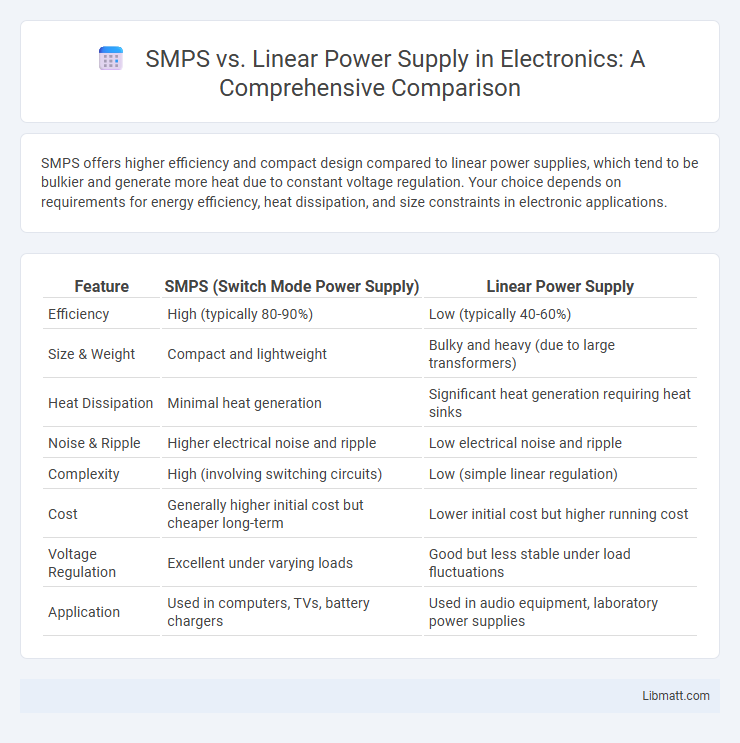
SMPS offers higher efficiency and compact design compared to linear power supplies, which tend to be bulkier and generate more heat due to constant voltage regulation. Your choice depends on requirements for energy efficiency, heat dissipation, and size constraints in electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply) | Linear Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (typically 80-90%) | Low (typically 40-60%) |
| Size & Weight | Compact and lightweight | Bulky and heavy (due to large transformers) |
| Heat Dissipation | Minimal heat generation | Significant heat generation requiring heat sinks |
| Noise & Ripple | Higher electrical noise and ripple | Low electrical noise and ripple |
| Complexity | High (involving switching circuits) | Low (simple linear regulation) |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost but cheaper long-term | Lower initial cost but higher running cost |
| Voltage Regulation | Excellent under varying loads | Good but less stable under load fluctuations |
| Application | Used in computers, TVs, battery chargers | Used in audio equipment, laboratory power supplies |
Introduction to Power Supplies
Power supplies convert electrical energy to the appropriate voltage and current required by electronic devices. SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) uses high-frequency switching and energy storage components to achieve higher efficiency and smaller size compared to traditional Linear Power Supplies, which rely on resistive elements and transformers for voltage regulation. Your choice between SMPS and Linear Power Supply impacts factors such as energy efficiency, heat dissipation, noise levels, and application suitability.
What is an SMPS?
A Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) is an electronic power supply that efficiently converts electrical power using high-frequency switching regulators. It operates by rapidly switching transistors on and off to regulate output voltage, resulting in a compact, lightweight design with improved energy efficiency compared to linear power supplies. SMPS units are widely used in computers, telecommunications, and industrial applications due to their ability to provide stable, regulated power in varying load conditions.
Understanding Linear Power Supplies
Linear power supplies regulate output voltage by dissipating excess electrical energy as heat through a series pass transistor, ensuring a stable and low-noise DC output ideal for sensitive analog circuits. Their design typically involves a transformer, rectifier, and linear regulator, resulting in simplicity and reliability but lower efficiency and larger size compared to switching power supplies. Linear power supplies excel in applications requiring minimal electrical noise and precise voltage regulation despite generating more heat and consuming more power.
Key Functional Differences
Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) converts electrical power using high-frequency switching regulators, resulting in higher efficiency and lighter weight compared to Linear Power Supply, which relies on linear voltage regulation by dissipating excess power as heat. SMPS operates with complex circuitry including inductors, capacitors, and transformers optimized for switching frequencies, whereas Linear Power Supply uses simpler transformers and linear pass elements like transistors for voltage control. The main functional difference lies in efficiency and heat dissipation: SMPS achieves 80-90% efficiency with minimal heat generation, while Linear Power Supplies typically offer 50-60% efficiency with significant heat produced during voltage regulation.
Efficiency Comparison
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) typically achieve efficiency levels between 80% to 95%, making them significantly more efficient than Linear Power Supplies, which usually operate around 40% to 60% efficiency. The high efficiency in SMPS results from their ability to regulate voltage by switching elements on and off rapidly, minimizing energy loss as heat. Linear Power Supplies dissipate excess voltage as heat through a linear regulator, causing greater energy loss and lower overall efficiency.
Size and Weight Considerations
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) offer significant advantages in size and weight, being much more compact and lighter than traditional Linear Power Supplies due to their high-frequency switching components and efficient power conversion. Linear Power Supplies rely on large transformers and heat sinks, resulting in bulkier and heavier units that are less suitable for portable or space-constrained applications. SMPS designs enable more efficient thermal management and reduced material usage, making them ideal for modern electronic devices where minimizing size and weight is critical.
Output Quality and Noise
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) deliver high efficiency with compact size but generate more electrical noise and ripple due to high-frequency switching, affecting sensitive electronic components. Linear Power Supplies provide superior output quality with extremely low noise and ripple, making them ideal for audio, laboratory, and precision instrumentation applications. The choice depends on balancing noise sensitivity requirements against efficiency and size constraints.
Application Suitability
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency, compact size, and lightweight design, such as computers, telecommunications, and portable devices. Linear power supplies suit low-noise, sensitive audio equipment, and laboratory instruments where voltage stability and minimal electromagnetic interference are critical. SMPS excels in high power, industrial environments, while linear supplies are preferred in precision and low-power scenarios.
Cost and Maintenance
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) generally offer a lower initial cost and reduced maintenance expenses compared to Linear Power Supplies due to their higher efficiency and fewer heat-related component failures. Linear Power Supplies typically incur higher operational costs because of energy loss through heat dissipation and more frequent replacement of bulky transformers and voltage regulators. The compact design and advanced electronic components in SMPS contribute to longer lifespan and lower overall maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Power Supply
Selecting the right power supply depends on your specific application requirements, where an SMPS offers higher efficiency, compact size, and better heat dissipation, making it ideal for modern, energy-sensitive electronics. In contrast, a linear power supply delivers cleaner and more stable output with minimal noise and ripple, crucial for sensitive audio or laboratory equipment. You should evaluate factors such as power efficiency, output stability, size constraints, and budget to determine the optimal choice between SMPS and linear power supplies.
SMPS vs Linear Power Supply Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com