Wind turbines generate clean, renewable energy by converting wind into electricity, reducing your carbon footprint and operating costs over time. Gas turbines rely on fossil fuels, producing higher emissions and fuel expenses but offering consistent power output and reliability.
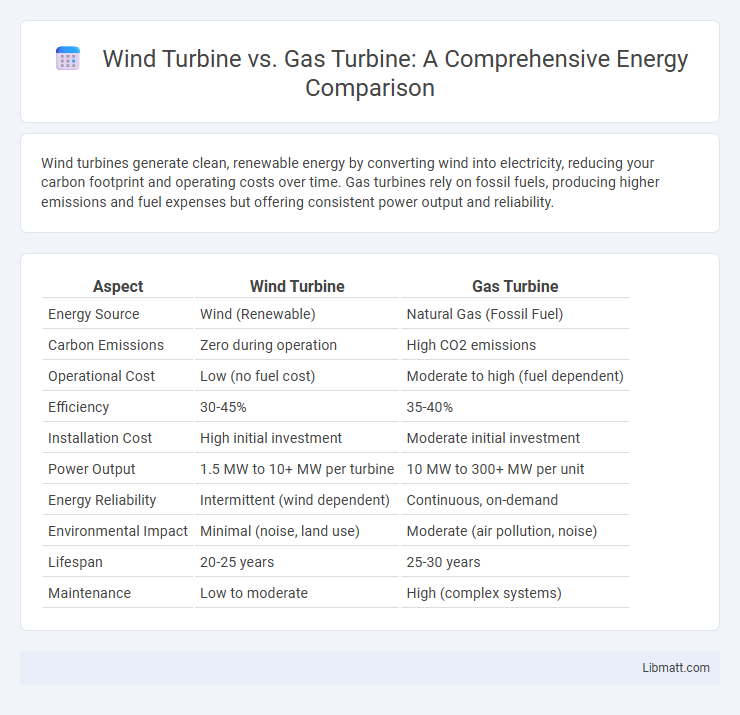
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wind Turbine | Gas Turbine |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Wind (Renewable) | Natural Gas (Fossil Fuel) |
| Carbon Emissions | Zero during operation | High CO2 emissions |
| Operational Cost | Low (no fuel cost) | Moderate to high (fuel dependent) |
| Efficiency | 30-45% | 35-40% |
| Installation Cost | High initial investment | Moderate initial investment |
| Power Output | 1.5 MW to 10+ MW per turbine | 10 MW to 300+ MW per unit |
| Energy Reliability | Intermittent (wind dependent) | Continuous, on-demand |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal (noise, land use) | Moderate (air pollution, noise) |
| Lifespan | 20-25 years | 25-30 years |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | High (complex systems) |
Introduction to Wind Turbines and Gas Turbines
Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into mechanical power, generating clean, renewable electricity with low environmental impact. Gas turbines operate by burning natural gas or other fuels to produce high-temperature combustion gases that spin the turbine blades, driving mechanical energy for electricity generation. Your decision between wind turbines and gas turbines depends on factors like fuel availability, environmental goals, and energy demand reliability.
Key Differences Between Wind and Gas Turbines
Wind turbines generate electricity using kinetic energy from wind, featuring large blades that rotate around a horizontal axis to convert wind flow into mechanical energy. Gas turbines operate by burning natural gas or other fuels to produce high-temperature, high-pressure gas that spins turbine blades connected to an electrical generator. Key differences include fuel dependency, with wind turbines harnessing renewable wind energy and gas turbines relying on fossil fuels, and operational reliability, as gas turbines provide continuous power regardless of weather conditions, unlike the intermittent nature of wind energy.
Energy Output and Efficiency Comparison
Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into electricity with efficiency rates typically between 35% and 45%, producing variable output depending on wind conditions, while gas turbines achieve higher efficiency levels around 40% to 60% by combusting natural gas for consistent power generation. Wind turbine energy output fluctuates and is best suited for renewable, clean energy demands, whereas gas turbines provide reliable, high-capacity energy ideal for base-load or peak power supply. Your choice depends on balancing the need for sustainable energy with the reliability and scale of power production required.
Environmental Impact: Clean vs Conventional Power
Wind turbines generate electricity using renewable wind energy, producing zero emissions and significantly reducing your carbon footprint compared to gas turbines, which burn fossil fuels and emit greenhouse gases like CO2 and nitrogen oxides. Wind energy contributes to cleaner air and mitigates climate change, while gas turbines, though efficient for peak power needs, release pollutants that affect air quality and contribute to global warming. Choosing wind turbines supports sustainable energy goals by harnessing natural resources without depleting fuel reserves or generating harmful waste.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Wind turbine installation involves higher upfront costs due to site assessment, foundation construction, and grid connection, but operational expenses remain low as wind is free and maintenance costs are minimal. Gas turbines have lower initial installation costs, mainly from modular equipment setup and fuel infrastructure, yet ongoing operational costs are significantly higher due to continuous fuel consumption and more frequent maintenance. Your choice between wind and gas turbines should consider long-term cost efficiency, with wind turbines offering more savings over time through reduced fuel and operational expenditures.
Reliability and Maintenance Requirements
Wind turbines exhibit higher reliability due to fewer moving parts and less mechanical complexity compared to gas turbines, which require regular inspections and overhauls of combustion chambers, turbines, and compressors. Maintenance for wind turbines primarily involves blade inspections, gearbox lubrication, and generator servicing, typically resulting in lower operational downtime. Gas turbines demand more frequent and intensive maintenance schedules to ensure safe operation under high temperatures and pressures, increasing operational costs and complexity.
Scalability and Site Requirements
Wind turbines require larger, open spaces with consistent wind patterns for optimal scalability, often favoring rural or coastal areas, while gas turbines can be deployed in more compact, urban settings due to their smaller footprint. Scalability of wind turbines depends on available land and wind resources, whereas gas turbines scale efficiently with modular units that can quickly adjust to demand fluctuations. Site requirements for wind turbines include low environmental impact and minimal obstructions, contrasting with the infrastructure needs of gas turbines, such as fuel supply lines and emission controls.
Applications and Use Cases
Wind turbines excel in renewable energy generation, powering residential, commercial, and large-scale wind farms with sustainable electricity while reducing carbon emissions. Gas turbines are widely used in power plants and aviation for their high efficiency and reliability in producing electricity and propelling aircraft engines. Your choice depends on project goals, with wind turbines ideal for green energy initiatives and gas turbines suited for consistent power supply and transportation needs.
Future Trends in Turbine Technology
Wind turbines are evolving with advancements in larger blade designs and enhanced materials, leading to higher efficiency and energy output in offshore and onshore applications. Gas turbine technology is shifting towards hybrid systems and increased integration with renewable energy sources, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and improve fuel flexibility. Innovations such as digital twin technology and advanced combustion techniques are driving the future of both turbine types towards greater sustainability and operational optimization.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Turbine
Selecting the appropriate turbine depends on energy goals, environmental impact, and operational costs. Wind turbines offer renewable, clean energy with low emissions and decreasing costs, ideal for sustainable power generation. Gas turbines provide reliable, high-efficiency output with quick startup times, suited for meeting peak electricity demand and backup power.
Wind Turbine vs Gas Turbine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com