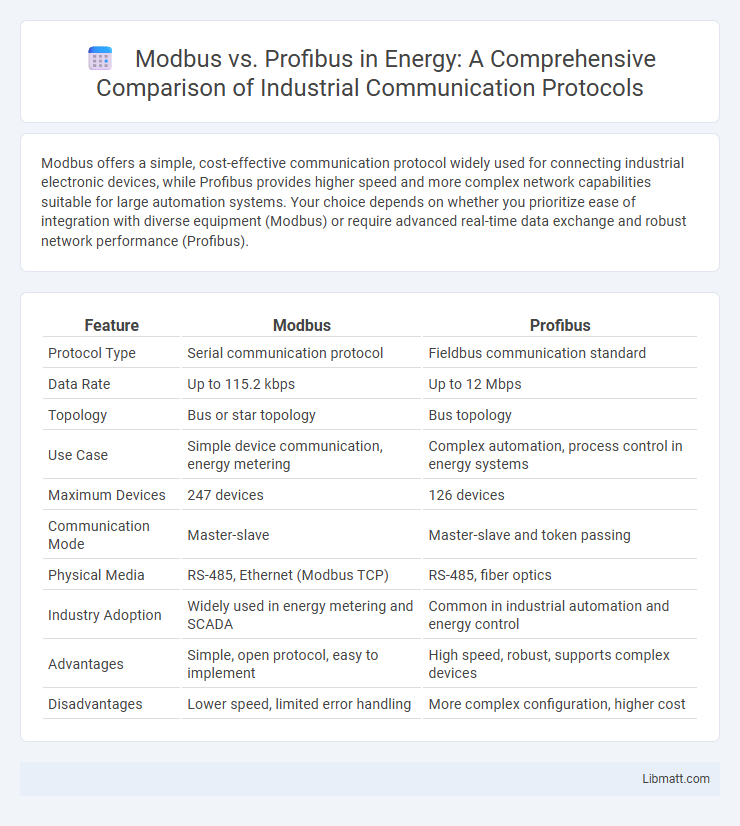
Modbus offers a simple, cost-effective communication protocol widely used for connecting industrial electronic devices, while Profibus provides higher speed and more complex network capabilities suitable for large automation systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of integration with diverse equipment (Modbus) or require advanced real-time data exchange and robust network performance (Profibus).
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modbus | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Serial communication protocol | Fieldbus communication standard |
| Data Rate | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 12 Mbps |
| Topology | Bus or star topology | Bus topology |
| Use Case | Simple device communication, energy metering | Complex automation, process control in energy systems |
| Maximum Devices | 247 devices | 126 devices |
| Communication Mode | Master-slave | Master-slave and token passing |
| Physical Media | RS-485, Ethernet (Modbus TCP) | RS-485, fiber optics |
| Industry Adoption | Widely used in energy metering and SCADA | Common in industrial automation and energy control |
| Advantages | Simple, open protocol, easy to implement | High speed, robust, supports complex devices |
| Disadvantages | Lower speed, limited error handling | More complex configuration, higher cost |
Introduction to Modbus and Profibus
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation, designed for serial networks and enabling master-slave communication between devices like sensors and controllers. Profibus, developed by Siemens, is a robust fieldbus protocol supporting high-speed data exchange and distributed control systems in complex automation environments. Both protocols facilitate interoperability but differ in architecture, data transmission speed, and application scope within industrial networks.
Historical Background and Development
Modbus, developed by Modicon in 1979, was one of the earliest protocols designed for simple communication between industrial electronic devices, especially programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Profibus originated in the late 1980s through a Siemens-led consortium to provide a more complex and versatile fieldbus standard, supporting higher data rates and real-time communication. While Modbus emphasizes wide adoption in legacy systems with straightforward serial communication, Profibus evolved to meet the demands of automation networks requiring structured and high-speed data exchange.
Core Technologies Explained
Modbus uses a master-slave communication protocol based on serial communication standards such as RS-232, RS-485, and TCP/IP, enabling simple, low-cost, and reliable data exchange primarily in industrial automation. Profibus employs a token-passing mechanism within a deterministic fieldbus system, supporting real-time data communication through cyclic and acyclic data transfer over RS-485 or fiber optics. Core technologies in Modbus focus on ease of implementation and flexibility, while Profibus excels in complex automation environments requiring high-speed, synchronized data transmission and enhanced diagnostics.
Communication Protocol Comparison
Modbus and Profibus are widely used industrial communication protocols that serve different automation needs. Modbus is a simpler, open protocol ideal for basic serial communication with a master/slave architecture, while Profibus offers higher speed, more complex network structures, and enhanced diagnostics, supporting both master-slave and peer-to-peer interactions. Your choice between Modbus and Profibus should consider factors like network size, communication speed, and device compatibility to ensure optimal performance in industrial automation.
Network Topologies and Architecture
Modbus primarily supports simple, linear bus topologies using RS-485 or TCP/IP networks, making it ideal for straightforward master-slave communication in industrial automation. Profibus offers more complex network architectures, including tree and star topologies, supporting both cyclic and acyclic data exchange through DP (Decentralized Peripherals) and PA (Process Automation) variants for enhanced flexibility and scalability. Understanding these differences in network topologies and architecture can help you select the best protocol to optimize your industrial communication systems.
Data Transmission Speed and Efficiency
Modbus typically operates at lower data transmission speeds, usually up to 115.2 kbps, making it suitable for simpler, slower industrial applications. In contrast, Profibus supports much higher speeds, reaching up to 12 Mbps, which enables more efficient data transfer for complex automation processes. The higher transmission rate of Profibus results in faster communication cycles and improved overall system performance in demanding industrial environments.
Scalability and Integration Capabilities
Modbus offers high scalability with simple integration into legacy systems due to its open protocol and wide adoption in industrial automation. Profibus provides robust integration capabilities with complex devices and systems, supporting both cyclic and acyclic communication tailored for large-scale industrial networks. Scalability in Profibus excels in multi-device environments, while Modbus remains versatile for flexible network expansions and basic interoperability.
Reliability and Error Handling
Modbus offers straightforward error detection through parity checks and cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), ensuring reliable communication in less complex industrial environments. Profibus provides advanced error handling mechanisms, including automatic retransmission and comprehensive diagnostic features, making it highly reliable for real-time control applications. Your choice between Modbus and Profibus should consider the level of reliability and error management required by your specific industrial automation system.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Modbus excels in simple, cost-effective industrial applications such as HVAC systems, remote monitoring, and PLC communication due to its ease of implementation and wide device support. Profibus is preferred in complex automation environments like manufacturing plants, robotics, and process control, offering high-speed, deterministic data transfer and extensive diagnostics. Your choice depends on the required network complexity, data speed, and compatibility with existing industrial equipment.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Needs
Choosing the right communication protocol between Modbus and Profibus depends on the specific requirements of your industrial automation system. Modbus offers simplicity, ease of implementation, and wide compatibility, making it ideal for basic data exchange and small to medium-sized networks. Profibus provides higher speed, advanced diagnostics, and robust performance suited for complex, large-scale applications requiring real-time data and integration with various devices.
Modbus vs Profibus Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com