Heat sinks dissipate heat from electronic components by increasing surface area for better thermal conduction, while fan cooling actively moves air across the heat sink or device to accelerate heat removal. Your system's overall thermal management improves when combining both methods, ensuring efficient temperature regulation and preventing overheating.
Table of Comparison
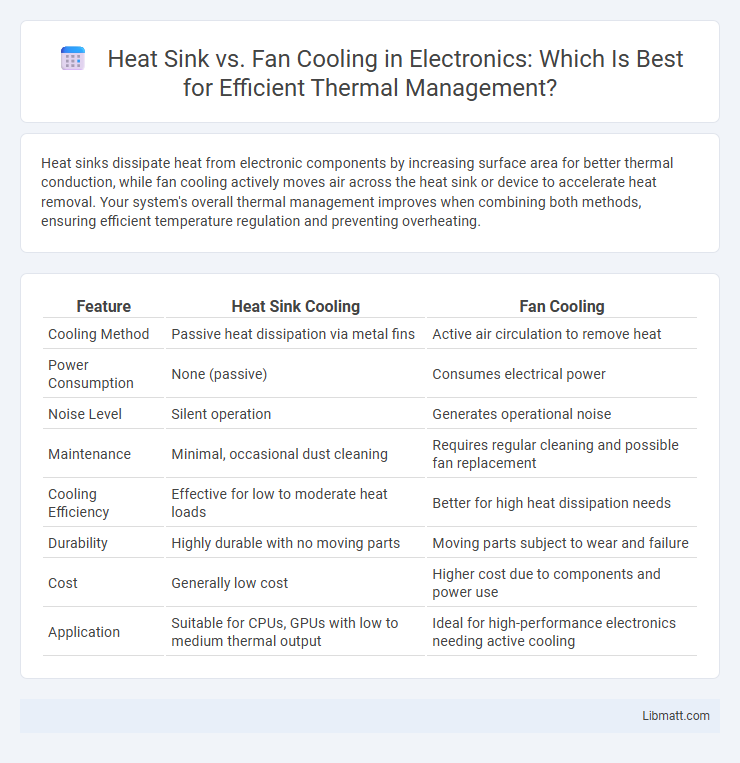
| Feature | Heat Sink Cooling | Fan Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Passive heat dissipation via metal fins | Active air circulation to remove heat |
| Power Consumption | None (passive) | Consumes electrical power |
| Noise Level | Silent operation | Generates operational noise |
| Maintenance | Minimal, occasional dust cleaning | Requires regular cleaning and possible fan replacement |
| Cooling Efficiency | Effective for low to moderate heat loads | Better for high heat dissipation needs |
| Durability | Highly durable with no moving parts | Moving parts subject to wear and failure |
| Cost | Generally low cost | Higher cost due to components and power use |
| Application | Suitable for CPUs, GPUs with low to medium thermal output | Ideal for high-performance electronics needing active cooling |
Introduction to Cooling Systems
Heat sink and fan cooling systems both play crucial roles in managing device temperatures to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Heat sinks absorb and dissipate heat from components through conduction and increased surface area, while fans actively circulate air to enhance heat dissipation and maintain airflow. Choosing the right cooling system depends on your device's heat output and space constraints for effective thermal management.
What is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is a passive cooling device designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components, such as CPUs and GPUs, by increasing surface area contact with the surrounding air. It is typically made of thermally conductive materials like aluminum or copper to efficiently transfer heat away from the component. Heat sinks are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing thermal throttling or hardware damage.
What is Fan Cooling?
Fan cooling utilizes a mechanical fan to increase airflow over electronic components, dissipating heat more efficiently than passive methods. This active cooling system improves heat transfer rates by constantly circulating air, which helps maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevents thermal throttling. Fan cooling is commonly integrated into computers, power supplies, and other devices requiring consistent temperature regulation for enhanced performance and longevity.
Heat Dissipation Mechanisms
Heat sinks dissipate heat through conduction and convection by transferring thermal energy from a hot surface to cooler air, often using aluminum or copper materials with fins to increase surface area. Fans enhance heat dissipation by actively moving air over the heat sink or components, improving convective heat transfer and reducing thermal resistance. Your choice between heat sink and fan cooling depends on the required cooling efficiency, noise tolerance, and system design constraints.
Efficiency Comparison: Heat Sink vs Fan
Heat sinks provide passive cooling by dissipating heat through a large surface area, making them energy-efficient and silent but less effective under high thermal loads. Fan cooling actively circulates air, significantly improving heat dissipation efficiency and maintaining lower temperatures for your components during intense usage. Choosing between heat sink and fan cooling depends on your system's thermal demands and noise tolerance.
Noise Levels and Operation
Heat sinks operate silently by dissipating heat through passive conduction and convection, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Fans actively cool components by forcing air over heat sinks but generate noise proportional to their speed and design, which can vary from barely audible to disruptive. Your choice between heat sink and fan cooling depends on balancing cooling efficiency needs with acceptable noise levels in your setup.
Energy Consumption Analysis
Heat sinks operate passively and consume no electrical power, making them highly energy-efficient for dissipating heat through conduction and convection. Fan cooling requires additional energy to power the fan motor, increasing overall system energy consumption but providing active airflow that enhances heat dissipation. Energy consumption analysis shows that heat sinks offer a low-power solution suitable for devices with moderate heat output, while fan cooling supports higher thermal loads at the cost of increased energy use.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Heat sink cooling systems generally involve lower upfront costs and minimal maintenance due to their passive operation and lack of moving parts. Fan cooling solutions, while often more effective at dissipating heat, incur higher expenses from both initial purchase and ongoing maintenance, including fan replacements and dust cleaning. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals heat sinks as more economical for low-power devices, whereas fan cooling suits higher-performance systems requiring active airflow management.
Best Use Cases for Each Solution
Heat sinks excel in passive cooling for low to moderate thermal loads, ideal for compact electronics and devices requiring silent operation such as laptops and small routers. Fans provide active cooling, making them suitable for high-performance systems like gaming PCs and servers where heat dissipation demands exceed passive methods. Combining heat sinks with fans maximizes cooling efficiency in environments with fluctuating or heavy thermal output.
Choosing the Right Cooling Method
Choosing the right cooling method depends on your device's power consumption and space constraints; heat sinks offer passive, silent cooling ideal for low to moderate heat dissipation, while fans provide active cooling suitable for higher thermal loads. Consider your system's airflow design and noise tolerance to balance performance and comfort effectively. Ensuring optimal cooling enhances longevity and maintains stable operation of your electronics.
Heat Sink vs Fan Cooling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com