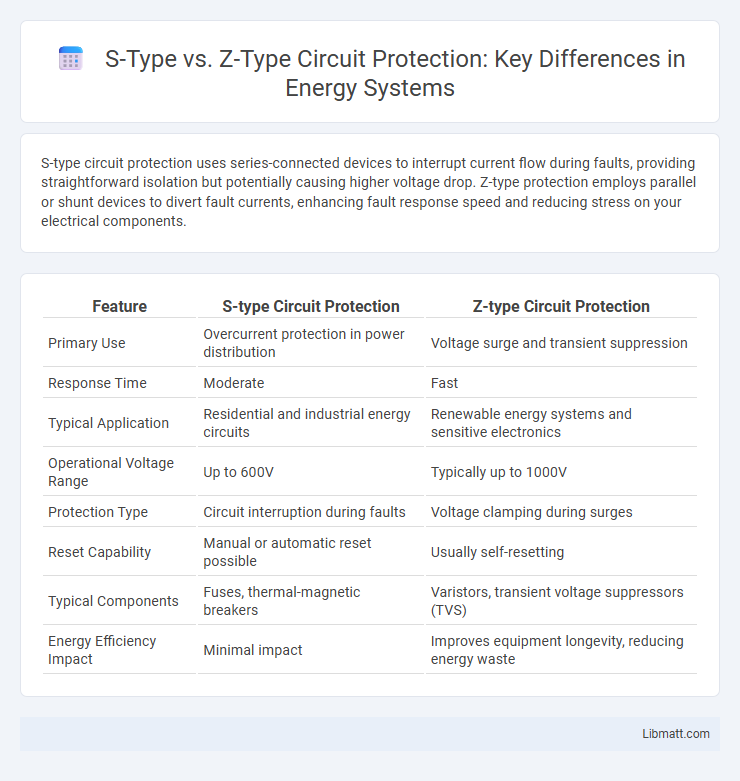
S-type circuit protection uses series-connected devices to interrupt current flow during faults, providing straightforward isolation but potentially causing higher voltage drop. Z-type protection employs parallel or shunt devices to divert fault currents, enhancing fault response speed and reducing stress on your electrical components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | S-type Circuit Protection | Z-type Circuit Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Overcurrent protection in power distribution | Voltage surge and transient suppression |
| Response Time | Moderate | Fast |
| Typical Application | Residential and industrial energy circuits | Renewable energy systems and sensitive electronics |
| Operational Voltage Range | Up to 600V | Typically up to 1000V |
| Protection Type | Circuit interruption during faults | Voltage clamping during surges |
| Reset Capability | Manual or automatic reset possible | Usually self-resetting |
| Typical Components | Fuses, thermal-magnetic breakers | Varistors, transient voltage suppressors (TVS) |
| Energy Efficiency Impact | Minimal impact | Improves equipment longevity, reducing energy waste |
Introduction to S-type and Z-type Circuit Protection
S-type and Z-type circuit protection devices are designed to safeguard electrical systems from overcurrent and short circuits, each offering distinct characteristics for specific applications. S-type protectors typically provide rapid response to sudden surges, ideal for sensitive equipment, while Z-type protectors handle prolonged fault conditions with enhanced thermal stability. Understanding the differences between these types helps you select appropriate protection that maximizes safety and reliability in your electrical installations.
Key Differences Between S-type and Z-type Devices
S-type circuit protection devices are designed to provide short-circuit protection with fast response times, whereas Z-type devices focus on providing overvoltage protection with high surge current capacity. S-type devices typically have lower voltage ratings and interrupt current rapidly to prevent equipment damage, while Z-type devices can absorb large transient energy spikes without failing. The choice between S-type and Z-type relies on the specific application requirements, such as the need for interrupting short circuits versus suppressing voltage surges in power distribution systems.
Circuit Protection Principles: S-type Explained
S-type circuit protection relies on a rapid response to overloads by interrupting current flow through a bimetallic strip that bends when heated, preventing damage to electrical components. This thermal mechanism resets automatically once cooled, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent protection without manual replacement. Your system benefits from S-type devices when continuous protection and automatic recovery are essential for operational safety.
Circuit Protection Principles: Z-type Explained
Z-type circuit protection devices operate by quickly interrupting current flow when transient voltages exceed a specific threshold, primarily using a voltage-triggered mechanism to safeguard sensitive electronics. Unlike S-type protectors that focus on current-based responses, Z-type devices rely on the intrinsic properties of components like Zener diodes or voltage-dependent resistors to clamp voltage spikes effectively. This principle ensures rapid dissipation of excess energy, preventing damage from surges and maintaining circuit integrity under fluctuating voltage conditions.
Advantages of S-type Circuit Protection
S-type circuit protection offers superior reliability by providing swift and accurate fault detection, minimizing damage to sensitive electronic components. Its modular design simplifies installation and maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Enhanced thermal stability and precise current interruption characteristics make S-type devices ideal for applications requiring high-performance overcurrent protection.
Advantages of Z-type Circuit Protection
Z-type circuit protection offers superior surge current handling and faster response times compared to S-type, making it ideal for environments with frequent transient voltage spikes. Its advanced design minimizes residual voltage, enhancing the safety and longevity of sensitive electronic devices. This type of protection reduces downtime and maintenance costs by effectively managing high-energy surges in industrial and commercial applications.
Applications: When to Use S-type vs Z-type
S-type circuit protection is ideal for applications requiring fast response to transient surges, such as semiconductor devices and sensitive electronics, due to its superior voltage clamping capabilities. Z-type circuit protection is better suited for situations where slower response time is acceptable, like power distribution networks or general-purpose equipment, as it provides robust overload protection. You should choose S-type devices when precision and rapid suppression of voltage spikes are critical, while Z-type devices offer effective protection in less sensitive, high-current environments.
Performance Comparison: S-type vs Z-type
S-type circuit protection offers superior response speed and lower power dissipation, making it ideal for sensitive electronic applications requiring fast fault interruption. Z-type protection devices provide enhanced voltage clamping capabilities and higher surge tolerance, ensuring robust defense against transient overvoltages in industrial environments. Understanding these performance differences helps you select the appropriate protection device tailored to your circuit's reliability and safety needs.
Common Standards and Regulations
S-type and Z-type circuit protection devices comply with distinct common standards and regulations to ensure safety and performance in electrical systems. S-type breakers often adhere to IEC 60947-2 for low voltage switchgear, while Z-type devices are typically designed under stricter standards like UL 489 or IEC 60947-6-2 for semiconductor protection. Compliance with these standards ensures reliable fault interruption, thermal-magnetic operation, and coordination with other protective components in industrial and residential applications.
Choosing the Right Protection: S-type or Z-type
Choosing the right circuit protection involves understanding the key differences between S-type and Z-type devices, where S-type offers fast response to short circuits and Z-type provides stable protection against overloads. Your decision should factor in the specific application requirements such as current rating, response time, and the nature of potential faults to ensure optimal system safety and longevity. Proper selection enhances performance by minimizing downtime and preventing damage to sensitive components.
S-type vs Z-type Circuit Protection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com