Y capacitors are designed for electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression in circuits connected between line and ground, ensuring safety by withstanding high voltage surges; X capacitors are used across the line for noise reduction and are built to handle differential mode interference. Your device's electrical safety and noise filtering depend on selecting the correct capacitor type based on its location and function in the circuit.
Table of Comparison
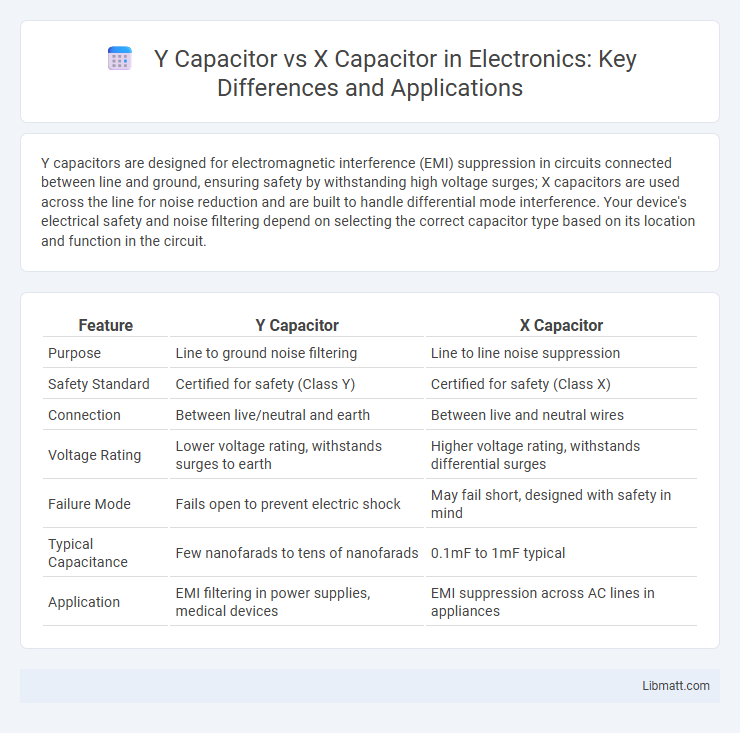
| Feature | Y Capacitor | X Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Line to ground noise filtering | Line to line noise suppression |
| Safety Standard | Certified for safety (Class Y) | Certified for safety (Class X) |
| Connection | Between live/neutral and earth | Between live and neutral wires |
| Voltage Rating | Lower voltage rating, withstands surges to earth | Higher voltage rating, withstands differential surges |
| Failure Mode | Fails open to prevent electric shock | May fail short, designed with safety in mind |
| Typical Capacitance | Few nanofarads to tens of nanofarads | 0.1mF to 1mF typical |
| Application | EMI filtering in power supplies, medical devices | EMI suppression across AC lines in appliances |
Introduction to X and Y Capacitors
X capacitors are designed to connect across the AC power line between the live and neutral wires, suppressing differential mode interference, while Y capacitors connect from live or neutral to ground, targeting common mode noise. These safety-rated capacitors play critical roles in electromagnetic interference (EMI) filtering within power supplies and electronic devices. Understanding the distinction allows you to select the appropriate capacitor to ensure optimal performance and compliance with safety standards.
What Are X Capacitors?
X capacitors, also known as line-to-line capacitors, are designed to suppress differential mode electromagnetic interference (EMI) in electrical circuits by filtering noise between the live and neutral lines. These capacitors are rated for high-voltage surges and meet strict safety standards to prevent failures that could lead to electrical hazards. Commonly used in power supplies and EMI filters, X capacitors improve the efficiency and safety of electronic devices by reducing conducted noise.
What Are Y Capacitors?
Y capacitors are safety capacitors designed to connect between the line and ground in electrical circuits, providing electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression and protecting against electrical shock. They are specifically rated for high-voltage surges and isolation, ensuring reliable performance in power supplies and household appliances. These capacitors comply with strict safety standards such as IEC and UL certifications to prevent fire hazards and maintain user safety.
Key Differences Between X and Y Capacitors
X capacitors are designed for across-the-line applications to suppress differential mode noise, while Y capacitors are used for line-to-ground interference to reduce common mode noise. X capacitors have higher voltage ratings to withstand surges on the AC input line, whereas Y capacitors prioritize safety with reinforced insulation to prevent electric shock. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate component for electromagnetic interference (EMI) filtering in power supplies.
Applications of X Capacitors
X capacitors are primarily used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression across power supply lines, designed to filter noise and transients in AC mains applications. Commonly found in devices such as power strips, household appliances, and industrial equipment, they ensure stable operation by reducing differential mode interference. Your electronic systems benefit from X capacitors by improving safety and performance in environments subject to electrical noise.
Applications of Y Capacitors
Y capacitors are primarily used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression for line-to-ground filtering in power supplies and electronic devices. They help protect users from electric shock by safely handling high-voltage surges and transient voltages in AC mains circuits. Your equipment's compliance with safety standards often depends on the proper implementation of Y capacitors in its design.
Safety Standards for X and Y Capacitors
X and Y capacitors are designed to meet specific safety standards set by international bodies such as IEC, UL, and CSA to ensure reliable performance in EMI suppression and transient voltage scenarios. X capacitors are rated for across-the-line applications and must comply with strict test voltages and self-healing properties to prevent fire hazards during high-voltage surges. Y capacitors, used for line-to-ground filtering, have even stricter insulation and leakage current requirements due to their direct connection to protective earth, minimizing the risk of electric shock and satisfying Class I and Class II safety standards.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: X vs Y
Selecting the right capacitor between X and Y types depends on the application's safety and noise suppression requirements. X capacitors are designed for across-the-line (line-to-line) interference suppression in EMI filters, optimized to handle high-energy surges without failure. Y capacitors are used for line-to-ground (line-to-earth) surge suppression, providing safety isolation to prevent electric shock by meeting stringent insulation standards and leakage current limits.
Failure Modes and Risks
Y capacitors, designed for line-to-ground applications, primarily fail due to dielectric breakdown, which can lead to electric shock hazards if not properly rated or maintained. X capacitors, used across the line, typically experience failure through short circuits, posing fire risks and potential damage to connected equipment. Understanding these failure modes helps you select the appropriate capacitor type to mitigate safety and performance risks in electrical systems.
Frequently Asked Questions on X and Y Capacitors
X capacitors are designed for across-the-line interference suppression in AC power applications, while Y capacitors provide safety isolation between line and ground to protect against electrical shock. Common questions include their voltage ratings, where X capacitors handle high transient voltages across phases and Y capacitors meet stringent safety standards like IEC 60384-14 for grounding protection. Users often inquire about their placement in circuits, with X capacitors connected across live and neutral, and Y capacitors connected between line and earth to ensure compliance with EMC and safety regulations.
Y capacitor vs X capacitor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com