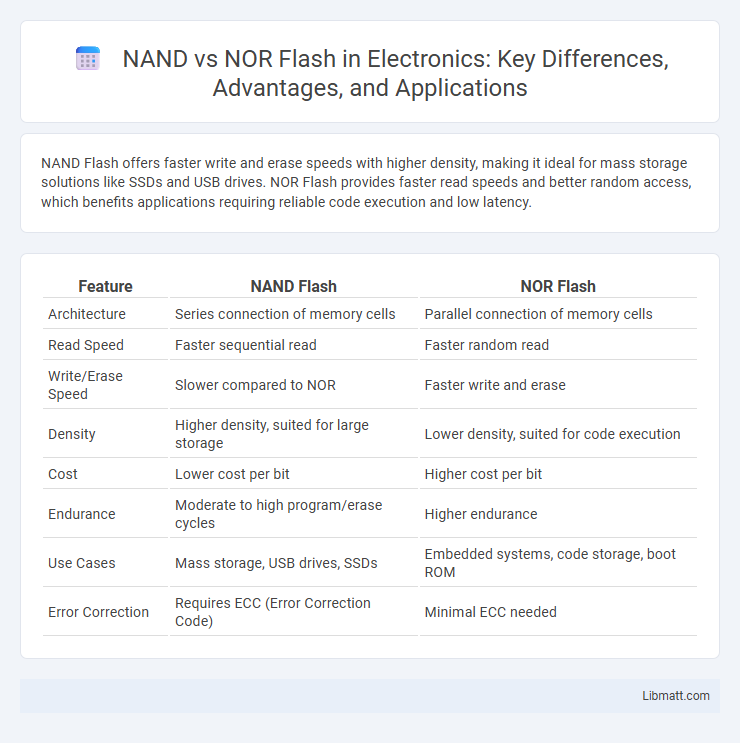
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NAND Flash | NOR Flash |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Series connection of memory cells | Parallel connection of memory cells |
| Read Speed | Faster sequential read | Faster random read |
| Write/Erase Speed | Slower compared to NOR | Faster write and erase |
| Density | Higher density, suited for large storage | Lower density, suited for code execution |
| Cost | Lower cost per bit | Higher cost per bit |
| Endurance | Moderate to high program/erase cycles | Higher endurance |
| Use Cases | Mass storage, USB drives, SSDs | Embedded systems, code storage, boot ROM |
| Error Correction | Requires ECC (Error Correction Code) | Minimal ECC needed |
Introduction to Flash Memory Technologies
NAND and NOR Flash are two primary types of non-volatile memory technologies used in data storage, each offering distinct architectures and performance characteristics. NAND Flash is favored for high-density storage and faster write/erase cycles, making it ideal for SSDs and USB drives, whereas NOR Flash excels in executing code directly due to its fast read speeds and random access capability. Both technologies leverage floating-gate transistors to retain data without power, but their structural differences influence their application in consumer electronics, embedded systems, and memory cards.
What is NAND Flash?
NAND Flash is a type of non-volatile memory that stores data in a compact and efficient manner by using floating-gate transistors arranged in a grid, enabling high-density storage suitable for SSDs, USB drives, and mobile devices. Its architecture allows for faster write and erase times compared to NOR Flash, making it ideal for large data storage needs. Understanding NAND Flash technology can help you make informed decisions when selecting storage solutions for performance and capacity.
What is NOR Flash?
NOR Flash is a type of non-volatile memory known for its fast random read speeds and reliable execute-in-place (XIP) capabilities, making it ideal for code storage in embedded systems. It stores data using a parallel architecture where each memory cell is directly accessible, enabling efficient byte-level access and booting without needing to copy code to RAM. Compared to NAND Flash, NOR Flash offers higher endurance and better data integrity but typically has lower density and slower write speeds, positioning it for applications requiring frequent, reliable reads rather than bulk data storage.
Key Differences Between NAND and NOR Flash
NAND Flash features faster write and erase speeds, higher storage density, and lower cost per bit, making it ideal for mass storage in SSDs and USB drives. NOR Flash offers faster read speeds and byte-level random access, which suits code execution in embedded systems and firmware storage. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize read performance and reliability (NOR) or maximize capacity and write efficiency (NAND).
Performance Comparison: Speed and Endurance
NAND flash memory delivers faster write and erase speeds compared to NOR flash, making it ideal for high-capacity storage and applications requiring rapid data transfer. NOR flash excels in read speed and random access performance, providing better endurance for code execution in embedded systems. While NAND flash offers higher storage density and cost-efficiency, NOR flash maintains superior reliability for frequent read operations due to its robust endurance cycle counts.
Cost Analysis: NAND vs NOR Flash
NAND flash memory offers a lower cost per bit compared to NOR flash due to its higher density and simpler cell architecture, making it ideal for large-capacity storage such as SSDs and USB drives. NOR flash, with its faster read speeds and random access capabilities, typically comes at a higher cost and is preferred for code execution in embedded systems. When evaluating your storage needs, consider NAND flash for cost-effective bulk data storage and NOR flash if your application demands rapid, reliable code execution with higher memory access speeds.
Applications of NAND Flash
NAND Flash is widely used in applications requiring high-density storage and fast write/erase cycles, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and memory cards. Its cost-effectiveness and durability make it ideal for smartphones, tablets, and embedded systems where reliable non-volatile memory is critical. Your devices benefit from NAND Flash's ability to store large amounts of data efficiently while maintaining quick access speeds.
Applications of NOR Flash
NOR Flash is widely used in applications requiring fast read speeds and reliable random access, such as embedded systems, firmware storage, and code execution in microcontrollers. Its high endurance and durability make it ideal for automotive electronics, industrial control systems, and BIOS storage in computers. You can depend on NOR Flash for critical read-intensive tasks where data integrity and quick retrieval are essential.
Pros and Cons: NAND Flash
NAND Flash offers higher storage density and faster write and erase speeds compared to NOR Flash, making it ideal for large data storage such as SSDs and USB drives. Its cost per bit is lower, enabling more affordable mass production, but it has slower read speeds and limited random access capabilities. NAND Flash cells are more prone to wear over time, requiring robust error correction and wear leveling techniques to maintain data integrity and device lifespan.
Pros and Cons: NOR Flash
NOR Flash offers fast read speeds and random access capabilities, making it ideal for code execution and reliable firmware storage. However, it has slower write and erase times compared to NAND Flash, resulting in lower overall write endurance and higher costs per megabyte. Your choice of NOR Flash suits applications requiring frequent read access and stability over write speed or storage density.
NAND vs NOR Flash Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com