Shielded cable offers superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for environments with high electrical noise, while unshielded cable is more flexible and cost-effective for general use with minimal interference. Choosing the right cable depends on your specific installation needs, balancing performance with budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
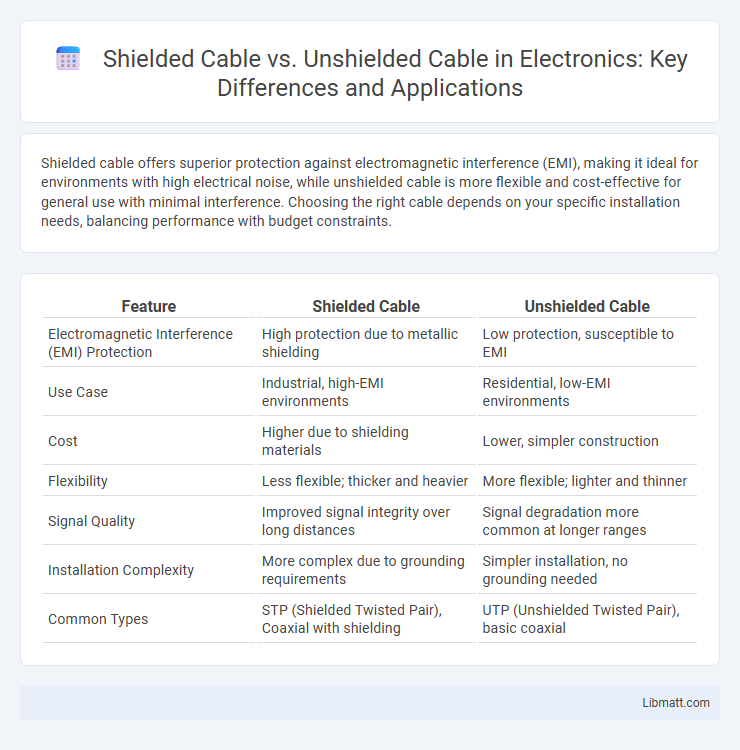
| Feature | Shielded Cable | Unshielded Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection | High protection due to metallic shielding | Low protection, susceptible to EMI |
| Use Case | Industrial, high-EMI environments | Residential, low-EMI environments |
| Cost | Higher due to shielding materials | Lower, simpler construction |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; thicker and heavier | More flexible; lighter and thinner |
| Signal Quality | Improved signal integrity over long distances | Signal degradation more common at longer ranges |
| Installation Complexity | More complex due to grounding requirements | Simpler installation, no grounding needed |
| Common Types | STP (Shielded Twisted Pair), Coaxial with shielding | UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair), basic coaxial |
Introduction to Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables contain a conductive layer that protects the internal wires from electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise. Unshielded cables lack this protective layer, offering greater flexibility and lower cost but are more susceptible to signal degradation from external interference. Choosing the right cable depends on your specific application requirements and the level of exposure to EMI.
Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables feature a protective layer of conductive material, such as foil or braided wire, which minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for environments with high levels of electrical noise. Unshielded cables lack this additional layer, resulting in greater susceptibility to EMI but offering greater flexibility and lower cost for applications with minimal interference. The choice between shielded and unshielded cables primarily depends on the specific requirements for signal integrity, environmental noise levels, and budget constraints.
Construction and Design Features
Shielded cables feature an outer conductive layer, such as braided copper or aluminum foil, which protects against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring reliable signal transmission in noisy environments. Unshielded cables rely solely on insulated conductors without additional shielding, making them lighter, more flexible, and easier to install but more susceptible to interference. Choosing between shielded and unshielded cables depends on your specific installation needs, environmental conditions, and the level of signal integrity required.
Applications in Various Industries
Shielded cables are commonly used in industries such as telecommunications, aerospace, and medical equipment manufacturing, where protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is crucial for maintaining signal integrity. Unshielded cables are preferred in residential and office environments where EMI is minimal and cost efficiency is prioritized. Industrial automation and automotive sectors utilize both types depending on environmental conditions and specific application requirements for noise reduction and durability.
Performance in Electromagnetic Environments
Shielded cables provide superior performance in electromagnetic environments by preventing interference and maintaining signal integrity, essential for sensitive data transmissions or audio applications. Unshielded cables, while more flexible and cost-effective, are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), potentially causing data loss or noise in your connections. Choosing shielded cable is crucial when working in areas with high EMI or where consistent signal quality is a priority.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Shielded cables typically cost more due to the additional materials and manufacturing processes required to reduce electromagnetic interference, making them a higher initial investment compared to unshielded cables. Budget considerations should account for potential savings in troubleshooting and signal quality over time, as shielded cables minimize data loss and external noise, which can reduce maintenance expenses. Unshielded cables offer cost advantages for installations in low-interference environments, providing a budget-friendly solution when electromagnetic interference is minimal.
Installation Requirements and Challenges
Shielded cable requires careful handling during installation to maintain the integrity of its shielding, which protects against electromagnetic interference (EMI) but can be compromised by improper grounding or physical damage. Unshielded cable offers easier installation with fewer constraints since it lacks a shielding layer, making it more flexible and less susceptible to installation errors. Your choice depends on the environment; shielded cables are necessary in high-EMI areas but demand stricter installation standards to ensure performance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Shielded cables offer superior durability and lifespan due to their protective outer metal layer, which safeguards against electromagnetic interference (EMI), physical damage, and environmental factors such as moisture and abrasion. In contrast, unshielded cables lack this protective layer, making them more susceptible to interference and wear, leading to a shorter operational lifespan in demanding environments. The enhanced durability of shielded cables makes them ideal for industrial applications and outdoor installations where long-term reliability is critical.
Selecting the Right Cable for Your Needs
Shielded cable offers superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for environments with high electrical noise or critical signal integrity requirements. Unshielded cable provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness for applications where interference is minimal, such as in residential or light commercial settings. You should evaluate factors like environmental conditions, signal sensitivity, and budget to select the right cable for your needs.
Conclusion: Making the Best Choice
Shielded cables offer superior protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for environments with high electrical noise or sensitive equipment. Unshielded cables typically provide cost-effective and flexible solutions for general-purpose networking where EMI is minimal. Choosing between shielded and unshielded cables depends on the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget considerations to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Shielded Cable vs Unshielded Cable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com