Twisted pair cables offer flexibility and ease of installation, making them ideal for Ethernet networks and voice communication, while coaxial cables provide better shielding and higher bandwidth, suitable for cable TV and broadband internet. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right cable for your specific connectivity and performance needs.
Table of Comparison
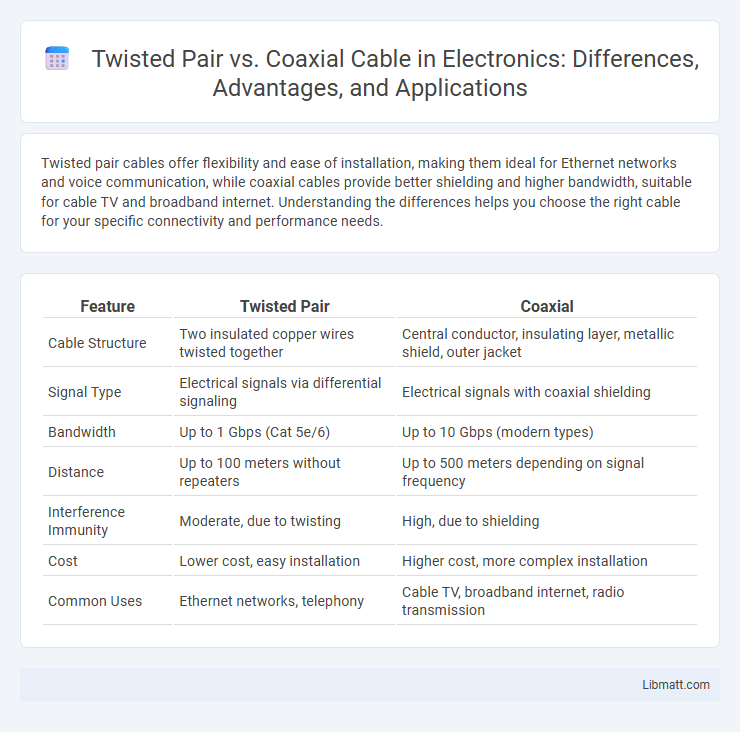
| Feature | Twisted Pair | Coaxial |
|---|---|---|
| Cable Structure | Two insulated copper wires twisted together | Central conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, outer jacket |
| Signal Type | Electrical signals via differential signaling | Electrical signals with coaxial shielding |
| Bandwidth | Up to 1 Gbps (Cat 5e/6) | Up to 10 Gbps (modern types) |
| Distance | Up to 100 meters without repeaters | Up to 500 meters depending on signal frequency |
| Interference Immunity | Moderate, due to twisting | High, due to shielding |
| Cost | Lower cost, easy installation | Higher cost, more complex installation |
| Common Uses | Ethernet networks, telephony | Cable TV, broadband internet, radio transmission |
Introduction to Twisted Pair and Coaxial Cables
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, commonly used in telephone networks and Ethernet connections. Coaxial cables feature a single central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator, a metallic shield, and an outer plastic sheath, offering higher bandwidth and signal integrity for cable television and broadband internet. Both cable types serve critical roles in data transmission, with twisted pair favored for shorter distances and coaxial preferred for higher-frequency signals and extended reach.
Structure and Composition of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, enhancing signal integrity over distances. Each pair is wrapped in a plastic polymer insulation, while outer protective jackets shield against physical damage and environmental factors. You benefit from their flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for telecommunications and local area networks compared to the thicker, more rigid coaxial cables with a central conductor and layered shielding.
Design and Characteristics of Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables feature a central copper conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator, a metallic shield, and an outer plastic jacket, which provides excellent protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). Their design allows for higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to twisted pair cables, making them ideal for cable television and broadband internet. The shielded structure maintains signal integrity by minimizing signal loss and external noise, enhancing performance in environments with high EMI.
Signal Transmission Performance: Twisted Pair vs Coaxial
Twisted pair cables typically support signal transmission with moderate bandwidth and shorter distances, often suffering from electromagnetic interference (EMI) without proper shielding. Coaxial cables offer superior signal integrity and higher bandwidth over longer distances due to their concentric shielding, which reduces signal loss and EMI significantly. These characteristics make coaxial cable preferred for applications requiring stable, high-frequency transmissions such as cable TV and broadband internet services.
Bandwidth and Data Rate Comparison
Twisted pair cables typically support bandwidths up to 600 MHz and data rates reaching 10 Gbps with advanced categories like Cat6a and Cat7, while coaxial cables can handle wider bandwidths up to several GHz and data rates exceeding 10 Gbps in modern applications. Your choice depends on network requirements, as coaxial cables often provide better shielding from interference, making them suitable for high-frequency data transmission over longer distances. Twisted pair remains cost-effective and easier to install for most LAN environments, balancing performance and budget.
Noise Immunity and Interference Resistance
Twisted pair cables offer moderate noise immunity through their twisted design, which helps cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) but are more susceptible to crosstalk and external interference compared to coaxial cables. Coaxial cables provide superior noise immunity and interference resistance due to their layered shielding and solid copper core, making them more effective for transmitting signals over longer distances without degradation. The shielding in coaxial cables reduces signal loss and guards against electromagnetic interference, ensuring better performance in environments with high EMI.
Installation and Flexibility Considerations
Twisted pair cables offer easier installation and greater flexibility due to their thin, lightweight design, making them ideal for tight spaces and complex routing in structured cabling systems. Coaxial cables, while more rigid and bulkier, provide superior shielding against electromagnetic interference but require more careful handling and specialized connectors during installation. Your choice depends on balancing the need for flexible, cost-effective deployment against performance requirements in signal integrity.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Twisted pair cables generally offer lower initial costs and wider availability compared to coaxial cables, making them a cost-effective choice for most residential and commercial networking needs. Coaxial cables tend to be more expensive due to their robust shielding and higher bandwidth capabilities, but they are less commonly stocked in retail outlets, potentially increasing procurement time. Budget-conscious projects often prefer twisted pair wiring for its balance of affordability and accessibility, while specialized applications requiring superior signal integrity may invest in coaxial despite its higher cost and lower availability.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Twisted pair cables are widely used in Ethernet networks, telephone lines, and local area networks (LANs) due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Coaxial cables are preferred for cable television distribution, broadband internet connections, and satellite signal transmission because of their higher bandwidth and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Both cable types serve critical roles in telecommunications but are chosen based on specific application requirements for distance, bandwidth, and environment.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Twisted Pair and Coaxial Cables
Choosing between twisted pair and coaxial cables depends on your network requirements and environmental conditions. Twisted pair cables offer higher flexibility and better noise resistance for short to medium distances, making them ideal for home and office setups. Coaxial cables provide superior shielding and bandwidth for long-distance transmissions, often preferred in cable TV and broadband internet applications.
Twisted Pair vs Coaxial Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com