Rigid PCBs offer a solid and durable structure ideal for devices requiring stable and reliable connections, while flexible PCBs provide adaptability and can conform to complex shapes, making them perfect for compact or irregularly shaped electronics. Your choice between rigid and flexible PCBs depends on the application's mechanical and spatial requirements, balancing durability with design versatility.
Table of Comparison
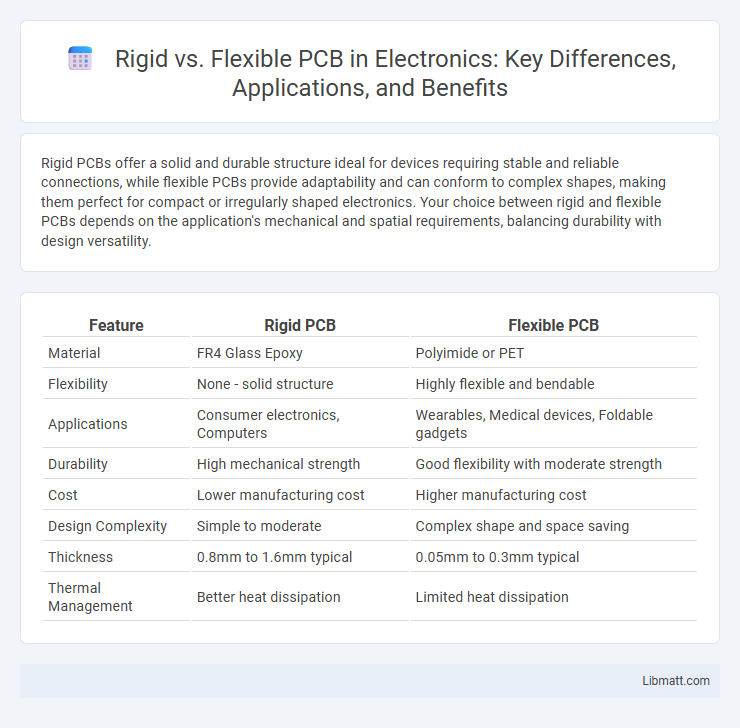
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flexible PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | FR4 Glass Epoxy | Polyimide or PET |
| Flexibility | None - solid structure | Highly flexible and bendable |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, Computers | Wearables, Medical devices, Foldable gadgets |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Good flexibility with moderate strength |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Design Complexity | Simple to moderate | Complex shape and space saving |
| Thickness | 0.8mm to 1.6mm typical | 0.05mm to 0.3mm typical |
| Thermal Management | Better heat dissipation | Limited heat dissipation |
Introduction to Rigid vs Flexible PCB
Rigid PCBs consist of solid, non-bendable substrates made from materials like FR4, providing stable mechanical support and high durability for electronic circuits. Flexible PCBs utilize thin, bendable materials such as polyimide, enabling circuits to conform to complex shapes and dynamic applications in compact devices. The choice between rigid and flexible PCBs directly influences device design, weight, space efficiency, and performance reliability in fields like aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
What is a Rigid PCB?
A rigid PCB is a printed circuit board made from solid, non-bendable materials such as fiberglass or epoxy resin, providing a stable and durable platform for electronic components. These PCBs maintain their shape and offer excellent mechanical strength, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term stability and high reliability. Commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial machinery, rigid PCBs support complex circuit designs with multiple layers and dense component placement.
What is a Flexible PCB?
A Flexible PCB is a type of printed circuit board designed with flexible plastic substrates such as polyimide, allowing it to bend, fold, and twist without damaging the circuitry. This flexibility enables compact and dynamic electronic designs, commonly used in wearable devices, medical equipment, and aerospace applications. Unlike rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs reduce space and assembly complexity by conforming to irregular shapes and supporting multi-dimensional configurations.
Key Differences Between Rigid and Flexible PCBs
Rigid PCBs consist of a solid, inflexible substrate, typically made from fiberglass or epoxy, providing durable support for electronic components, whereas flexible PCBs use a bendable polyimide substrate that allows them to conform to dynamic or irregular shapes. Rigid PCBs offer superior mechanical strength and stability for high-density circuits, while flexible PCBs excel in applications requiring reduced space, lightweight design, and resistance to vibration. The manufacturing process for rigid PCBs is generally simpler and more cost-effective, but flexible PCBs demand specialized techniques to ensure reliability during constant bending and flexing.
Advantages of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs offer superior mechanical strength and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability and resistance to physical stress. Their stable structure provides excellent electrical performance and allows for high-density component placement, enhancing circuit functionality in compact devices. Rigid PCBs also support complex multilayer designs, facilitating efficient signal routing and improved heat dissipation.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs offer significant advantages such as space-saving design, improved durability under vibration and bending, and enhanced thermal management due to their ability to conform to complex shapes. These characteristics make them ideal for compact electronic devices and applications requiring dynamic movement, ensuring longer life and reliable performance. Your projects benefit from easier assembly and reduced weight, contributing to overall system efficiency.
Common Applications for Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are widely used in consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles due to their durability and stable circuit performance. Industrial equipment and automotive systems also rely on rigid PCBs for their ability to withstand harsh environments and provide reliable electrical connections. Your projects requiring robust and long-lasting circuit boards benefit significantly from the structural integrity offered by rigid PCBs.
Common Applications for Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are widely used in wearable technology, medical devices, and aerospace applications due to their ability to bend and conform to complex shapes. These circuits enable compact, lightweight designs in smartphones, cameras, and automotive electronics where space constraints and mechanical flexibility are critical. Their adaptability allows integration into dynamic environments, improving reliability and performance in flexible connectors and foldable consumer devices.
Cost Comparison: Rigid vs Flexible PCB
Rigid PCBs generally have a lower initial manufacturing cost due to simpler materials and processes, making them ideal for high-volume production. Flexible PCBs, while more expensive per unit because of advanced materials and complex fabrication, offer cost savings in applications requiring space-saving and dynamic movement. Your choice between rigid and flexible PCBs will depend on balancing budget constraints with design requirements and performance needs.
Choosing the Right PCB for Your Project
Selecting the right PCB between rigid and flexible types depends on the specific mechanical and environmental requirements of your project. Rigid PCBs offer durability and stable circuitry ideal for devices needing strong structural support, while flexible PCBs provide versatile designs that fit compact or dynamic applications requiring bending or folding. Evaluating factors like space constraints, vibration resistance, and thermal performance ensures optimal functionality and longevity of your electronic device.
Rigid vs Flexible PCB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com