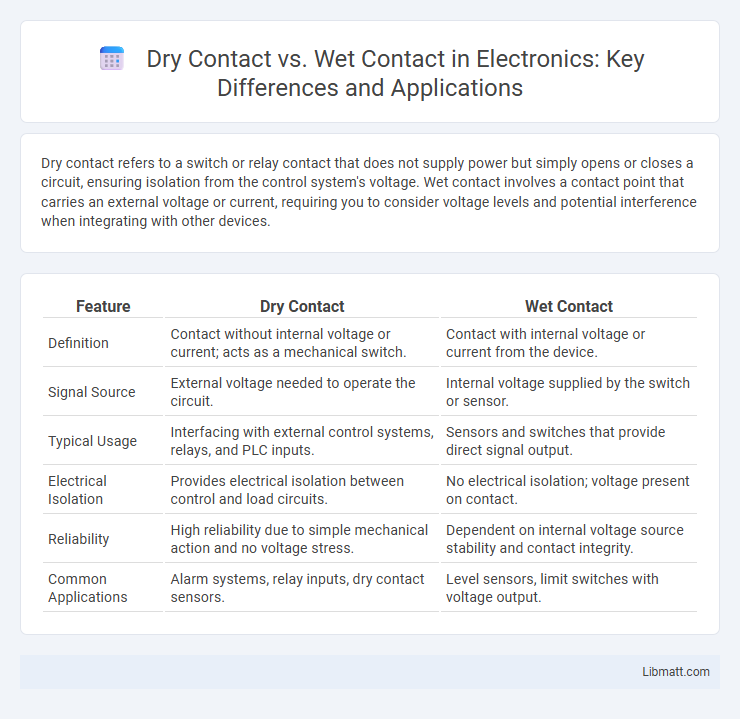
Dry contact refers to a switch or relay contact that does not supply power but simply opens or closes a circuit, ensuring isolation from the control system's voltage. Wet contact involves a contact point that carries an external voltage or current, requiring you to consider voltage levels and potential interference when integrating with other devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dry Contact | Wet Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contact without internal voltage or current; acts as a mechanical switch. | Contact with internal voltage or current from the device. |
| Signal Source | External voltage needed to operate the circuit. | Internal voltage supplied by the switch or sensor. |
| Typical Usage | Interfacing with external control systems, relays, and PLC inputs. | Sensors and switches that provide direct signal output. |
| Electrical Isolation | Provides electrical isolation between control and load circuits. | No electrical isolation; voltage present on contact. |
| Reliability | High reliability due to simple mechanical action and no voltage stress. | Dependent on internal voltage source stability and contact integrity. |
| Common Applications | Alarm systems, relay inputs, dry contact sensors. | Level sensors, limit switches with voltage output. |
Understanding Dry Contact and Wet Contact
Dry contact refers to a simple switch or relay output that does not supply voltage or current on its own, acting as a passive contact used for signaling or control in circuits. Wet contact, on the other hand, involves a relay or switch output that provides a voltage or current, requiring compatibility with your system's power specifications to ensure proper operation. Understanding the distinction between dry and wet contacts is crucial for integrating devices and preventing electrical mismatches in control applications.
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Contacts
Dry contact refers to a switch or relay contact that operates without any external voltage or current applied, acting as a simple mechanical switch, while wet contact involves contacts that carry an electrical voltage or current during operation. The key difference lies in the presence of voltage; dry contacts provide isolation from the control circuitry, ensuring no voltage is present, whereas wet contacts handle signals or power, making them integral to circuits that require active current flow. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate contact type for applications demanding either signal isolation or direct electrical control.
How Dry Contacts Work
Dry contacts function as simple, voltage-free switches that open or close a circuit without supplying any power themselves. These contacts rely on an external power source to activate connected devices, ensuring no current flows through the switch when it's inactive. Your control systems benefit from the isolation and reduced risk of electrical interference provided by dry contact operation.
How Wet Contacts Work
Wet contacts operate by using an external voltage source to energize the relay coil, resulting in the closing or opening of the contact points that carry current directly from this external circuit. Unlike dry contacts, wet contacts have voltage and current present on their output terminals, allowing them to switch higher voltages or currents within a controlled system. Your choice between dry and wet contacts depends on the voltage and current requirements of your application and the need for electrical isolation.
Common Applications for Dry Contacts
Dry contacts are widely used in industrial control systems where devices such as relays, switches, and sensors need to interface without electrical interference or voltage. Common applications include alarm systems, HVAC controls, and security access panels where isolation between circuits ensures reliable signal transmission. They are preferred in scenarios requiring low-voltage switching and protection against current leakage or interference.
Typical Uses of Wet Contacts
Wet contacts are commonly used in industrial automation and electrical control systems where the relay or switch handles higher voltages and requires a powered output to activate devices such as motors, alarms, or lighting circuits. These contacts are ideal for situations demanding electrical isolation and stable power delivery, ensuring secure and reliable operation in environments prone to electrical noise or interference. Understanding your system's voltage and current requirements helps determine when wet contacts are necessary for optimal performance and safety.
Advantages of Dry Contact Systems
Dry contact systems offer significant advantages such as enhanced reliability and reduced risk of corrosion since they operate without an external voltage. These systems provide greater safety and longevity in control circuits, making them ideal for critical industrial applications where insulation and electrical isolation are crucial. Their ability to interface seamlessly with various control devices also simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance processes.
Benefits and Limitations of Wet Contacts
Wet contacts provide the benefit of a voltage or current supplied directly to the switch contacts, ensuring reliable signal transmission and reducing noise interference in control systems. This feature enhances compatibility with a variety of devices requiring powered inputs, offering greater flexibility in industrial automation. However, the dependence on an external power source introduces potential safety risks and increases maintenance requirements, which can impact overall system reliability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Contact Types
When choosing between dry contact and wet contact, key factors include the voltage and current requirements, environmental conditions, and the nature of the connected devices. Dry contacts are ideal for low voltage, low current applications and provide isolation without electrical power, while wet contacts supply a live voltage suitable for directly powering circuits or activating devices. Consideration of signal integrity, safety standards, and compatibility with control systems ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Dry Contact vs Wet Contact: Which Is Right for You?
Dry contact switches provide an isolated, voltage-free connection ideal for low-voltage control systems, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of equipment without electrical interference. Wet contact switches include their own voltage supply, making them suitable for applications requiring direct power signaling or where signal integrity is critical. Choosing between dry and wet contacts depends on your system's voltage requirements, the nature of the control signals, and the need for electrical isolation.
Dry Contact vs Wet Contact Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com