Split ground separates analog and digital circuits to minimize noise interference by routing their return paths independently, while star ground connects all grounds to a single central point to prevent ground loops and maintain a common reference. Understanding the differences helps you design circuits with improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference.
Table of Comparison
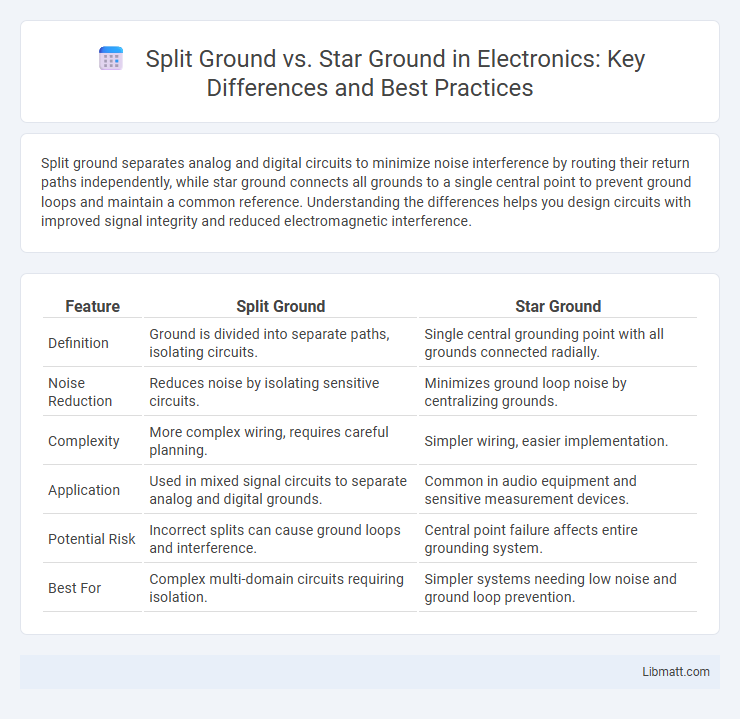
| Feature | Split Ground | Star Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ground is divided into separate paths, isolating circuits. | Single central grounding point with all grounds connected radially. |
| Noise Reduction | Reduces noise by isolating sensitive circuits. | Minimizes ground loop noise by centralizing grounds. |
| Complexity | More complex wiring, requires careful planning. | Simpler wiring, easier implementation. |
| Application | Used in mixed signal circuits to separate analog and digital grounds. | Common in audio equipment and sensitive measurement devices. |
| Potential Risk | Incorrect splits can cause ground loops and interference. | Central point failure affects entire grounding system. |
| Best For | Complex multi-domain circuits requiring isolation. | Simpler systems needing low noise and ground loop prevention. |
Introduction to Grounding in Electronic Circuits
Grounding in electronic circuits serves as a reference point for voltage levels and a return path for current, essential for circuit stability and safety. Split ground refers to separating analog and digital ground planes to minimize noise interference between sensitive analog signals and noisy digital circuits. Star ground involves connecting all ground returns at a single point, reducing ground loop interference and ensuring consistent ground potential across the system.
What is Split Ground?
Split ground refers to a grounding technique in electronics where analog and digital grounds are separated to minimize noise interference. This approach uses distinct return paths for sensitive analog signals and noisy digital signals, reducing electromagnetic interference and improving signal integrity. Split ground is commonly implemented in mixed-signal circuits to enhance overall system performance and reduce ground loop issues.
What is Star Ground?
Star ground is a grounding technique where all ground connections converge at a single central point, minimizing ground loops and interference in electronic circuits. This method improves signal integrity and reduces noise by ensuring that currents return through a common node, preventing unintended voltage differences across the ground plane. Star grounding is essential in sensitive audio, RF, and mixed-signal systems to maintain stable and clean reference voltages.
Key Differences Between Split Ground and Star Ground
Split ground separates analog and digital grounds by creating distinct return paths to reduce noise interference, often used in mixed-signal circuits to prevent digital switching noise from affecting sensitive analog signals. Star ground connects all ground returns to a single central point, minimizing ground loop currents and voltage differences by ensuring all parts share a common reference, ideal for low-frequency or RF applications. The key difference lies in noise management strategy: split grounds isolate noise sources physically, while star grounds unify grounds electrically to maintain signal integrity.
Applications of Split Grounding
Split grounding is commonly applied in audio and mixed-signal circuits to minimize noise by separating analog and digital grounds, reducing interference and improving signal integrity. Your audio equipment benefits from split grounding in studio environments to prevent ground loops and hum, ensuring clearer sound reproduction. This technique is also vital in sensitive measurement systems, where isolating grounds enhances accuracy by preventing noise coupling between different circuit sections.
Applications of Star Grounding
Star grounding is widely used in sensitive electronic systems and audio equipment to minimize ground loops and reduce electromagnetic interference. This grounding technique benefits precision measurement instruments and communication devices by providing a single reference point that improves signal integrity and noise performance. Ensuring your system uses star grounding can enhance overall reliability and audio clarity, especially in complex, multi-component setups.
Common Issues in Improper Grounding
Improper grounding in split ground and star ground systems often leads to ground loops, causing unwanted noise and interference in audio and electronic circuits. Split grounds can create voltage differences between ground points, resulting in signal degradation and hum, while star grounds minimize these issues by providing a single reference point for all returns. Failure to maintain proper grounding can also increase electromagnetic interference (EMI) susceptibility, adversely affecting system performance and reliability.
Noise Reduction: Split Ground vs Star Ground
Split ground and star ground are two common grounding techniques used to minimize electrical noise in circuits, with star ground offering superior noise reduction by connecting all ground paths to a single central point, preventing ground loops and interference. Split ground separates analog and digital grounds, reducing noise coupling between different circuit sections but can risk creating ground loops if not carefully implemented. Your choice between these methods depends on your circuit complexity and noise sensitivity, with star ground generally preferred for high-precision, low-noise applications.
Best Practices for Implementing Grounding Schemes
Split ground and star ground are essential grounding schemes in electronics, where split ground separates analog and digital grounds to reduce noise, while star ground connects all grounds at a single point to minimize ground loop interference. Best practices for implementing grounding schemes include maintaining low impedance paths, ensuring a single connection point in star grounding to avoid loops, and using ground planes to provide shielding and reduce electromagnetic interference. Properly designed grounding protects your circuits from noise and enhances overall signal integrity, crucial for high-performance electronic systems.
Choosing the Right Grounding Method for Your Project
Selecting the right grounding method between split ground and star ground depends on the specific noise sensitivity and circuit complexity of your project. Star grounding minimizes ground loops by connecting all ground points to a single reference node, ideal for audio or precision analog circuits. Split ground separates digital and analog grounds to reduce interference in mixed-signal designs but requires careful layout to prevent ground potential differences.
Split ground vs Star ground Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com