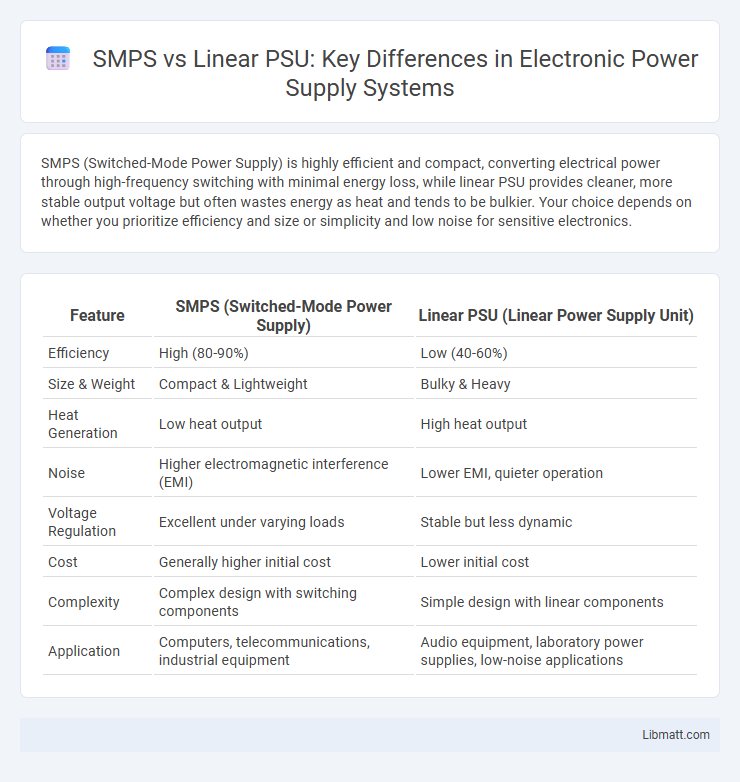
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) is highly efficient and compact, converting electrical power through high-frequency switching with minimal energy loss, while linear PSU provides cleaner, more stable output voltage but often wastes energy as heat and tends to be bulkier. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize efficiency and size or simplicity and low noise for sensitive electronics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) | Linear PSU (Linear Power Supply Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (80-90%) | Low (40-60%) |
| Size & Weight | Compact & Lightweight | Bulky & Heavy |
| Heat Generation | Low heat output | High heat output |
| Noise | Higher electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Lower EMI, quieter operation |
| Voltage Regulation | Excellent under varying loads | Stable but less dynamic |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Complexity | Complex design with switching components | Simple design with linear components |
| Application | Computers, telecommunications, industrial equipment | Audio equipment, laboratory power supplies, low-noise applications |
Introduction to Power Supply Units
Power Supply Units (PSUs) convert electrical power to the correct voltage and current for electronic devices, with SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) using high-frequency switching to provide efficiency and compact size, while Linear PSU relies on linear regulation for stable and low-noise output. SMPS offers higher efficiency and lighter weight, making it ideal for modern applications, whereas Linear PSU excels in providing consistent, ripple-free power suitable for sensitive audio or analog equipment. Understanding these differences helps you select the right PSU for your device's performance and energy requirements.
What is a Linear Power Supply?
A Linear Power Supply (Linear PSU) converts AC voltage to a lower, regulated DC voltage using a transformer, rectifier, and linear voltage regulator, ensuring stable and low-noise output. Linear PSUs typically provide excellent signal quality and minimal electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for audio equipment and sensitive electronics. However, they are less efficient and bulkier compared to Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS), resulting in higher heat dissipation and larger size.
Understanding SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply)
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) efficiently converts electrical power by rapidly switching transistors on and off, significantly reducing energy loss compared to Linear PSU. Its compact design improves thermal management and allows for a wider range of input voltages, making it ideal for diverse electronic devices. Understanding SMPS helps you choose a power supply that maximizes energy efficiency and adapts to modern power demands.
Efficiency Comparison: SMPS vs Linear PSU
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) achieve efficiencies typically between 80% and 90%, significantly outperforming Linear Power Supply Units (PSUs), which often operate at 40% to 60% efficiency due to energy lost as heat. The higher efficiency of SMPS results in less power wastage, reduced heat generation, and lower electricity costs, making them ideal for applications where energy conservation is critical. Your choice of PSU affects both operational costs and device longevity, with SMPS providing a more sustainable and cost-effective power solution.
Size and Weight Differences
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are significantly smaller and lighter than Linear Power Supply Units (PSU) due to their high-frequency operation and efficient transformer design. Your electronic devices benefit from SMPS's compact size, which enhances portability and saves space in applications ranging from laptops to industrial equipment. In contrast, Linear PSUs use bulky transformers and heavy heat sinks, making them bulky and less suitable for modern, space-constrained environments.
Noise and Ripple Performance
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) typically generates higher noise and ripple due to high-frequency switching components, affecting sensitive audio or communication equipment. Linear PSU provides exceptionally low noise and ripple performance by regulating voltage through linear components, ideal for applications requiring clean power signals. Your choice between SMPS and linear PSU should consider the acceptable noise level for your specific electronic device or circuit.
Heat Generation and Thermal Management
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) generates significantly less heat compared to Linear PSU (Power Supply Unit) due to higher efficiency and reduced energy loss during voltage conversion, typically operating at efficiencies above 80-90%. Linear PSUs convert excess voltage into heat, causing considerable thermal output that necessitates robust heat sinks and cooling systems to prevent overheating. Managing thermal conditions is easier with SMPS, allowing Your devices to run cooler and more reliably under varying loads.
Cost Analysis: SMPS vs Linear PSU
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) typically offer lower initial costs and higher energy efficiency compared to Linear Power Supply Units (PSU), leading to reduced operational expenses over time. While Linear PSUs have simpler designs with fewer components, their higher energy loss and heat dissipation result in increased electricity costs and potential cooling requirements. For applications prioritizing cost-effectiveness and energy saving, SMPS is generally the more economical option despite slightly higher complexity and design costs.
Applications and Use Cases
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are ideal for modern electronic devices requiring high efficiency and compact size, such as computers, LED drivers, and telecommunications equipment. Linear Power Supply Units (PSUs) are preferred in audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and sensitive analog circuits due to their low noise and stable output voltage. Your choice between SMPS and linear PSU depends on whether efficiency and size or noise performance and precision are prioritized in your application.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
Choosing between an SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) and a Linear PSU depends on your efficiency, size, and noise requirements. SMPS offers higher efficiency, compact size, and better heat management, making it ideal for modern electronics and devices requiring stable output with minimal energy loss. Your application's sensitivity to electrical noise and budget constraints also influence the decision, as Linear PSUs provide cleaner power but are typically larger and less energy-efficient.
SMPS vs Linear PSU Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com