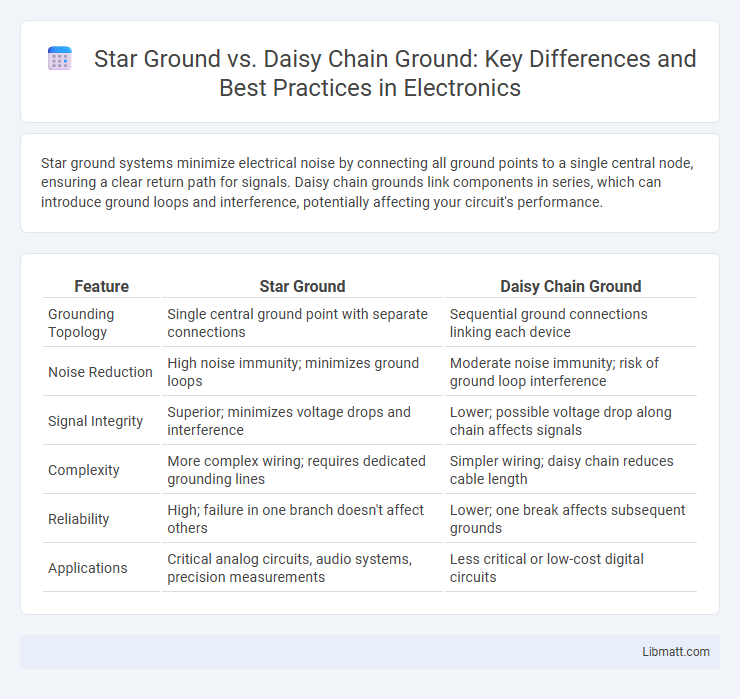
Star ground systems minimize electrical noise by connecting all ground points to a single central node, ensuring a clear return path for signals. Daisy chain grounds link components in series, which can introduce ground loops and interference, potentially affecting your circuit's performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Star Ground | Daisy Chain Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Grounding Topology | Single central ground point with separate connections | Sequential ground connections linking each device |
| Noise Reduction | High noise immunity; minimizes ground loops | Moderate noise immunity; risk of ground loop interference |
| Signal Integrity | Superior; minimizes voltage drops and interference | Lower; possible voltage drop along chain affects signals |
| Complexity | More complex wiring; requires dedicated grounding lines | Simpler wiring; daisy chain reduces cable length |
| Reliability | High; failure in one branch doesn't affect others | Lower; one break affects subsequent grounds |
| Applications | Critical analog circuits, audio systems, precision measurements | Less critical or low-cost digital circuits |
Introduction to Grounding Methods
Star Ground and Daisy Chain Ground are two common grounding methods used in electrical systems to reduce noise and interference. Star Ground systems connect all ground points to a single, central grounding node, minimizing ground loops and ensuring a low-impedance path for interference currents. Daisy Chain Ground links ground points sequentially, which can increase susceptibility to noise and voltage differences, making Star Ground preferable for sensitive electronic equipment to protect Your circuits.
Understanding Star Grounding
Star grounding involves connecting all ground points individually to a single central node, minimizing ground loops and reducing electromagnetic interference in electronic circuits. This technique ensures a low-impedance path for return currents, improving signal integrity especially in sensitive analog and digital systems. In contrast, daisy chain grounding links ground points sequentially, which can introduce voltage drops and noise, making star grounding the preferred method for precise and reliable grounding.
Understanding Daisy Chain Grounding
Daisy chain grounding involves connecting multiple devices in series to a single grounding path, which can lead to increased ground resistance and potential voltage differences between devices. This method contrasts with star grounding, where each device has an independent ground connection converging at a central point, reducing noise and interference. Understanding daisy chain grounding is essential for minimizing ground loops and ensuring signal integrity in sensitive electronic systems.
Key Differences Between Star and Daisy Chain Grounds
Star ground features a single central grounding point where all ground connections converge, minimizing ground loop interference and reducing noise in sensitive electronic circuits. Daisy chain ground involves connecting ground points sequentially along a path, which can introduce varying ground potentials and increase susceptibility to noise and interference. Star grounding is preferred in high-precision applications for improved signal integrity, while daisy chain grounding may be suitable for simpler or less noise-sensitive systems.
Advantages of Star Grounding
Star grounding minimizes ground loops and reduces electromagnetic interference by connecting all ground points to a single reference node, ensuring a stable and consistent ground potential. This configuration enhances signal integrity and noise immunity, making it ideal for sensitive analog and digital circuits. Star grounding simplifies troubleshooting and improves overall system reliability compared to daisy chain grounding, which can introduce voltage drops and noise due to shared return paths.
Disadvantages of Star Grounding
Star grounding can simplify circuit design by reducing ground loops, but it has notable disadvantages such as increased wiring complexity and potential signal interference due to high current flow at the single grounding point. The centralized nature of star grounding may cause voltage drops and noise accumulation, negatively impacting sensitive analog or digital circuits. When implementing your grounding system, consider these limitations to avoid compromised performance in precision electronic applications.
Pros and Cons of Daisy Chain Grounding
Daisy chain grounding offers simplicity in wiring by connecting multiple devices sequentially to a single ground path, making installation cost-effective for small setups. However, it poses risks such as increased ground resistance and potential ground loop interference, which can degrade signal integrity and cause noise in sensitive electronic systems. This method is less reliable than star grounding, especially in complex or critical applications where maintaining a low-resistance and stable ground reference is essential.
Impact on Signal Integrity and Noise
Star ground topology minimizes ground loops by providing a single, low-impedance reference point, significantly improving signal integrity and reducing noise coupling between circuits. Daisy chain ground connections can lead to voltage drops and ground loops, increasing noise susceptibility and degrading signal quality due to shared path impedance. For high-frequency or sensitive analog designs, star grounding ensures cleaner signals by isolating return currents and minimizing interference.
Best Practices for Implementing Grounding Solutions
Star Grounding minimizes potential differences by connecting all grounds to a single central point, reducing noise and interference in sensitive electronic systems. Daisy Chain Grounding links components sequentially, which can introduce voltage drops and ground loops, increasing the risk of signal degradation. For best practices, ensure your grounding design prioritizes a low-impedance path and minimizes loop areas, making Star Grounding preferable for precision applications where your system's signal integrity is critical.
Choosing the Right Grounding Method for Your Application
Star ground and daisy chain ground are two common grounding methods used to minimize electrical noise and ground loops in electronic circuits; star grounding connects all ground points to a single reference point, reducing interference, while daisy chain grounding links ground points sequentially, which can introduce noise in sensitive applications. Choosing the right grounding method for your application depends on the complexity of your circuit, noise sensitivity, and layout constraints, with star grounding preferred in high-precision systems and daisy chain grounding suitable for simpler, less noise-sensitive designs. Ensuring your grounding strategy matches your system's requirements can enhance signal integrity and overall performance.
Star Ground vs Daisy Chain Ground Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com