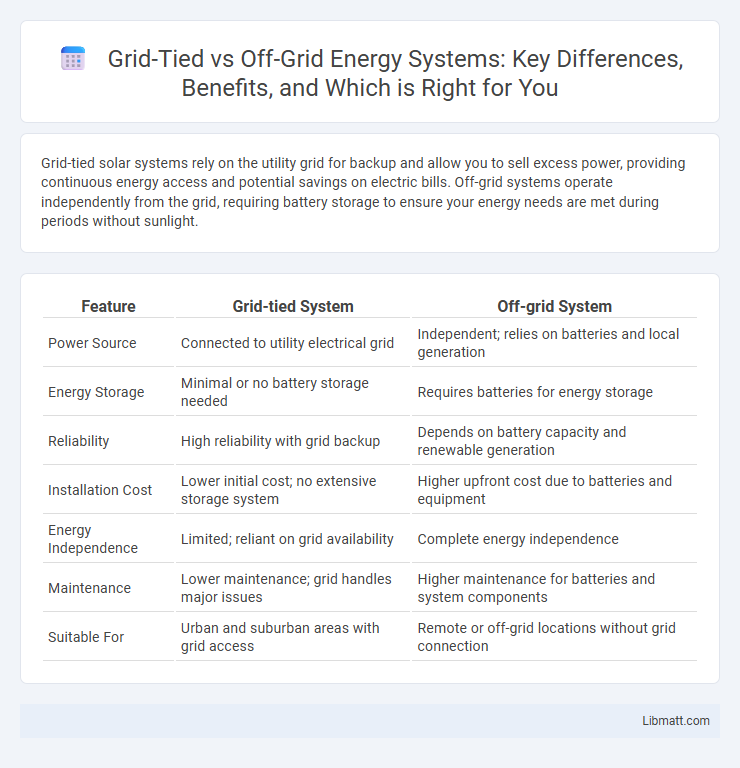
Grid-tied solar systems rely on the utility grid for backup and allow you to sell excess power, providing continuous energy access and potential savings on electric bills. Off-grid systems operate independently from the grid, requiring battery storage to ensure your energy needs are met during periods without sunlight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Grid-tied System | Off-grid System |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Connected to utility electrical grid | Independent; relies on batteries and local generation |
| Energy Storage | Minimal or no battery storage needed | Requires batteries for energy storage |
| Reliability | High reliability with grid backup | Depends on battery capacity and renewable generation |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost; no extensive storage system | Higher upfront cost due to batteries and equipment |
| Energy Independence | Limited; reliant on grid availability | Complete energy independence |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance; grid handles major issues | Higher maintenance for batteries and system components |
| Suitable For | Urban and suburban areas with grid access | Remote or off-grid locations without grid connection |
Introduction to Grid-tied and Off-grid Systems
Grid-tied systems connect solar energy setups directly to the public electricity grid, allowing users to feed excess power back to the utility and draw energy when needed. Off-grid systems operate independently, relying solely on renewable sources and battery storage to provide electricity in remote or isolated locations. Understanding the differences in energy flow, reliability, and infrastructure requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate solar power system.
How Grid-tied Solar Systems Work
Grid-tied solar systems operate by converting sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic panels, which is then used to power home appliances while any excess energy is fed back into the utility grid. These systems include an inverter to change direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) compatible with the grid. When solar production is insufficient, power is automatically drawn from the utility grid, ensuring a seamless energy supply without the need for battery storage.
How Off-grid Solar Systems Work
Off-grid solar systems operate independently from the traditional utility grid by storing energy in batteries, allowing you to generate and use electricity without relying on external power sources. These systems use solar panels to convert sunlight into direct current (DC), which is then stored in battery banks for later use during periods of low sunlight or nighttime. An inverter converts the stored DC power into alternating current (AC) to power your home appliances, ensuring energy self-sufficiency even in remote locations.
Key Differences Between Grid-tied and Off-grid Solutions
Grid-tied solar systems connect directly to the public electricity grid, allowing you to feed excess energy back and draw power when needed, ensuring reliable energy supply and potential cost savings through net metering. Off-grid solutions operate independently, relying solely on batteries and renewable sources, making them ideal for remote locations without access to utility services but requiring careful energy management. Key differences include dependence on grid infrastructure, energy storage needs, and system costs, which influence your choice based on location, budget, and energy goals.
Advantages of Grid-tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied solar systems offer significant advantages such as the ability to feed excess energy back into the utility grid, resulting in potential credits or reduced electricity bills through net metering. These systems provide reliable power by supplementing your solar energy with grid electricity during low sunlight periods, ensuring consistent energy availability without the need for costly battery storage. Maintenance and installation are generally simpler and more cost-effective compared to off-grid systems, making grid-tied solutions ideal for homeowners looking to maximize energy savings while remaining connected to the utility grid.
Benefits of Off-grid Solar Installations
Off-grid solar installations provide energy independence by allowing you to generate and store your own electricity without relying on utility companies or grid access. These systems enhance resilience during power outages and reduce long-term energy costs through sustainable solar power generation. Off-grid solar solutions are ideal for remote locations where grid connection is unavailable or prohibitively expensive.
Cost Comparison: Grid-tied vs Off-grid
Grid-tied solar systems generally have lower initial installation costs due to the absence of expensive battery storage, making them more affordable upfront. Off-grid systems require significant investment in batteries and backup power solutions to ensure energy independence, resulting in higher initial and maintenance costs. Over time, off-grid setups can be more cost-effective in remote areas without access to utility grids, but grid-tied systems benefit from feed-in tariffs and net metering, reducing overall electricity expenses.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Grid-tied solar systems typically require less maintenance since they rely on the utility grid for backup power and system monitoring, enhancing overall reliability. Off-grid systems demand more frequent maintenance of batteries and inverters to ensure consistent energy storage and supply, with a higher risk of power outages during adverse weather or equipment failure. Reliability in grid-tied setups benefits from continuous energy availability, while off-grid systems depend heavily on well-maintained components and accurate energy management.
Ideal Use Cases and Applications
Grid-tied systems are ideal for residential and commercial properties located in urban or suburban areas with reliable utility access, enabling users to reduce electricity bills through net metering and maintain consistent power supply. Off-grid systems suit remote locations, cabins, or emergency backup scenarios where grid connection is unavailable or unreliable, relying on solar panels, batteries, and generators for complete energy independence. Hybrid applications combine both to optimize energy security and cost savings in areas with intermittent grid connectivity.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between grid-tied and off-grid solar systems depends on factors like location, energy independence goals, and budget. Grid-tied systems offer cost savings through net metering and are ideal for areas with reliable utility connections. Off-grid systems provide complete self-sufficiency, requiring adequate battery storage and higher initial investment for remote or rural applications.
Grid-tied vs Off-grid Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com