USB 3.0 offers significantly faster data transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps compared to USB 2.0's 480 Mbps, enhancing your device's performance for large file transfers. The improved power efficiency and backward compatibility of USB 3.0 ensure seamless integration with older devices while boosting charging and data transfer capabilities.
Table of Comparison
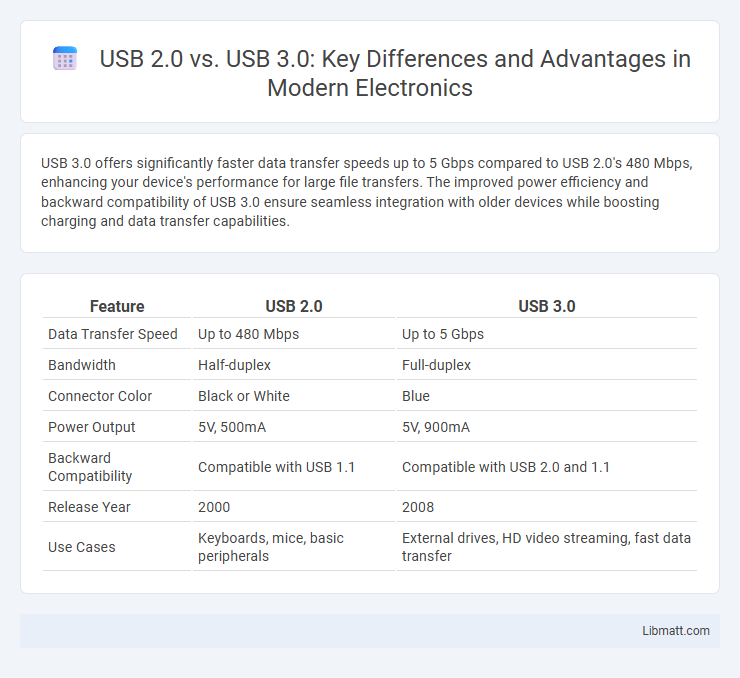
| Feature | USB 2.0 | USB 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 480 Mbps | Up to 5 Gbps |
| Bandwidth | Half-duplex | Full-duplex |
| Connector Color | Black or White | Blue |
| Power Output | 5V, 500mA | 5V, 900mA |
| Backward Compatibility | Compatible with USB 1.1 | Compatible with USB 2.0 and 1.1 |
| Release Year | 2000 | 2008 |
| Use Cases | Keyboards, mice, basic peripherals | External drives, HD video streaming, fast data transfer |
Introduction to USB Standards
USB 2.0 supports data transfer speeds up to 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 significantly increases this rate to 5 Gbps, enhancing device performance and efficiency. USB 3.0 introduces additional pins and improved power management, allowing faster charging and better connectivity for modern peripherals. Your choice between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 impacts data transfer speed and compatibility with current technology standards.
Overview of USB 2.0 Technology
USB 2.0 technology offers a data transfer rate of up to 480 Mbps, significantly improving upon its predecessor USB 1.1. It supports plug-and-play functionality and backward compatibility with USB 1.1 devices, making it widely used for peripherals such as keyboards, mice, and external storage. USB 2.0 also provides power delivery up to 500mA, enabling efficient charging and powering of connected devices.
Overview of USB 3.0 Technology
USB 3.0 technology offers transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps, significantly faster than USB 2.0's maximum of 480 Mbps, enabling quicker data transfer and enhanced performance for modern devices. It includes improved power management and increased bandwidth with dual-bus architecture, allowing simultaneous read and write operations. Your devices benefit from better efficiency and compatibility with USB 2.0 ports while achieving higher throughput with USB 3.0-enabled hardware.
Speed and Performance Comparison
USB 2.0 offers a maximum data transfer speed of 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 significantly improves performance with speeds up to 5 Gbps, making it over ten times faster. The enhanced bandwidth of USB 3.0 supports faster data transfer rates, reduced latency, and improved power management for connected devices. This speed difference greatly benefits tasks involving large file transfers, HD video streaming, and external SSD storage, providing a more efficient and responsive user experience.
Physical Differences and Compatibility
USB 2.0 connectors typically have four pins, while USB 3.0 connectors contain nine pins to support higher data transfer rates up to 5 Gbps compared to USB 2.0's 480 Mbps. The USB 3.0 ports are usually identifiable by their blue color and extra pins that enable simultaneous bi-directional data transfer, enhancing performance. USB 3.0 maintains backward compatibility with USB 2.0 devices and cables, but using a USB 2.0 port limits the data transfer speed to USB 2.0 standards.
Power Delivery and Charging Capabilities
USB 3.0 offers enhanced power delivery capabilities with a maximum current output of up to 900mA compared to USB 2.0's 500mA, enabling faster and more efficient charging of connected devices. USB 3.0 supports BC 1.2 (Battery Charging Specification), allowing higher current draw for quicker battery replenishment, while USB 2.0 provides limited charging speeds suitable for smaller peripherals. This increased power capacity in USB 3.0 supports charging larger devices such as tablets and external hard drives effectively, improving overall performance in power delivery applications.
Data Transfer Efficiency
USB 3.0 offers significantly higher data transfer efficiency compared to USB 2.0, with speeds up to 5 Gbps, which is more than ten times faster than USB 2.0's 480 Mbps. USB 3.0 achieves this by utilizing additional data lanes and improved signaling technology, reducing latency and increasing throughput. This efficiency boost enables faster file transfers, smoother streaming, and better performance for external storage devices.
Backward and Forward Compatibility
USB 3.0 offers backward compatibility, allowing it to work seamlessly with USB 2.0 devices, albeit at USB 2.0 speeds when connected to older ports. Forward compatibility is not applicable to USB 2.0 since it cannot support the enhanced data transfer rates or features of USB 3.0. You can use USB 3.0 devices on USB 2.0 systems, but to fully benefit from USB 3.0's speed and performance, a compatible USB 3.0 port is required.
Ideal Uses for USB 2.0 and USB 3.0
USB 2.0 is ideal for basic peripherals like keyboards, mice, and printers where high data transfer speeds are not critical, supporting transfer rates up to 480 Mbps. USB 3.0, offering speeds up to 5 Gbps and improved power management, is better suited for data-intensive tasks such as external hard drives, HD video streaming, and large file transfers. Choosing between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 depends on the device's bandwidth requirements and performance needs.
Choosing the Right USB Standard for Your Needs
USB 3.0 offers transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps, significantly faster than USB 2.0's 480 Mbps, making it ideal for transferring large files and high-definition media. USB 2.0 remains compatible and sufficient for basic peripherals like keyboards and mice, where speed is less critical. Choosing the right USB standard depends on your device requirements, with USB 3.0 preferred for speed-intensive tasks and USB 2.0 suitable for everyday low-bandwidth uses.
USB 2.0 vs USB 3.0 Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com