Power Island focuses on integrating the main power-generating components such as turbines, generators, and transformers in a compact, efficient unit, while Balance of Plant includes all supporting systems like cooling, controls, and electrical distribution necessary for overall plant operation. Optimizing Your energy project requires understanding these distinctions to ensure seamless coordination between core generation assets and auxiliary infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
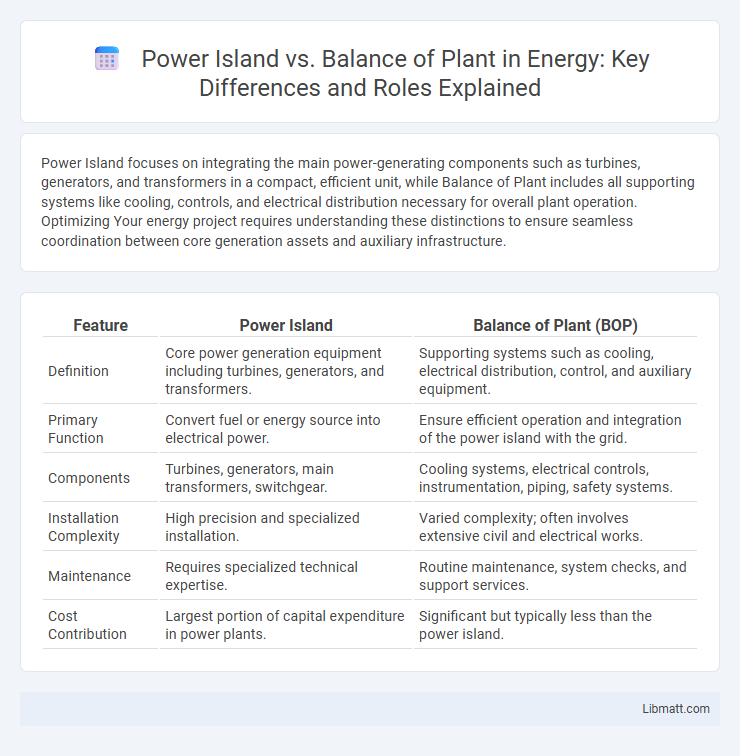
| Feature | Power Island | Balance of Plant (BOP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core power generation equipment including turbines, generators, and transformers. | Supporting systems such as cooling, electrical distribution, control, and auxiliary equipment. |
| Primary Function | Convert fuel or energy source into electrical power. | Ensure efficient operation and integration of the power island with the grid. |
| Components | Turbines, generators, main transformers, switchgear. | Cooling systems, electrical controls, instrumentation, piping, safety systems. |
| Installation Complexity | High precision and specialized installation. | Varied complexity; often involves extensive civil and electrical works. |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized technical expertise. | Routine maintenance, system checks, and support services. |
| Cost Contribution | Largest portion of capital expenditure in power plants. | Significant but typically less than the power island. |
Introduction to Power Island and Balance of Plant
Power Island refers to the core components of a power generation facility, including the generator, turbine, and associated controls that convert energy into electricity. Balance of Plant encompasses all auxiliary systems and supporting infrastructure such as cooling, fuel handling, electrical interconnections, and safety systems that ensure the reliable operation of the power plant. Understanding the distinction between Power Island and Balance of Plant is crucial for optimizing the design, maintenance, and performance of your energy facility.
Defining Power Island: Core Components and Functions
Power Island refers to the core components of a power generation system, including the prime mover, generator, and essential control systems responsible for converting fuel into electrical energy. Balance of Plant (BOP) encompasses all supporting infrastructure such as transformers, switchgear, cooling systems, and auxiliary equipment that ensure efficient operation and integration of the Power Island within the overall facility. Understanding the distinction helps you optimize design and maintenance strategies for reliable and efficient power plant performance.
Understanding Balance of Plant: Scope and Elements
Balance of Plant (BoP) encompasses all supporting components and auxiliary systems essential for the operation of a power generation facility, excluding the Power Island which houses the main generation equipment like turbines or engines. Key elements of BoP include electrical switchgear, transformers, fuel handling and storage, cooling systems, control and instrumentation, and civil works such as foundations and access roads. Understanding the scope of Balance of Plant is crucial for ensuring seamless integration, operational reliability, and compliance with safety and environmental standards in energy projects.
Key Differences Between Power Island and Balance of Plant
Power Island refers to the core components of a power generation system, including the main power generation unit such as turbines, generators, and control systems. Balance of Plant (BoP) encompasses all auxiliary components and infrastructure supporting the Power Island, such as transformers, cooling systems, fuel handling, and electrical connections. The key difference lies in their functions: Power Island focuses on energy conversion, while Balance of Plant ensures operational support and integration within the overall power facility.
Importance of Power Island in Power Generation Systems
Power Island plays a critical role in power generation systems by housing essential components such as turbines, generators, and transformers that directly convert fuel energy into electrical power. Its efficient design and operation are vital for maximizing energy output, reducing losses, and ensuring stable power generation. Compared to Balance of Plant, which supports auxiliary functions like cooling and fuel supply, the Power Island significantly influences overall plant performance and reliability.
The Role of Balance of Plant in Facility Operations
The Balance of Plant (BoP) encompasses all supporting components and auxiliary systems essential for the operation of a power generation facility, excluding the main Power Island. It includes equipment such as transformers, cooling towers, water treatment systems, and electrical switchgear that facilitate efficient energy transfer and ensure operational reliability. Effective BoP management is crucial for minimizing downtime, optimizing facility performance, and maintaining safety standards across power plants.
Integration of Power Island and Balance of Plant
Power Island and Balance of Plant (BoP) are crucial components of power generation systems, where Power Island includes core generating equipment like turbines and generators, while BoP encompasses auxiliary systems necessary for operation, such as cooling, fuel supply, and electrical connections. Effective integration between Power Island and BoP enhances overall system efficiency, reliability, and safety by ensuring seamless coordination and communication among subsystems. Your energy project benefits significantly from optimized integration, reducing downtime and operational costs through streamlined processes and robust control systems.
Cost Implications: Power Island vs Balance of Plant
Power Island components typically involve higher upfront costs due to advanced generation technologies like turbines and generators, whereas Balance of Plant expenses encompass extensive civil works, electrical infrastructure, and auxiliary systems critical for overall project integration. Investment in Power Island drives core energy production efficiency, while Balance of Plant costs influence operational reliability and maintenance expenditures over the plant's lifecycle. Project budgeting must balance these cost implications to optimize capital allocation, ensuring efficient performance and long-term economic viability.
Challenges in Managing Power Island and Balance of Plant
Managing Power Island involves challenges such as integrating high-voltage electrical components and ensuring reliable grid connection, while Balance of Plant requires addressing complex auxiliary systems like cooling, water treatment, and structural support. Coordinating these systems demands precise control strategies and robust maintenance protocols to prevent downtime and optimize efficiency. Your success depends on balancing these technical intricacies to achieve seamless overall plant performance.
Future Trends in Power Island and Balance of Plant Technologies
Future trends in Power Island focus on integrating advanced modular designs and digital twins to enhance efficiency and scalability in power generation. Balance of Plant technologies are evolving through smart sensors and predictive maintenance systems to reduce downtime and optimize resource management. Your energy infrastructure will benefit from these innovations by achieving higher reliability and lower operational costs.
Power Island vs Balance of Plant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com