TVS diodes provide fast and precise clamping of voltage spikes, protecting sensitive electronic circuits from transient surges with minimal response time. Your choice between a TVS diode and a varistor depends on the required response speed and energy absorption, as varistors offer higher surge current capacity but slower response.
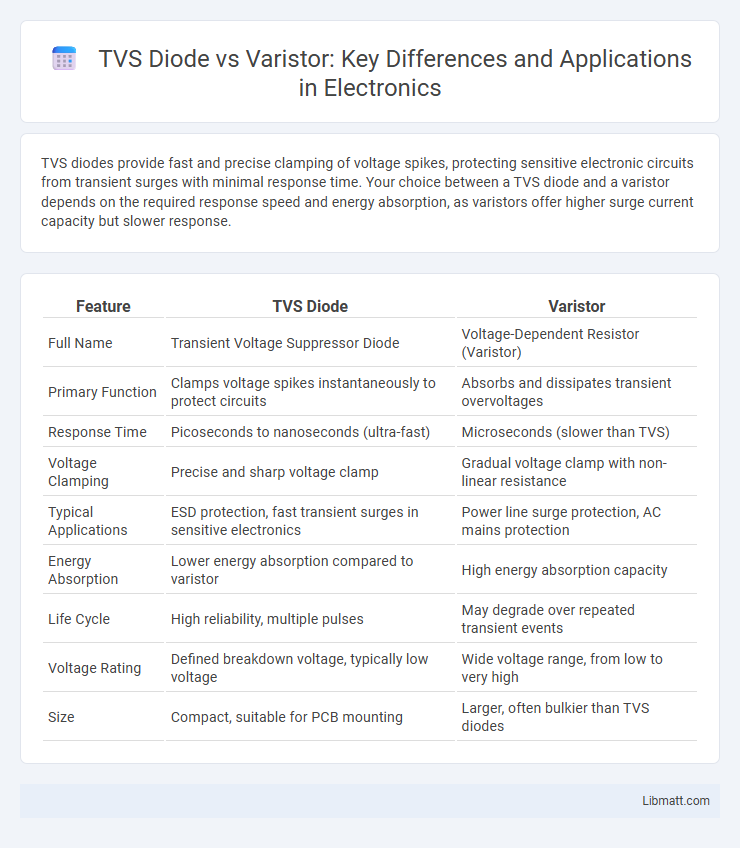
Table of Comparison
| Feature | TVS Diode | Varistor |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Transient Voltage Suppressor Diode | Voltage-Dependent Resistor (Varistor) |
| Primary Function | Clamps voltage spikes instantaneously to protect circuits | Absorbs and dissipates transient overvoltages |
| Response Time | Picoseconds to nanoseconds (ultra-fast) | Microseconds (slower than TVS) |
| Voltage Clamping | Precise and sharp voltage clamp | Gradual voltage clamp with non-linear resistance |
| Typical Applications | ESD protection, fast transient surges in sensitive electronics | Power line surge protection, AC mains protection |
| Energy Absorption | Lower energy absorption compared to varistor | High energy absorption capacity |
| Life Cycle | High reliability, multiple pulses | May degrade over repeated transient events |
| Voltage Rating | Defined breakdown voltage, typically low voltage | Wide voltage range, from low to very high |
| Size | Compact, suitable for PCB mounting | Larger, often bulkier than TVS diodes |
Overview of TVS Diode and Varistor
TVS diodes and varistors serve as crucial overvoltage protection components in electronic circuits. TVS diodes offer rapid response times and precise clamping voltage characteristics, making them ideal for sensitive semiconductor devices and ESD protection. Varistors, typically metal oxide varistors (MOVs), provide nonlinear resistance to absorb large surge currents, commonly used in power line and lightning surge suppression applications.
Fundamental Operating Principles
TVS diodes operate by clamping voltage spikes through rapid avalanche breakdown, providing fast, single-event transient suppression ideal for circuit protection. Varistors, composed of metal oxide materials, exhibit nonlinear resistance that decreases sharply under high voltage stress, absorbing energy across a wider range of transient voltages. The key distinction lies in the TVS diode's precise voltage clamping and rapid response, whereas varistors act more like energy absorbers with a slower response time and higher leakage currents.
Response Time Comparison
TVS diodes provide ultra-fast response times in the order of picoseconds to nanoseconds, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from sudden voltage spikes. Varistors respond more slowly, typically in microseconds, which may not be sufficient for high-speed transient protection. When choosing protection for your circuit, the faster response of TVS diodes ensures quicker suppression of voltage surges, reducing the risk of component damage.
Voltage Clamping Characteristics
TVS diodes exhibit faster response times and a precise clamping voltage, typically within nanoseconds, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from transient voltage spikes. Varistors have a nonlinear voltage-current characteristic with a variable clamping voltage that depends on the magnitude of the surge, providing broader but less precise protection. The controlled voltage clamping of TVS diodes offers superior transient voltage suppression compared to the more gradual voltage clamping offered by varistors.
Energy Handling Capability
TVS diodes provide rapid response to transient voltage spikes with energy handling capabilities typically ranging from a few joules up to several tens of joules, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronics from fast, high-energy surges. Varistors can absorb larger energy levels, often exceeding hundreds of joules, which suits them for applications involving high-energy surges like lightning strikes or power line transients. Your choice between a TVS diode and a varistor should consider the specific surge energy and response time requirements of your circuit protection needs.
Typical Applications
TVS diodes are commonly used for protecting sensitive electronics in automotive systems, communication devices, and power supply circuits by clamping transient voltage spikes. Varistors are typically preferred in high-energy surge protection scenarios like power distribution networks, industrial equipment, and household appliances due to their ability to absorb large transient currents. Your choice depends on the required response time and energy absorption capacity for effective circuit protection.
Advantages of TVS Diodes
TVS diodes offer faster response times and precise clamping voltage protection against transient voltage spikes, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. Unlike varistors, TVS diodes provide consistent and repeatable performance over millions of transient events, enhancing device reliability. Your circuits benefit from lower leakage current and superior energy absorption capabilities, ensuring better overall surge protection.
Advantages of Varistors
Varistors provide superior energy absorption and can handle higher transient voltage spikes compared to TVS diodes, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from large surge currents. They offer nonlinear resistance characteristics that allow for effective voltage clamping and longer service life under repetitive surge conditions. Their cost-effectiveness and wide voltage rating range enhance their applicability across industrial and consumer electronics for transient voltage suppression.
Key Differences Summarized
TVS diodes provide fast response times in protecting circuits from voltage spikes, whereas varistors clamp voltage by changing resistance but respond more slowly. TVS diodes offer precise clamping voltages and consistent performance for transient suppression, while varistors are typically used for broader surge protection with variable clamping thresholds. Your choice depends on required response speed; TVS diodes excel in sensitive electronics, and varistors suit general protection in power systems.
Choosing Between TVS Diode and Varistor
Choosing between a TVS diode and a varistor depends on the specific surge protection requirements of your electronic circuit. TVS diodes offer fast response times and precise clamping voltages, making them ideal for protecting sensitive semiconductor devices from transient voltage spikes. Varistors provide a wide voltage range and high energy absorption capacity, suitable for handling large surges in power distribution systems but with slower response times compared to TVS diodes.
TVS diode vs Varistor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com