Wireless charging offers the convenience of cable-free power transfer, reducing wear on your devices and eliminating clutter. Wired charging provides faster and more efficient energy delivery, making it ideal for quick battery replenishment needs.
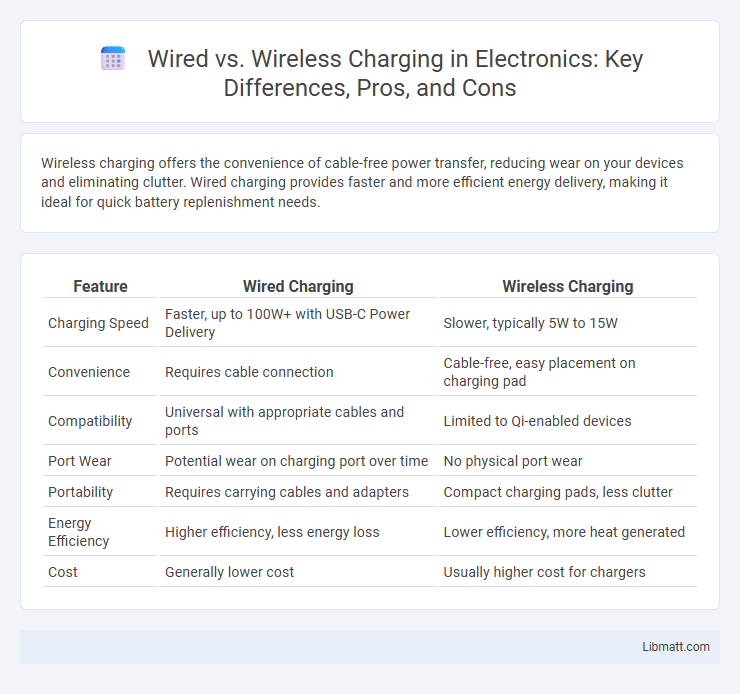
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wired Charging | Wireless Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Faster, up to 100W+ with USB-C Power Delivery | Slower, typically 5W to 15W |
| Convenience | Requires cable connection | Cable-free, easy placement on charging pad |
| Compatibility | Universal with appropriate cables and ports | Limited to Qi-enabled devices |
| Port Wear | Potential wear on charging port over time | No physical port wear |
| Portability | Requires carrying cables and adapters | Compact charging pads, less clutter |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher efficiency, less energy loss | Lower efficiency, more heat generated |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost for chargers |
Introduction to Wired and Wireless Charging
Wired charging uses a physical cable connection to transfer power directly from a power source to a device, offering faster and more efficient energy delivery. Wireless charging relies on electromagnetic induction to transmit energy between a charging pad and the device, providing convenience and reducing cable clutter. Both methods serve to recharge batteries in smartphones, tablets, and other electronic gadgets, each with distinct advantages related to speed, portability, and user experience.
How Wired Charging Works
Wired charging transfers electrical energy directly through a cable connected between the power source and the device, typically using USB or proprietary connectors. This direct connection enables faster and more efficient power delivery due to minimal energy loss and stable current flow. Devices regulate the voltage and current through built-in charging circuits to protect battery health and optimize charging speed.
How Wireless Charging Works
Wireless charging operates through electromagnetic induction, where an induction coil in the charging pad generates an alternating electromagnetic field that transfers energy to a receiver coil in the device. The receiver coil converts this energy back into electrical current to charge the battery without the need for physical connectors. This technology utilizes standards like Qi to ensure compatibility and efficient power transfer between chargers and devices.
Speed Comparison: Wired vs Wireless Charging
Wired charging typically offers faster power delivery, with speeds reaching up to 65W or more depending on the device and charger, enabling a smartphone to charge from 0 to 100% in under an hour. Wireless charging generally delivers lower wattage, often ranging between 5W and 15W for most consumer devices, resulting in longer charging times and reduced efficiency. Advanced wireless chargers using Qi technology and proprietary enhancements can improve speeds but still lag behind the rapid charging capabilities of wired connections.
Convenience and Usability
Wireless charging offers enhanced convenience by eliminating the need for cables, allowing users to simply place their devices on a charging pad for effortless power replenishment. Wired charging provides faster energy transfer rates but requires physical connection, which can be less practical for on-the-go scenarios. The usability of wireless charging is ideal for desk or bedside use, while wired charging remains essential for rapid battery top-ups and compatibility with various devices.
Safety and Heat Management
Wired charging typically offers better heat management by providing a stable and consistent power flow, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical faults. Wireless charging generates more heat due to energy loss during induction, which can impact battery lifespan and device safety if not properly regulated. Advanced wireless chargers incorporate temperature sensors and adaptive power control to enhance safety, but wired charging remains more efficient in minimizing thermal risks.
Compatibility with Devices
Wired charging offers broad compatibility with most smartphones, tablets, and laptops through universal standards like USB-C and Lightning ports, ensuring reliable power delivery across diverse devices. Wireless charging depends on the Qi standard, which is supported by many modern smartphones and accessories, but compatibility varies with device design and charging pad specifications. Some devices support fast wireless charging only with proprietary chargers, limiting universal use compared to wired solutions.
Portability and Design Considerations
Wireless charging offers superior portability by eliminating cables, allowing you to charge devices on the go without hunting for power outlets or managing tangled cords. Designed for sleek, minimalist setups, wireless chargers often feature compact pads or stands that complement modern aesthetics and reduce desk clutter. Wired charging, while less flexible in placement due to cable constraints, typically provides faster power delivery and compatibility with a wider range of devices.
Cost Analysis
Wired charging typically costs less upfront due to the simplicity of cables and connectors, with prices ranging from $10 to $30 for standard chargers. Wireless charging pads and stands generally carry higher initial costs, often priced between $30 and $100 or more, influenced by technology like Qi standards and power output. Long-term expenses may vary based on durability and energy efficiency, where wireless chargers can incur higher electricity consumption but reduce wear on device ports, potentially lowering maintenance costs.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
Future trends in charging technology emphasize the integration of ultra-fast wireless charging and advanced graphene-based batteries to significantly reduce charging times and improve energy efficiency. Innovations such as resonant inductive coupling and dynamic charging mats are expected to enable seamless power transfer for electric vehicles and mobile devices without physical connectors. Enhanced AI-driven power management systems will optimize charging cycles, extending battery lifespan and supporting the widespread adoption of smart, autonomous charging networks.
Wired vs Wireless Charging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com